View in other NatureServe Network Field Guides
NatureServe
Montana
Utah
Wyoming
Idaho
Wisconsin
British Columbia
South Carolina
Yukon
California
New York
Kellogg's Spurred Lupine - Lupinus caudatus
State Rank Reason (see State Rank above)
Reported for Montana (Dorn 1984). Taxonomy and specimen identification a problem. Taxonomic issues of this group need to be resolved, as well as identification of Montana specimens. Not reported for MT by Lesica (2012).
General Description
Perennial with shortly branching caudex; stems 1-several, 20-40(-60) cm tall, strigose. Petioles twice the length of blades or the upper ones shorter than blades. Leaves mainly cauline; leaflets 7-9, 2-5 cm long, acute or rarely rounded, equally hairy on both surfaces. Racemes terminal, 6-20 cm long. Flowers 10-12 mm long, calyx 3-4 mm long, base spurred or strongly saccate, upper lob bidentate, lower lobe entire; upper lobe bidentate, lower lobe entire; corrola light to deep blue or purple; banner lighter blue or whitish in the middle, reflected, normally hairy in the middle of lower half; wings glabrous or hairy near the base; keel ciliate. Pods 2-2.5 cm long, silky; seeds 4-4.5 mm long, smooth (adapted from: McGregor, 1986, Flora of the Grea Plains).
Range Comments
WA to CA, east to TX and barely into SD and OK, the distribution centered in the Great Basin between the Sierra Madres and western slope of the Rocky Mountains (Kartesz in prep. 2012).
Observations in Montana Natural Heritage Program Database
Number of Observations: 55
(Click on the following maps and charts to see full sized version)
Map Help and Descriptions
Relative Density
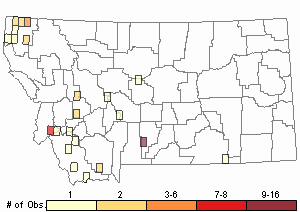
Recency
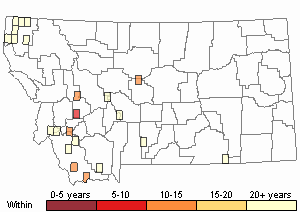
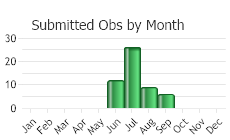
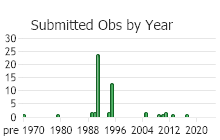
 (Observations spanning multiple months or years are excluded from time charts)
(Observations spanning multiple months or years are excluded from time charts)
Habitat
Rare in rocky prairie and gravelly stremas valleys (McGregor, 1986, in Flora of the Great Plains).
Ecology
POLLINATORS The following animal species have been reported as pollinators of this plant species or its genus where their geographic ranges overlap:
Bombus vagans,
Bombus bifarius,
Bombus centralis,
Bombus fervidus,
Bombus flavifrons,
Bombus frigidus,
Bombus huntii,
Bombus melanopygus,
Bombus mixtus,
Bombus nevadensis,
Bombus rufocinctus,
Bombus sylvicola,
Bombus sitkensis,
Bombus occidentalis,
Bombus pensylvanicus,
Bombus bimaculatus,
Bombus griseocollis,
Bombus impatiens, and
Bombus kirbiellus (Macior 1974, Thorp et al. 1983, Bauer 1983, Mayer et al. 2000, Wilson et al. 2010, Colla and Dumesh 2010, Koch et al. 2012, Miller-Struttmann and Galen 2014, Williams et al. 2014).
Stewardship Responsibility
References
- Literature Cited AboveLegend:
 View Online Publication
View Online Publication Bauer, P.J. 1983. Bumblebee pollination relationships on the Beartooth Plateau tundra of Southern Montana. American Journal of Botany. 70(1): 134-144.
Bauer, P.J. 1983. Bumblebee pollination relationships on the Beartooth Plateau tundra of Southern Montana. American Journal of Botany. 70(1): 134-144. Colla, S.R. and S. Dumesh. 2010. The bumble bees of southern Ontario: notes on natural history and distribution. Journal of the Entomological Society of Ontario 141:39-68.
Colla, S.R. and S. Dumesh. 2010. The bumble bees of southern Ontario: notes on natural history and distribution. Journal of the Entomological Society of Ontario 141:39-68. Koch, J., J. Strange, and P. Williams. 2012. Bumble bees of the western United States. Washington, DC: USDA Forest Service, Pollinator Partnership. 143 p.
Koch, J., J. Strange, and P. Williams. 2012. Bumble bees of the western United States. Washington, DC: USDA Forest Service, Pollinator Partnership. 143 p. Lesica, P., M.T. Lavin, and P.F. Stickney. 2012. Manual of Montana Vascular Plants. Fort Worth, TX: BRIT Press. viii + 771 p.
Lesica, P., M.T. Lavin, and P.F. Stickney. 2012. Manual of Montana Vascular Plants. Fort Worth, TX: BRIT Press. viii + 771 p. Macior, L.M. 1974. Pollination ecology of the Front Range of the Colorado Rocky Mountains. Melanderia 15: 1-59.
Macior, L.M. 1974. Pollination ecology of the Front Range of the Colorado Rocky Mountains. Melanderia 15: 1-59. Mayer, D.F., E.R. Miliczky, B.F. Finnigan, and C.A. Johnson. 2000. The bee fauna (Hymenoptera: Apoidea) of southeastern Washington. Journal of the Entomological Society of British Columbia 97: 25-31.
Mayer, D.F., E.R. Miliczky, B.F. Finnigan, and C.A. Johnson. 2000. The bee fauna (Hymenoptera: Apoidea) of southeastern Washington. Journal of the Entomological Society of British Columbia 97: 25-31. Miller-Struttmann, N.E. and C. Galen. 2014. High-altitude multi-taskers: bumble bee food plant use broadens along an altitudinal productivity gradient. Oecologia 176:1033-1045.
Miller-Struttmann, N.E. and C. Galen. 2014. High-altitude multi-taskers: bumble bee food plant use broadens along an altitudinal productivity gradient. Oecologia 176:1033-1045. Thorp, R.W., D.S. Horning, and L.L. Dunning. 1983. Bumble bees and cuckoo bumble bees of California (Hymenoptera: Apidae). Bulletin of the California Insect Survey 23:1-79.
Thorp, R.W., D.S. Horning, and L.L. Dunning. 1983. Bumble bees and cuckoo bumble bees of California (Hymenoptera: Apidae). Bulletin of the California Insect Survey 23:1-79. Williams, P., R. Thorp, L. Richardson, and S. Colla. 2014. Bumble Bees of North America. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press. 208 p.
Williams, P., R. Thorp, L. Richardson, and S. Colla. 2014. Bumble Bees of North America. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press. 208 p. Wilson, J.S., L.E. Wilson, L.D. Loftis, and T. Griswold. 2010. The montane bee fauna of north central Washington, USA, with floral associations. Western North American Naturalist 70(2): 198-207.
Wilson, J.S., L.E. Wilson, L.D. Loftis, and T. Griswold. 2010. The montane bee fauna of north central Washington, USA, with floral associations. Western North American Naturalist 70(2): 198-207.
- Additional ReferencesLegend:
 View Online Publication
View Online Publication
Do you know of a citation we're missing? Lesica, P., M.T. Lavin, and P.F. Stickney. 2022. Manual of Montana Vascular Plants, Second Edition. Fort Worth, TX: BRIT Press. viii + 779 p.
Lesica, P., M.T. Lavin, and P.F. Stickney. 2022. Manual of Montana Vascular Plants, Second Edition. Fort Worth, TX: BRIT Press. viii + 779 p. Steerey, W. F. 1979. Distribution, range use and population characteristics of Mule Deer associated with the Schafer Creek winter range, Bridger Mountains, Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, Montana: Montana State University. 119 p.
Steerey, W. F. 1979. Distribution, range use and population characteristics of Mule Deer associated with the Schafer Creek winter range, Bridger Mountains, Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, Montana: Montana State University. 119 p.
- Web Search Engines for Articles on "Kellogg's Spurred Lupine"





