View in other NatureServe Network Field Guides
NatureServe
Montana
Utah
Wyoming
Idaho
Wisconsin
British Columbia
South Carolina
Yukon
California
New York
Half-black Bumble Bee - Bombus vagans
Other Names:
Pyrobombus vagans
Native Species
Global Rank:
G4
State Rank:
S5
(see State Rank Reason below)
Agency Status
USFWS:
USFS:
BLM:
State Rank Reason (see State Rank above)
Species is widely distributed across Montana and relatively common within suitable habitat. Trend is unknown and it does not appear to face significant threats.
General Description
For definitions and diagrams of bumble bee morphology please see the
Montana State Entomology Collection's Bumble Bee Morphology page. A long-tongued medium-sized species: queens 17-21 mm in length, workers 11-14 mm. Hair medium, head length medium with cheek just longer than wide; mid-leg basitarsus with back far corner rounded, hind-leg tibia outer surface flat and lacking long hair (except fringe), pollen basket present; hair of face black; upperside of head (occiput) yellow especially centrally; upper surface of thorax yellow with a central black dot between wings, sides of thorax entirely yellow; T2 mostly yellow at front, sometimes black along back; T3-4 and S3-5 usually black at the sides unless T3-4 black on upper surface. Male 11-14 mm in length; eyes similar in size and shape to eyes of any female
Bombus; antennae medium length, flagellum 3X longer than scape; hair of face yellow with black intermixed at least around base of antennae; upper surface of thorax predominantly yellow; T3 usually black in the middle, T5-6 often yellow at the sides (Colla et al. 2011, Koch et al. 2012, Williams et al. 2014).
Phenology
Across the range, queens reported April to October, workers May to November, males May to November (Colla et al. 2011, Williams et al. 2014). In eastern Washington, queens reported April to July, workers May to November, males July to November (Koch et al. 2012).
Diagnostic Characteristics
Please see the
Montana State Entomology Collection's Key to Female Bumble Bees in Montana. Females told from other Montana
Bombus by a combination of hind-leg tibia outer surface concave and hairless (except or fringe), pollen basket present; cheek longer than wide; face predominantly with black hairs; T2 yellow, T3 mostly black, T4-6 black; sides of thorax predominantly yellow.
Species Range
Montana Range
Range Descriptions
 Native
Native
Recorded Montana Distribution

Click the map for additional distribution information.
Range Comments
Central and northeastern US and adjacent southern Canada west to eastern Washington, northern Alberta and British Columbia, with scattered records south in the Rocky Mountains to central Colorado (Williams et al. 2014). Experiencing moderate declines in range and abundance in the east (Colla and Packer 2008, Colla et al. 2012).
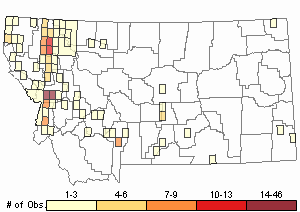
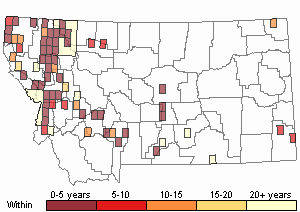
Observations in Montana Natural Heritage Program Database
Number of Observations: 293
(Click on the following maps and charts to see full sized version)
Map Help and Descriptions
Relative Density
Recency
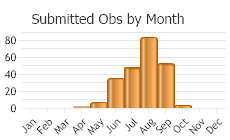
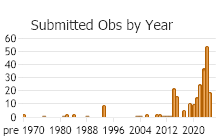
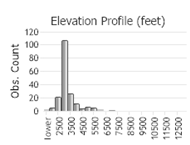 (Observations spanning multiple months or years are excluded from time charts)
(Observations spanning multiple months or years are excluded from time charts)
Habitat
Forests, wetlands, urban parks and gardens, tall grass prairie, irrigated prairie and woodland riparian, prairie parkland, foothill grassland-forest ecotone (Hobbs 1967, Hines and Hendrix 2005, Grixti et al. 2009, Williams et al. 2014).
Food Habits
Feeds on a wide variety of plants (more than 60 genera), including Anaphalis, Apocynum, Aquilegia, Aralia, Arctium, Asclepias, Astragalus, Berberis, Carduus, Centaurea, Cichorium, Cirsium, Claytonia, Clematis, Cornus, Crataegus, Daucus, Delphinium, Dicentra, Dipsacus, Dodecatheon, Echium, Ellisia, Erythronium, Eupatorium, Eurybia, Fragaria, Geranium, Helianthus, Hesperis, Hydrophyllum, Hypericum, Impatiens, Ipomoea, Lactuca, Ledum, Leonurus, Liatris, Linaria, Lonicera, Lotus, Lupinus, Malus, Medicago, Melilotus, Mentha, Mertensia, Mimulus, Monarda, Nepeta, Nymphaea, Onobrychis, Onopordum, Pedicularis, Penstemon, Phlox, Physostegia, Polemonium, Prunella, Prunus, Rhododendron, Ribes, Rubus, Salix, Satureja, Scrophularia, Scutellaria, Silene, Sisyrinchium, Solanum, Solidago, Sonchus, Spiraea, Stachys, Symphoricarpos, Symphyotrichum, Symphytum, Tamarix, Taraxacum, Teucrium, Tradescantia, Trifolium, Vaccinium, Verbascum, Verbena, Veronica, Vicia, Viola and Zizia (Plath 1934, Macior 1968, Heinrich 1976, MacKenzie and Averill 1995, Mayer et al. 2000, Colla and Dumesh 2010, Colla et al. 2011, Koch et al. 2012, Williams et al. 2014).
Reproductive Characteristics
Nests built mostly underground, although occasionally on the surface or above ground (Hobbs 1967, Colla et al. 2011, Williams et al. 2014). In southern Alberta, nests established mid to late June; mean number of pupae in first broods is 8-10 (Hobbs 1967). Males patrol circuits in search of queens. Nests sometimes parasitized by the cuckoo bumble bee Bombus citrinus.
Stewardship Responsibility
References
- Literature Cited AboveLegend:
 View Online Publication
View Online Publication Colla, S., L. Richardson, and P. Williams. 2011. Bumble bees of the eastern United States. Washington, DC: USDA Forest Service, Pollinator Partnership. 103 p.
Colla, S., L. Richardson, and P. Williams. 2011. Bumble bees of the eastern United States. Washington, DC: USDA Forest Service, Pollinator Partnership. 103 p. Colla, S.R. and L. Packer. 2008. Evidence for decline in eastern North American bumble bees (Hymenoptera: Apidae), with special focus on Bombus affinis Cresson. Biodiversity Conservation 17: 1379-1391.
Colla, S.R. and L. Packer. 2008. Evidence for decline in eastern North American bumble bees (Hymenoptera: Apidae), with special focus on Bombus affinis Cresson. Biodiversity Conservation 17: 1379-1391. Colla, S.R. and S. Dumesh. 2010. The bumble bees of southern Ontario: notes on natural history and distribution. Journal of the Entomological Society of Ontario 141:39-68.
Colla, S.R. and S. Dumesh. 2010. The bumble bees of southern Ontario: notes on natural history and distribution. Journal of the Entomological Society of Ontario 141:39-68. Colla, S.R., F. Gadallah, L. Richarson, D. Wagner, and L. Gall. 2012. Assessing declines of North American bumble bees (Bombus spp.) using museum specimens. Biodiversity and Conservation 21: 3585-3595.
Colla, S.R., F. Gadallah, L. Richarson, D. Wagner, and L. Gall. 2012. Assessing declines of North American bumble bees (Bombus spp.) using museum specimens. Biodiversity and Conservation 21: 3585-3595. Grixti, J.C., L.T. Wong, S.A. Cameron, and C. Favret. 2009. Decline of bumble bees (Bombus) in the North American Midwest. Biological Conservation 142: 75-84.
Grixti, J.C., L.T. Wong, S.A. Cameron, and C. Favret. 2009. Decline of bumble bees (Bombus) in the North American Midwest. Biological Conservation 142: 75-84. Hines, H.M. and S.D. Hendrix. 2005. Bumble bee (Hymenoptera: Apidae) diversity and abundance in tallgrass priaire patches: effects of local and landscape floral resources. Environmental Entomology 34(6): 1477-1484.
Hines, H.M. and S.D. Hendrix. 2005. Bumble bee (Hymenoptera: Apidae) diversity and abundance in tallgrass priaire patches: effects of local and landscape floral resources. Environmental Entomology 34(6): 1477-1484. Hobbs, G.A. 1967. Ecology of species of Bombus Latr. (Hymenoptera: Apidae) in southern Alberta. VI. Subgenus Pyrobombus. Canadian Entomologist 99: 1271-1292.
Hobbs, G.A. 1967. Ecology of species of Bombus Latr. (Hymenoptera: Apidae) in southern Alberta. VI. Subgenus Pyrobombus. Canadian Entomologist 99: 1271-1292. Koch, J., J. Strange, and P. Williams. 2012. Bumble bees of the western United States. Washington, DC: USDA Forest Service, Pollinator Partnership. 143 p.
Koch, J., J. Strange, and P. Williams. 2012. Bumble bees of the western United States. Washington, DC: USDA Forest Service, Pollinator Partnership. 143 p. Macior, L.M. 1968. Bombus (Hymenoptera, Apidae) queen foraging in relation to vernal pollination in Wisconsin. Ecology 49:20-25.
Macior, L.M. 1968. Bombus (Hymenoptera, Apidae) queen foraging in relation to vernal pollination in Wisconsin. Ecology 49:20-25. MacKenzie, K.E. and A. L. Averill. 1995. Bee (Hymenoptera: Apoidea) diversity and abundance on cranberry in southeastern Massachusetts. Annals of the Entomological Society of America 88(3): 334-341.
MacKenzie, K.E. and A. L. Averill. 1995. Bee (Hymenoptera: Apoidea) diversity and abundance on cranberry in southeastern Massachusetts. Annals of the Entomological Society of America 88(3): 334-341. Mayer, D.F., E.R. Miliczky, B.F. Finnigan, and C.A. Johnson. 2000. The bee fauna (Hymenoptera: Apoidea) of southeastern Washington. Journal of the Entomological Society of British Columbia 97: 25-31.
Mayer, D.F., E.R. Miliczky, B.F. Finnigan, and C.A. Johnson. 2000. The bee fauna (Hymenoptera: Apoidea) of southeastern Washington. Journal of the Entomological Society of British Columbia 97: 25-31. Plath, O.E. 1934. Bumblebees and their ways. New York, NY: Macmillan Company. 201 p.
Plath, O.E. 1934. Bumblebees and their ways. New York, NY: Macmillan Company. 201 p. Williams, P., R. Thorp, L. Richardson, and S. Colla. 2014. Bumble Bees of North America. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press. 208 p.
Williams, P., R. Thorp, L. Richardson, and S. Colla. 2014. Bumble Bees of North America. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press. 208 p.
- Additional ReferencesLegend:
 View Online Publication
View Online Publication
Do you know of a citation we're missing? Burkle L.A., M.P. Simanonok, J.S. Durney, J.A. Myers, and R.T. Belote. 2019. Wildfires influence abundance, diversity, and intraspecific and interspecific trait variation of native bees and flowering plants across burned and unburned landscapes. Frontiers in Ecology and Evolution 7(252):1-14.
Burkle L.A., M.P. Simanonok, J.S. Durney, J.A. Myers, and R.T. Belote. 2019. Wildfires influence abundance, diversity, and intraspecific and interspecific trait variation of native bees and flowering plants across burned and unburned landscapes. Frontiers in Ecology and Evolution 7(252):1-14. Dolan, A.C. 2016. Insects associated with Montana's huckleberry (Ericaceae: Vaccinium globulare) plants and the bumble bees (Hymenoptera: Apidae) of Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 160 p.
Dolan, A.C. 2016. Insects associated with Montana's huckleberry (Ericaceae: Vaccinium globulare) plants and the bumble bees (Hymenoptera: Apidae) of Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 160 p. Dolan, A.C., C.M. Delphia, K.M. O'Neill, and M.A. Ivie. 2017. Bumble Bees (Hymenoptera: Apidae) of Montana. Annals of the Entomological Society of America. 110(2): 129-144.
Dolan, A.C., C.M. Delphia, K.M. O'Neill, and M.A. Ivie. 2017. Bumble Bees (Hymenoptera: Apidae) of Montana. Annals of the Entomological Society of America. 110(2): 129-144. Kearns, C.A. and J.D. Thomson. 2001. The Natural History of Bumble Bees. Boulder, CO. University Press of Colorado.
Kearns, C.A. and J.D. Thomson. 2001. The Natural History of Bumble Bees. Boulder, CO. University Press of Colorado. McMenamin, A.J., and M.L. Flenniken. 2018. Recently identified bee viruses and their impact on bee pollinators. Current Opinion in Insect Science 26:120-129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cois.2018.02.009
McMenamin, A.J., and M.L. Flenniken. 2018. Recently identified bee viruses and their impact on bee pollinators. Current Opinion in Insect Science 26:120-129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cois.2018.02.009 Reese, E.G., L.A. Burkle, C.M. Delphia, and T. Griswold. 2018. A list of bees from three locations in the Northern Rockies Ecoregion (NRE) of western Montana. Biodiversity Data Journal 6: e27161.
Reese, E.G., L.A. Burkle, C.M. Delphia, and T. Griswold. 2018. A list of bees from three locations in the Northern Rockies Ecoregion (NRE) of western Montana. Biodiversity Data Journal 6: e27161. Simanonok, M. 2018. Plant-pollinator network assembly after wildfire. Ph.D. Dissertation. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 123 p.
Simanonok, M. 2018. Plant-pollinator network assembly after wildfire. Ph.D. Dissertation. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 123 p. Simanonok, M.P. and L.A. Burkle. 2019. Nesting success of wood-cavity-nesting bees declines with increasing time since wildfire. Ecology and Evolution 9:12436-12445.
Simanonok, M.P. and L.A. Burkle. 2019. Nesting success of wood-cavity-nesting bees declines with increasing time since wildfire. Ecology and Evolution 9:12436-12445.
- Web Search Engines for Articles on "Half-black Bumble Bee"
- Additional Sources of Information Related to "Insects"





