View in other NatureServe Network Field Guides
NatureServe
Montana
Utah
Wyoming
Idaho
Wisconsin
British Columbia
South Carolina
Yukon
California
New York
Timber Milkvetch - Astragalus miser
Native Species
Global Rank:
G5
State Rank:
S5
C-value:
4
Agency Status
USFWS:
USFS:
BLM:
External Links
General Description
Perennial with a branched caudex. Herbage glabrate to strigose or villous with dolabriform hairs. Stems 5–30 cm, prostrate to ascending. Leaves with 9 to 17 linear to ovate leaflets, 5–25 mm long with rounded to acute tips; stipules lanceolate, 2–4 mm long, basallay connate. Inflorescence barely longer than the leaves, open with 5 to 10 spreading flowers. Flowers white to purple; calyx black- and or white-strigose; sepals ca. 1 mm long; banner 8–12 mm long, reflexed; keel 6–10 mm long, often purple-tipped. Legume pendent, glabrous to white-strigillose, 15–30 mm long flattened, linear (
Lesica et al. 2012. Manual of Montana Vascular Plants. BRIT Press. Fort Worth, TX).
Six varieties occur in Montana: var.
miser, var.
crispatus (M.E. Jones) Cronq., var.
decumbens (Nutt. ex Torr. & A. Gray) Cronq., var.
hylophilus (Rydb.) Barneby, var.
praeteritus Barneby, and var.
serotinus (A. Gray ex Cooper) Barneby.
Species Range
Montana Range
Range Descriptions
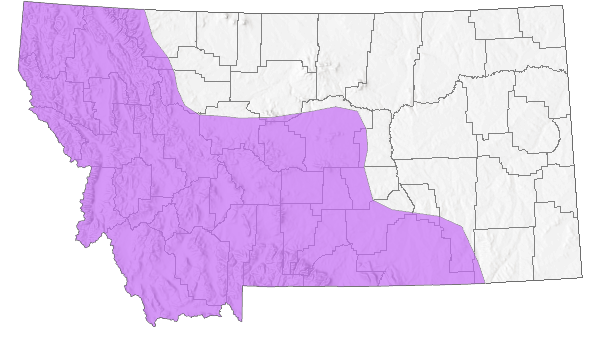
 Native
Native
Range Comments
BC, AB south to AZ, CO and SD (Lesica et al. 2012. Manual of Montana Vascular Plants. BRIT Press. Fort Worth, TX).
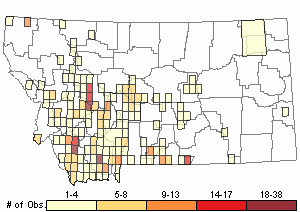
Observations in Montana Natural Heritage Program Database
Number of Observations: 624
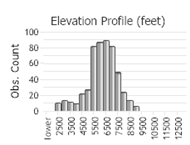
(Click on the following maps and charts to see full sized version)
Map Help and Descriptions
Relative Density
Recency
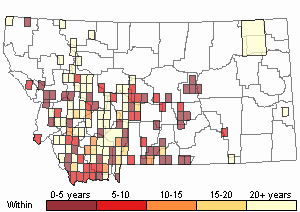
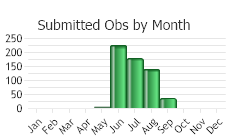
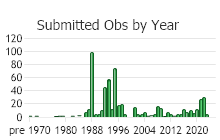
 (Observations spanning multiple months or years are excluded from time charts)
(Observations spanning multiple months or years are excluded from time charts)
Habitat
Ecology
POLLINATORS The following animal species have been reported as pollinators of this plant species or its genus where their geographic ranges overlap:
Bombus vagans,
Bombus appositus,
Bombus auricomus,
Bombus bifarius,
Bombus borealis,
Bombus centralis,
Bombus fervidus,
Bombus flavifrons,
Bombus huntii,
Bombus mixtus,
Bombus nevadensis,
Bombus rufocinctus,
Bombus ternarius,
Bombus terricola,
Bombus occidentalis,
Bombus pensylvanicus,
Bombus griseocollis, and
Bombus insularis (Macior 1974, Thorp et al. 1983, Mayer et al. 2000, Colla and Dumesh 2010, Wilson et al. 2010, Koch et al. 2012, Miller-Struttmann and Galen 2014, Williams et al. 2014).
Stewardship Responsibility
References
- Literature Cited AboveLegend:
 View Online Publication
View Online Publication Colla, S.R. and S. Dumesh. 2010. The bumble bees of southern Ontario: notes on natural history and distribution. Journal of the Entomological Society of Ontario 141:39-68.
Colla, S.R. and S. Dumesh. 2010. The bumble bees of southern Ontario: notes on natural history and distribution. Journal of the Entomological Society of Ontario 141:39-68. Koch, J., J. Strange, and P. Williams. 2012. Bumble bees of the western United States. Washington, DC: USDA Forest Service, Pollinator Partnership. 143 p.
Koch, J., J. Strange, and P. Williams. 2012. Bumble bees of the western United States. Washington, DC: USDA Forest Service, Pollinator Partnership. 143 p. Lesica, P., M.T. Lavin, and P.F. Stickney. 2012. Manual of Montana Vascular Plants. Fort Worth, TX: BRIT Press. viii + 771 p.
Lesica, P., M.T. Lavin, and P.F. Stickney. 2012. Manual of Montana Vascular Plants. Fort Worth, TX: BRIT Press. viii + 771 p. Macior, L.M. 1974. Pollination ecology of the Front Range of the Colorado Rocky Mountains. Melanderia 15: 1-59.
Macior, L.M. 1974. Pollination ecology of the Front Range of the Colorado Rocky Mountains. Melanderia 15: 1-59. Mayer, D.F., E.R. Miliczky, B.F. Finnigan, and C.A. Johnson. 2000. The bee fauna (Hymenoptera: Apoidea) of southeastern Washington. Journal of the Entomological Society of British Columbia 97: 25-31.
Mayer, D.F., E.R. Miliczky, B.F. Finnigan, and C.A. Johnson. 2000. The bee fauna (Hymenoptera: Apoidea) of southeastern Washington. Journal of the Entomological Society of British Columbia 97: 25-31. Miller-Struttmann, N.E. and C. Galen. 2014. High-altitude multi-taskers: bumble bee food plant use broadens along an altitudinal productivity gradient. Oecologia 176:1033-1045.
Miller-Struttmann, N.E. and C. Galen. 2014. High-altitude multi-taskers: bumble bee food plant use broadens along an altitudinal productivity gradient. Oecologia 176:1033-1045. Thorp, R.W., D.S. Horning, and L.L. Dunning. 1983. Bumble bees and cuckoo bumble bees of California (Hymenoptera: Apidae). Bulletin of the California Insect Survey 23:1-79.
Thorp, R.W., D.S. Horning, and L.L. Dunning. 1983. Bumble bees and cuckoo bumble bees of California (Hymenoptera: Apidae). Bulletin of the California Insect Survey 23:1-79. Williams, P., R. Thorp, L. Richardson, and S. Colla. 2014. Bumble Bees of North America. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press. 208 p.
Williams, P., R. Thorp, L. Richardson, and S. Colla. 2014. Bumble Bees of North America. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press. 208 p. Wilson, J.S., L.E. Wilson, L.D. Loftis, and T. Griswold. 2010. The montane bee fauna of north central Washington, USA, with floral associations. Western North American Naturalist 70(2): 198-207.
Wilson, J.S., L.E. Wilson, L.D. Loftis, and T. Griswold. 2010. The montane bee fauna of north central Washington, USA, with floral associations. Western North American Naturalist 70(2): 198-207.
- Additional ReferencesLegend:
 View Online Publication
View Online Publication
Do you know of a citation we're missing? Aho, Ken Andrew. 2006. Alpine and Cliff Ecosystems in the North-Central Rocky Mountains. Ph.D. Dissertation. Bozeman, Montana: Montana State University. 343 p.
Aho, Ken Andrew. 2006. Alpine and Cliff Ecosystems in the North-Central Rocky Mountains. Ph.D. Dissertation. Bozeman, Montana: Montana State University. 343 p. Ament, R.J. 1995. Pioneer Plant Communities Five Years After the 1988 Yellowstone Fires. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 216 p.
Ament, R.J. 1995. Pioneer Plant Communities Five Years After the 1988 Yellowstone Fires. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 216 p. Britton, M. P. 1955. An ecological study of a relict grassland and an adjacent grazed pasture in Beaverhead Valley, Montana. M.S. thesis. Montana State University, Bozeman. 23 pp.
Britton, M. P. 1955. An ecological study of a relict grassland and an adjacent grazed pasture in Beaverhead Valley, Montana. M.S. thesis. Montana State University, Bozeman. 23 pp. Clark, D. 1991. The effect of fire on Yellowstone ecosystem seed banks. M.Sc. Thesis. Montana State University, Bozeman. 115 pp.
Clark, D. 1991. The effect of fire on Yellowstone ecosystem seed banks. M.Sc. Thesis. Montana State University, Bozeman. 115 pp. Cope, M.G. 1992. Distribution, habitat selection and survival of transplanted Columbian Sharp-tailed Grouse (Tympanuchus phasianellus columbianus) in the Tobacco Valley, Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, Montana: Montana State University. 60 p.
Cope, M.G. 1992. Distribution, habitat selection and survival of transplanted Columbian Sharp-tailed Grouse (Tympanuchus phasianellus columbianus) in the Tobacco Valley, Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, Montana: Montana State University. 60 p. Cramer, P.C. 1992. Small mammal diversity and abundance in Douglas Fir old growth forests. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 64 p.
Cramer, P.C. 1992. Small mammal diversity and abundance in Douglas Fir old growth forests. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 64 p. Dale, D. 1973. Effects of trail use under forests in the Madison Range, Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 96 pp.
Dale, D. 1973. Effects of trail use under forests in the Madison Range, Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 96 pp. Durham, R. A., D. L. Mummey, L. Shreading, and P.W. Ramsey. 2017. Phenological patterns differ between exotic and native plants: Field observations from the Sapphire Mountains, Montana. Natural Areas Journal, 37(3), 361–381.
Durham, R. A., D. L. Mummey, L. Shreading, and P.W. Ramsey. 2017. Phenological patterns differ between exotic and native plants: Field observations from the Sapphire Mountains, Montana. Natural Areas Journal, 37(3), 361–381. Eversman, S.T. 1968. A comparison of plant communities and substrates of avalanche and non-avalanche areas in south central Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 39 pp.
Eversman, S.T. 1968. A comparison of plant communities and substrates of avalanche and non-avalanche areas in south central Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 39 pp. Harvey, S.J. 1990. Responses of steppe plants to gradients of water soil texture and disturbance in Montana, U.S.A. Ph.D. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 34 p.
Harvey, S.J. 1990. Responses of steppe plants to gradients of water soil texture and disturbance in Montana, U.S.A. Ph.D. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 34 p. Lesica, P., M.T. Lavin, and P.F. Stickney. 2022. Manual of Montana Vascular Plants, Second Edition. Fort Worth, TX: BRIT Press. viii + 779 p.
Lesica, P., M.T. Lavin, and P.F. Stickney. 2022. Manual of Montana Vascular Plants, Second Edition. Fort Worth, TX: BRIT Press. viii + 779 p. Picton, H.D. 1959. Use of vegetative types, migration, and hunter harvest of the Sun River elk herd, Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 39 p.
Picton, H.D. 1959. Use of vegetative types, migration, and hunter harvest of the Sun River elk herd, Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 39 p. Quire, R.L. 2013. The sagebrush steppe of Montana and southeastern Idaho shows evidence of high native plant diversity, stability, and resistance to the detrimental effects of nonnative plant species. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 124 p.
Quire, R.L. 2013. The sagebrush steppe of Montana and southeastern Idaho shows evidence of high native plant diversity, stability, and resistance to the detrimental effects of nonnative plant species. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 124 p. Seipel, T.F. 2006. Plant species diversity in the sagebrush steppe of Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 87 p.
Seipel, T.F. 2006. Plant species diversity in the sagebrush steppe of Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 87 p. Simanonok, M. 2018. Plant-pollinator network assembly after wildfire. Ph.D. Dissertation. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 123 p.
Simanonok, M. 2018. Plant-pollinator network assembly after wildfire. Ph.D. Dissertation. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 123 p. Steerey, W. F. 1979. Distribution, range use and population characteristics of Mule Deer associated with the Schafer Creek winter range, Bridger Mountains, Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, Montana: Montana State University. 119 p.
Steerey, W. F. 1979. Distribution, range use and population characteristics of Mule Deer associated with the Schafer Creek winter range, Bridger Mountains, Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, Montana: Montana State University. 119 p. Wiman, N.G. 2001. Dynamics of leafy spurge (Euphorbia esula L.) infested plant communities influenced by flea beetles in the Aphthona complex (Colepotera: Chrysomelidae). M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 148 p.
Wiman, N.G. 2001. Dynamics of leafy spurge (Euphorbia esula L.) infested plant communities influenced by flea beetles in the Aphthona complex (Colepotera: Chrysomelidae). M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 148 p. Wood, A.K. 1987. Ecology of a prairie mule deer population. Ph.D. Dissertation. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 205 p.
Wood, A.K. 1987. Ecology of a prairie mule deer population. Ph.D. Dissertation. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 205 p. Wood, M.A. 1981. Small mammal communities after two recent fires in Yellowstone National Park. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, Montana: Montana State University. 58 p.
Wood, M.A. 1981. Small mammal communities after two recent fires in Yellowstone National Park. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, Montana: Montana State University. 58 p.
- Web Search Engines for Articles on "Timber Milkvetch"





