View in other NatureServe Network Field Guides
NatureServe
Montana
Utah
Wyoming
Idaho
Wisconsin
British Columbia
South Carolina
Yukon
California
New York
Giant Goldenrod - Solidago gigantea
Native Species
Global Rank:
G5
State Rank:
S3S4
C-value:
6
Agency Status
USFWS:
USFS:
BLM:
External Links
General Description
Strongly rhizomatous. Stems erect, simple, 40–100 cm, sometimes clustered. Herbage glabrous; the inflorescence puberulent. Leaves cauline, sessile, short-petiolate; blades lanceolate, serrate, 4–12 cm long, gradually reduced upward. Inflorescence pyramidal; heads secund on arching branches. Involucres campanulate, 3–4 mm high; phyllaries linear-lanceolate, ciliate. Rays 9 to 15; ligules 2–3 mm long. Disk flowers 7 to 12; corollas 3–5 mm long. Achenes 1–1.5 mm long, sparsely strigose (
Lesica et al. 2012. Manual of Montana Vascular Plants. BRIT Press. Fort Worth, TX).
Species Range
Montana Range
Range Descriptions
 Native
Native
Range Comments
BC to NS south to TX, FL and Mexico (Lesica et al. 2012. Manual of Montana Vascular Plants. BRIT Press. Fort Worth, TX).
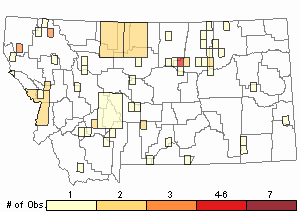
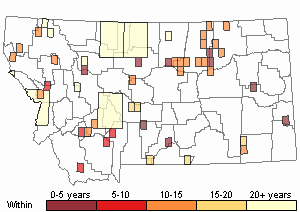
Observations in Montana Natural Heritage Program Database
Number of Observations: 74
(Click on the following maps and charts to see full sized version)
Map Help and Descriptions
Relative Density
Recency

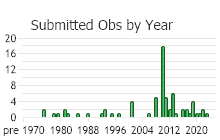
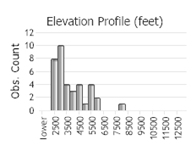 (Observations spanning multiple months or years are excluded from time charts)
(Observations spanning multiple months or years are excluded from time charts)
Habitat
Ecology
POLLINATORS The following animal species have been reported as pollinators of this plant species or its genus where their geographic ranges overlap:
Bombus vagans,
Bombus appositus,
Bombus bifarius,
Bombus borealis,
Bombus fervidus,
Bombus flavifrons,
Bombus huntii,
Bombus melanopygus,
Bombus mixtus,
Bombus nevadensis,
Bombus rufocinctus,
Bombus ternarius,
Bombus terricola,
Bombus sitkensis,
Bombus occidentalis,
Bombus pensylvanicus,
Bombus bimaculatus,
Bombus griseocollis,
Bombus impatiens,
Bombus insularis,
Bombus suckleyi,
Bombus bohemicus,
Bombus flavidus, and
Bombus kirbiellus (Plath 1934, Heinrich 1976, Thorp et al. 1983, Johnson 1986, Shaw and Taylor 1986, Mayer et al. 2000, Colla and Dumesh 2010, Colla et al. 2011, Koch et al. 2012, Williams et al. 2014, Tripoldi and Szalanski 2015).
Stewardship Responsibility
References
- Literature Cited AboveLegend:
 View Online Publication
View Online Publication Colla, S., L. Richardson, and P. Williams. 2011. Bumble bees of the eastern United States. Washington, DC: USDA Forest Service, Pollinator Partnership. 103 p.
Colla, S., L. Richardson, and P. Williams. 2011. Bumble bees of the eastern United States. Washington, DC: USDA Forest Service, Pollinator Partnership. 103 p. Colla, S.R. and S. Dumesh. 2010. The bumble bees of southern Ontario: notes on natural history and distribution. Journal of the Entomological Society of Ontario 141:39-68.
Colla, S.R. and S. Dumesh. 2010. The bumble bees of southern Ontario: notes on natural history and distribution. Journal of the Entomological Society of Ontario 141:39-68. Johnson, R.A. 1986. Intraspecific resource partitioning in the bumble bees Bombus ternarius and B. pennsylvanicus. Ecology 67:133-138.
Johnson, R.A. 1986. Intraspecific resource partitioning in the bumble bees Bombus ternarius and B. pennsylvanicus. Ecology 67:133-138. Koch, J., J. Strange, and P. Williams. 2012. Bumble bees of the western United States. Washington, DC: USDA Forest Service, Pollinator Partnership. 143 p.
Koch, J., J. Strange, and P. Williams. 2012. Bumble bees of the western United States. Washington, DC: USDA Forest Service, Pollinator Partnership. 143 p. Lesica, P., M.T. Lavin, and P.F. Stickney. 2012. Manual of Montana Vascular Plants. Fort Worth, TX: BRIT Press. viii + 771 p.
Lesica, P., M.T. Lavin, and P.F. Stickney. 2012. Manual of Montana Vascular Plants. Fort Worth, TX: BRIT Press. viii + 771 p. Mayer, D.F., E.R. Miliczky, B.F. Finnigan, and C.A. Johnson. 2000. The bee fauna (Hymenoptera: Apoidea) of southeastern Washington. Journal of the Entomological Society of British Columbia 97: 25-31.
Mayer, D.F., E.R. Miliczky, B.F. Finnigan, and C.A. Johnson. 2000. The bee fauna (Hymenoptera: Apoidea) of southeastern Washington. Journal of the Entomological Society of British Columbia 97: 25-31. Plath, O.E. 1934. Bumblebees and their ways. New York, NY: Macmillan Company. 201 p.
Plath, O.E. 1934. Bumblebees and their ways. New York, NY: Macmillan Company. 201 p. Shaw, D.C. and R.J. Taylor.1986. Pollination ecology of an alpine fell-field community in the North Cascades. Northwest Science 60:21-31.
Shaw, D.C. and R.J. Taylor.1986. Pollination ecology of an alpine fell-field community in the North Cascades. Northwest Science 60:21-31. Thorp, R.W., D.S. Horning, and L.L. Dunning. 1983. Bumble bees and cuckoo bumble bees of California (Hymenoptera: Apidae). Bulletin of the California Insect Survey 23:1-79.
Thorp, R.W., D.S. Horning, and L.L. Dunning. 1983. Bumble bees and cuckoo bumble bees of California (Hymenoptera: Apidae). Bulletin of the California Insect Survey 23:1-79. Tripoldi, A.D. and A.L. Szalanski. 2015. The bumble bees (Hymenoptera: Apidae: Bombus) of Arkansas, fifty years later. Journal of Melittology 50: doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.17161/jom.v0i50.4834
Tripoldi, A.D. and A.L. Szalanski. 2015. The bumble bees (Hymenoptera: Apidae: Bombus) of Arkansas, fifty years later. Journal of Melittology 50: doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.17161/jom.v0i50.4834 Williams, P., R. Thorp, L. Richardson, and S. Colla. 2014. Bumble Bees of North America. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press. 208 p.
Williams, P., R. Thorp, L. Richardson, and S. Colla. 2014. Bumble Bees of North America. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press. 208 p.
- Additional ReferencesLegend:
 View Online Publication
View Online Publication
Do you know of a citation we're missing? Boggs, K. W. 1984. Succession in riparian communities of the lower Yellowstone River, Montana. M.S. Thesis. Montana State University, Bozeman, 107 pp.
Boggs, K. W. 1984. Succession in riparian communities of the lower Yellowstone River, Montana. M.S. Thesis. Montana State University, Bozeman, 107 pp. Eggers, M.J.S. 2005. Riparian vegetation of the Montana Yellowstone and cattle grazing impacts thereon. M.Sc. Thesis. Montana State University, Bozeman, MT. 125 p.
Eggers, M.J.S. 2005. Riparian vegetation of the Montana Yellowstone and cattle grazing impacts thereon. M.Sc. Thesis. Montana State University, Bozeman, MT. 125 p. Lesica, P., M.T. Lavin, and P.F. Stickney. 2022. Manual of Montana Vascular Plants, Second Edition. Fort Worth, TX: BRIT Press. viii + 779 p.
Lesica, P., M.T. Lavin, and P.F. Stickney. 2022. Manual of Montana Vascular Plants, Second Edition. Fort Worth, TX: BRIT Press. viii + 779 p. Quire, R.L. 2013. The sagebrush steppe of Montana and southeastern Idaho shows evidence of high native plant diversity, stability, and resistance to the detrimental effects of nonnative plant species. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 124 p.
Quire, R.L. 2013. The sagebrush steppe of Montana and southeastern Idaho shows evidence of high native plant diversity, stability, and resistance to the detrimental effects of nonnative plant species. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 124 p. Sater, S. 2022. The insects of Sevenmile Creek, a pictorial guide to their diversity and ecology. Undergraduate Thesis. Helena, MT: Carroll College. 242 p.
Sater, S. 2022. The insects of Sevenmile Creek, a pictorial guide to their diversity and ecology. Undergraduate Thesis. Helena, MT: Carroll College. 242 p. Simanonok, M.P. and L.A. Burkle. 2019. Nesting success of wood-cavity-nesting bees declines with increasing time since wildfire. Ecology and Evolution 9:12436-12445.
Simanonok, M.P. and L.A. Burkle. 2019. Nesting success of wood-cavity-nesting bees declines with increasing time since wildfire. Ecology and Evolution 9:12436-12445. Zapatka, T.P. 1963. Some results of two limited hunting seasons on hen Pheasants in north central Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, Montana: Montana State University. 26 p.
Zapatka, T.P. 1963. Some results of two limited hunting seasons on hen Pheasants in north central Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, Montana: Montana State University. 26 p.
- Web Search Engines for Articles on "Giant Goldenrod"





