View in other NatureServe Network Field Guides
NatureServe
Montana
Utah
Wyoming
Idaho
Wisconsin
British Columbia
South Carolina
Yukon
California
New York
Bristly Black Currant - Ribes lacustre
General Description
Stems erect, 0.5–1 m, spiny at the nodes, bristly between. Twigs puberulent, red-brown, becoming gray. Leaf blades 1–7 cm wide, cordate, 5- to 7-lobed, deeply toothed, nearly glabrous and shiny above, glabrous to sparsely hairy and sometimes glandular on the veins beneath. Inflorescence drooping, 5- to 20-flowered. Flowers saucer-shaped, 3–4 mm long, greenish to reddish, glandular-hairy; calyx lobes ovate, 2–3 mm long; petals pink, 1–2 mm long; stamens shorter than petals; style glabrous, united more than half way. Berry 6–9 mm long, black, bristly-glandular, unpalatable (
Lesica et al. 2012. Manual of Montana Vascular Plants. BRIT Press. Fort Worth, TX).
Species Range
Montana Range
Range Descriptions
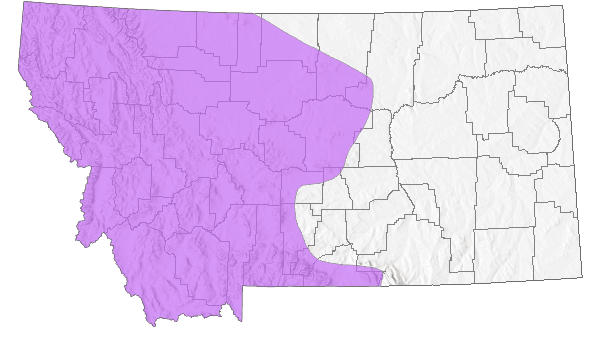
 Native
Native
Range Comments
AK to NL south to CA, CO, SD and PA (Lesica et al. 2012. Manual of Montana Vascular Plants. BRIT Press. Fort Worth, TX).
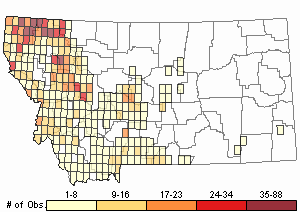
Observations in Montana Natural Heritage Program Database
Number of Observations: 2542
(Click on the following maps and charts to see full sized version)
Map Help and Descriptions
Relative Density
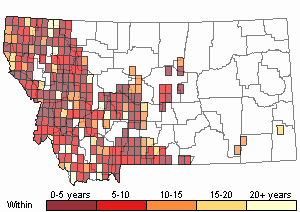
Recency
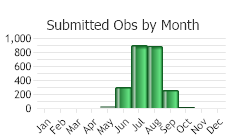
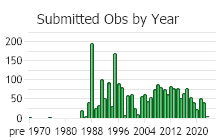
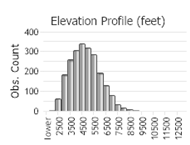 (Observations spanning multiple months or years are excluded from time charts)
(Observations spanning multiple months or years are excluded from time charts)
Habitat
Moist to wet forest, rock slides, avalanche slopes, cliffs, often along streams; montane, subalpine (
Lesica et al. 2012. Manual of Montana Vascular Plants. BRIT Press. Fort Worth, TX).
National Vegetation Classification System Groups Associated with this Species
Forest and Woodland
Montane - Subalpine Forest and Woodland
Shrubland
Foothills - Montane Shrubland
Ecology
POLLINATORS The following animal species have been reported as pollinators of this plant species or its genus where their geographic ranges overlap:
Bombus vagans,
Bombus bifarius,
Bombus centralis,
Bombus fervidus,
Bombus flavifrons,
Bombus huntii,
Bombus melanopygus,
Bombus mixtus,
Bombus nevadensis,
Bombus terricola,
Bombus sitkensis,
Bombus occidentalis,
Bombus pensylvanicus,
Bombus bimaculatus,
Bombus impatiens,
Bombus insularis, and
Bombus flavidus (Plath 1934, Thorp et al. 1983, Colla and Dumesh 2010, Koch et al. 2012, Williams et al. 2014).
Stewardship Responsibility
References
- Literature Cited AboveLegend:
 View Online Publication
View Online Publication Colla, S.R. and S. Dumesh. 2010. The bumble bees of southern Ontario: notes on natural history and distribution. Journal of the Entomological Society of Ontario 141:39-68.
Colla, S.R. and S. Dumesh. 2010. The bumble bees of southern Ontario: notes on natural history and distribution. Journal of the Entomological Society of Ontario 141:39-68. Koch, J., J. Strange, and P. Williams. 2012. Bumble bees of the western United States. Washington, DC: USDA Forest Service, Pollinator Partnership. 143 p.
Koch, J., J. Strange, and P. Williams. 2012. Bumble bees of the western United States. Washington, DC: USDA Forest Service, Pollinator Partnership. 143 p. Lesica, P., M.T. Lavin, and P.F. Stickney. 2012. Manual of Montana Vascular Plants. Fort Worth, TX: BRIT Press. viii + 771 p.
Lesica, P., M.T. Lavin, and P.F. Stickney. 2012. Manual of Montana Vascular Plants. Fort Worth, TX: BRIT Press. viii + 771 p. Plath, O.E. 1934. Bumblebees and their ways. New York, NY: Macmillan Company. 201 p.
Plath, O.E. 1934. Bumblebees and their ways. New York, NY: Macmillan Company. 201 p. Thorp, R.W., D.S. Horning, and L.L. Dunning. 1983. Bumble bees and cuckoo bumble bees of California (Hymenoptera: Apidae). Bulletin of the California Insect Survey 23:1-79.
Thorp, R.W., D.S. Horning, and L.L. Dunning. 1983. Bumble bees and cuckoo bumble bees of California (Hymenoptera: Apidae). Bulletin of the California Insect Survey 23:1-79. Williams, P., R. Thorp, L. Richardson, and S. Colla. 2014. Bumble Bees of North America. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press. 208 p.
Williams, P., R. Thorp, L. Richardson, and S. Colla. 2014. Bumble Bees of North America. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press. 208 p.
- Additional ReferencesLegend:
 View Online Publication
View Online Publication
Do you know of a citation we're missing? Ament, R.J. 1995. Pioneer Plant Communities Five Years After the 1988 Yellowstone Fires. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 216 p.
Ament, R.J. 1995. Pioneer Plant Communities Five Years After the 1988 Yellowstone Fires. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 216 p. Clark, D. 1991. The effect of fire on Yellowstone ecosystem seed banks. M.Sc. Thesis. Montana State University, Bozeman. 115 pp.
Clark, D. 1991. The effect of fire on Yellowstone ecosystem seed banks. M.Sc. Thesis. Montana State University, Bozeman. 115 pp. Culver, D.R. 1994. Floristic analysis of the Centennial Region, Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Montana State University, Bozeman. 199 pp.
Culver, D.R. 1994. Floristic analysis of the Centennial Region, Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Montana State University, Bozeman. 199 pp. Forcella, F. 1977. Flora, chorology, biomass and productivity of the Pinus albicaulis-Vaccinium scoparium association. M.S. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 99 pp.
Forcella, F. 1977. Flora, chorology, biomass and productivity of the Pinus albicaulis-Vaccinium scoparium association. M.S. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 99 pp. Jones, W. W. 1901. Preliminary flora of Gallatin County. M.S. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State College. 78 pp.
Jones, W. W. 1901. Preliminary flora of Gallatin County. M.S. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State College. 78 pp. Joslin, G.J. 1975. Behavior and environmental selection by Elk (Cervus canadensis nelsoni) during surrmer and fall in the First and Second Yellow Mule drainages, Madison County, Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, Montana: Montana State University, Bozeman. 65 p.
Joslin, G.J. 1975. Behavior and environmental selection by Elk (Cervus canadensis nelsoni) during surrmer and fall in the First and Second Yellow Mule drainages, Madison County, Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, Montana: Montana State University, Bozeman. 65 p. Law, D.J. 1999. A comparison of water table dynamics and soil texture under black cottonwood recent alluvial bar, beaked sedge, and Geyer's/Drummond's willow communities. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 68 p.
Law, D.J. 1999. A comparison of water table dynamics and soil texture under black cottonwood recent alluvial bar, beaked sedge, and Geyer's/Drummond's willow communities. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 68 p. Lesica, P., M.T. Lavin, and P.F. Stickney. 2022. Manual of Montana Vascular Plants, Second Edition. Fort Worth, TX: BRIT Press. viii + 779 p.
Lesica, P., M.T. Lavin, and P.F. Stickney. 2022. Manual of Montana Vascular Plants, Second Edition. Fort Worth, TX: BRIT Press. viii + 779 p. McColley, S.D. 2007. Restoring aspen riparian stands with beaver on the northern Yellowstone winter range. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 67 p.
McColley, S.D. 2007. Restoring aspen riparian stands with beaver on the northern Yellowstone winter range. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 67 p. Morgan, J.T. 1993. Summer habitat use of white-tailed deer on the Tally Lake ranger district, Flathead National Forest. Ph.D. Dissertation. Montana State University, Bozeman. pp. 103.
Morgan, J.T. 1993. Summer habitat use of white-tailed deer on the Tally Lake ranger district, Flathead National Forest. Ph.D. Dissertation. Montana State University, Bozeman. pp. 103. Saunders, J.K. Jr. 1955. Food habits and range use of the Rocky Mountain goat in the Crazy Mountains, Montana. Journal of Wildlife Management 19(4):429-437.
Saunders, J.K. Jr. 1955. Food habits and range use of the Rocky Mountain goat in the Crazy Mountains, Montana. Journal of Wildlife Management 19(4):429-437. Saunders, J.K., Jr. 1954. A two-year investigation of the food habits and range use of the Rocky Mountain goat in the Crazy Mountains, Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 22 p.
Saunders, J.K., Jr. 1954. A two-year investigation of the food habits and range use of the Rocky Mountain goat in the Crazy Mountains, Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 22 p. Simanonok, M. 2018. Plant-pollinator network assembly after wildfire. Ph.D. Dissertation. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 123 p.
Simanonok, M. 2018. Plant-pollinator network assembly after wildfire. Ph.D. Dissertation. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 123 p. Simanonok, M.P. and L.A. Burkle. 2019. Nesting success of wood-cavity-nesting bees declines with increasing time since wildfire. Ecology and Evolution 9:12436-12445.
Simanonok, M.P. and L.A. Burkle. 2019. Nesting success of wood-cavity-nesting bees declines with increasing time since wildfire. Ecology and Evolution 9:12436-12445. Singer, F. J. 1979. Habitat partitioning and wildfire relationships of cervids in Glacier National Park, Montana. Journal of Wildlife Management 43(2):437-444.
Singer, F. J. 1979. Habitat partitioning and wildfire relationships of cervids in Glacier National Park, Montana. Journal of Wildlife Management 43(2):437-444.
- Web Search Engines for Articles on "Bristly Black Currant"





