View in other NatureServe Network Field Guides
NatureServe
Montana
Utah
Wyoming
Idaho
Wisconsin
British Columbia
South Carolina
Yukon
California
New York
Gray Green Thistle - Cirsium canovirens
Other Names:
Cirsium cymosum, Cirsium subniveum, Cirsium inamoenum
Native Species
Global Rank:
G4G5
State Rank:
S3S4
(see State Rank Reason below)
C-value:
4
Agency Status
USFWS:
USFS:
BLM:
External Links
State Rank Reason (see State Rank above)
Cirsium canovirens is treated as a variety (Cirsium cymosum variety canovirens) by the Flora of North America (FNA 2006). Whether treated at the species or variety level this plant occurs in southwest Montana where it is fairly common. In general thistles are under-collected, and more location data would be welcomed.
- Details on Status Ranking and Review
Population Size
ScoreC - 250 - 1,000 individuals
Range Extent
ScoreD - 1,000-5,000 sq km (~400-2,000 sq mi)
Area of Occupancy
ScoreC - 3-5 4-km2 grid cells
Number of Populations
ScoreB - 6 - 20
Number of Occurrences or Percent Area with Good Viability / Ecological Integrity
ScoreC - Few (4-12) occurrences with excellent or good viability or ecological integrity
Environmental Specificity
ScoreC - Moderate. Generalist or community with some key requirements scarce
Threats
ScoreD - Low
CommentNo known threats.
General Description
Taprooted biennial. Stems erect, branched above or not, 30–100 cm, sometimes with spiny wings from leaf bases. Herbage tomentose to arachnoid, upper leaf surfaces sometimes sparsely so. Leaves short-petiolate; blade linear-oblanceolate, 8–25 cm long, pinnately lobed, becoming clasping or decurrent upward. Inflorescence heads 1 to few at tips of peduncles forming corymbiform arrays; peduncles 1–8 cm long. Involucres broadly campanulate, 15–30 mm high, sparsely arachnoid-tomentose; phyllaries imbricate in 6 to 10 series, green, linear-lanceolate; sometimes with a darkened, often resinous midvein; spines 2–6 mm long, spreading. Disk corollas white to light purple, 15–26 mm long. Achenes 5–8 mm long (
Lesica et al. 2012. Manual of Montana Vascular Plants. BRIT Press. Fort Worth, TX).
Species Range
Montana Range
Range Descriptions
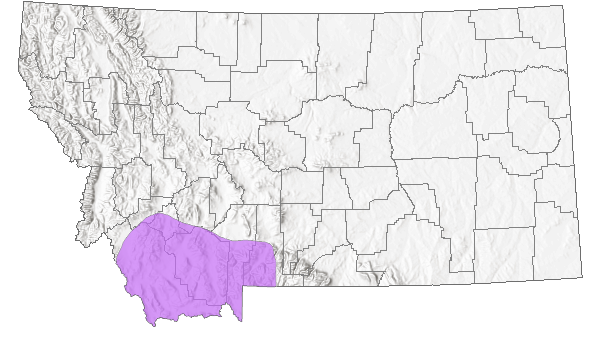
 Native
Native
Range Comments
OR to MT to CA, NV and WY (Lesica et al. 2012. Manual of Montana Vascular Plants. BRIT Press. Fort Worth, TX).
Observations in Montana Natural Heritage Program Database
Number of Observations: 41
(Click on the following maps and charts to see full sized version)
Map Help and Descriptions
Relative Density

Recency



 (Observations spanning multiple months or years are excluded from time charts)
(Observations spanning multiple months or years are excluded from time charts)
Habitat
Ecology
POLLINATORS The following animal species have been reported as pollinators of this plant species or its genus where their geographic ranges overlap:
Bombus vagans,
Bombus appositus,
Bombus auricomus,
Bombus bifarius,
Bombus borealis,
Bombus centralis,
Bombus fervidus,
Bombus flavifrons,
Bombus frigidus,
Bombus huntii,
Bombus mixtus,
Bombus nevadensis,
Bombus rufocinctus,
Bombus sylvicola,
Bombus ternarius,
Bombus terricola,
Bombus sitkensis,
Bombus occidentalis,
Bombus pensylvanicus,
Bombus bimaculatus,
Bombus griseocollis,
Bombus impatiens,
Bombus insularis,
Bombus suckleyi,
Bombus bohemicus, and
Bombus flavidus (Thorp et al. 1983, Mayer et al. 2000, Wilson et al. 2010, Colla and Dumesh 2010, Colla et al. 2011, Koch et al. 2012, Williams et al. 2014, Tripoldi and Szalanski 2015).
References
- Literature Cited AboveLegend:
 View Online Publication
View Online Publication Colla, S., L. Richardson, and P. Williams. 2011. Bumble bees of the eastern United States. Washington, DC: USDA Forest Service, Pollinator Partnership. 103 p.
Colla, S., L. Richardson, and P. Williams. 2011. Bumble bees of the eastern United States. Washington, DC: USDA Forest Service, Pollinator Partnership. 103 p. Colla, S.R. and S. Dumesh. 2010. The bumble bees of southern Ontario: notes on natural history and distribution. Journal of the Entomological Society of Ontario 141:39-68.
Colla, S.R. and S. Dumesh. 2010. The bumble bees of southern Ontario: notes on natural history and distribution. Journal of the Entomological Society of Ontario 141:39-68. Cronquist, A., A.H. Holmgren, N.H. Holmgren, J.L. Reveal, and P.K. Holmgren. 1994. Intermountain Flora: Vascular Plants of the Intermountain West. Asterales. U.S.A., Volume 5. Published for The New York Botanical Garden, Bronx, New York.
Cronquist, A., A.H. Holmgren, N.H. Holmgren, J.L. Reveal, and P.K. Holmgren. 1994. Intermountain Flora: Vascular Plants of the Intermountain West. Asterales. U.S.A., Volume 5. Published for The New York Botanical Garden, Bronx, New York. Koch, J., J. Strange, and P. Williams. 2012. Bumble bees of the western United States. Washington, DC: USDA Forest Service, Pollinator Partnership. 143 p.
Koch, J., J. Strange, and P. Williams. 2012. Bumble bees of the western United States. Washington, DC: USDA Forest Service, Pollinator Partnership. 143 p. Lesica, P., M.T. Lavin, and P.F. Stickney. 2012. Manual of Montana Vascular Plants. Fort Worth, TX: BRIT Press. viii + 771 p.
Lesica, P., M.T. Lavin, and P.F. Stickney. 2012. Manual of Montana Vascular Plants. Fort Worth, TX: BRIT Press. viii + 771 p. Mayer, D.F., E.R. Miliczky, B.F. Finnigan, and C.A. Johnson. 2000. The bee fauna (Hymenoptera: Apoidea) of southeastern Washington. Journal of the Entomological Society of British Columbia 97: 25-31.
Mayer, D.F., E.R. Miliczky, B.F. Finnigan, and C.A. Johnson. 2000. The bee fauna (Hymenoptera: Apoidea) of southeastern Washington. Journal of the Entomological Society of British Columbia 97: 25-31. Thorp, R.W., D.S. Horning, and L.L. Dunning. 1983. Bumble bees and cuckoo bumble bees of California (Hymenoptera: Apidae). Bulletin of the California Insect Survey 23:1-79.
Thorp, R.W., D.S. Horning, and L.L. Dunning. 1983. Bumble bees and cuckoo bumble bees of California (Hymenoptera: Apidae). Bulletin of the California Insect Survey 23:1-79. Tripoldi, A.D. and A.L. Szalanski. 2015. The bumble bees (Hymenoptera: Apidae: Bombus) of Arkansas, fifty years later. Journal of Melittology 50: doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.17161/jom.v0i50.4834
Tripoldi, A.D. and A.L. Szalanski. 2015. The bumble bees (Hymenoptera: Apidae: Bombus) of Arkansas, fifty years later. Journal of Melittology 50: doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.17161/jom.v0i50.4834 Williams, P., R. Thorp, L. Richardson, and S. Colla. 2014. Bumble Bees of North America. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press. 208 p.
Williams, P., R. Thorp, L. Richardson, and S. Colla. 2014. Bumble Bees of North America. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press. 208 p. Wilson, J.S., L.E. Wilson, L.D. Loftis, and T. Griswold. 2010. The montane bee fauna of north central Washington, USA, with floral associations. Western North American Naturalist 70(2): 198-207.
Wilson, J.S., L.E. Wilson, L.D. Loftis, and T. Griswold. 2010. The montane bee fauna of north central Washington, USA, with floral associations. Western North American Naturalist 70(2): 198-207.
- Additional ReferencesLegend:
 View Online Publication
View Online Publication
Do you know of a citation we're missing? Culver, D.R. 1994. Floristic analysis of the Centennial Region, Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Montana State University, Bozeman. 199 pp.
Culver, D.R. 1994. Floristic analysis of the Centennial Region, Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Montana State University, Bozeman. 199 pp. Harvey, S.J. 1990. Responses of steppe plants to gradients of water soil texture and disturbance in Montana, U.S.A. Ph.D. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 34 p.
Harvey, S.J. 1990. Responses of steppe plants to gradients of water soil texture and disturbance in Montana, U.S.A. Ph.D. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 34 p. Lesica, P., M.T. Lavin, and P.F. Stickney. 2022. Manual of Montana Vascular Plants, Second Edition. Fort Worth, TX: BRIT Press. viii + 779 p.
Lesica, P., M.T. Lavin, and P.F. Stickney. 2022. Manual of Montana Vascular Plants, Second Edition. Fort Worth, TX: BRIT Press. viii + 779 p. Quire, R.L. 2013. The sagebrush steppe of Montana and southeastern Idaho shows evidence of high native plant diversity, stability, and resistance to the detrimental effects of nonnative plant species. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 124 p.
Quire, R.L. 2013. The sagebrush steppe of Montana and southeastern Idaho shows evidence of high native plant diversity, stability, and resistance to the detrimental effects of nonnative plant species. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 124 p.
- Web Search Engines for Articles on "Gray Green Thistle"





