View in other NatureServe Network Field Guides
NatureServe
Montana
Utah
Wyoming
Idaho
Wisconsin
British Columbia
South Carolina
Yukon
California
New York
Coville Indian Paintbrush - Castilleja covilleana
State Rank Reason (see State Rank above)
This species is known in Montana, primarily from the West Fork of the Bitterroot River on the Bitterroot National Forest. 5 occurrences are known from historical collections or have unknown status. A few occurrences contain minor amounts of spotted knapweed and others occur in habitats that are susceptible to invasion by knapweed and other invasive species. Timber harvest activities may also pose a threat to some populations.
- Details on Status Ranking and Review
Population Size
Score1-2 - Small to Moderate. Population size is imprecisely known but is believed to be >2,000 individuals and <100,000 individuals.
Range Extent
Score2 - Regional or State Endemic or Small Montana Range: Generally restricted to an area <100,000 sq. miles (equivalent to 2/3 the size of Montana or less) or Montana contributes 50% or more of the species’ range or populations OR limited to 2-3 Sub-basins in Montana.
Area of Occupancy
Score1 - Moderate: Generally occurring in 11-25 Subwatersheds (6th Code HUC’s).
Environmental Specificity
Score1 - Moderate: Species is restricted to a specific habitat that is more widely distributed or to several restricted habitats and is typically dependent upon relatively unaltered, good-quality habitat (C Values of 5-7).
Trends
Score0-1 - Stable to Minor Declines:
CommentTrends unknown, though populations are likely stable or experiencing only minor declines.
Threats
Score1-2 - Medium to High.
Commentinvasive weeds are impacting some of the species' habitat.
Intrinsic Vulnerability
Score1 - Moderate Vulnerability: Specific biological attributes, unusual life history characteristics or limited reproductive potential makes the species susceptible to extirpation from stochastic events or other adverse impacts to its habitat and slow to recover.
Raw Conservation Status Score
Score
7 to 10 total points scored out of a possible 19.
General Description
Coville Indian Paintbrush is a perennial with clusters of several unbranched, erect or ascending stems, which can be up to 30 cm tall. All leaves but the lowermost are deeply divided into 3-7 spreading, linear lobes, and are alternate on the stem. The herbage is covered with long, soft hairs. The inflorescence is usually bright red or scarlet, but may be orangish-yellow; it is short and compact at first, but elongates greatly at maturity. The colored flower bracts are deeply 5-7 parted and at least as long as the flowers. The corolla is 20-35 mm long, and the hooded upper lip is 1/2-2/3 the length of the tubular portion. The calyx is 15-25 mm long and more deeply divided above than below.
Phenology
Flowering late June-early August.
Diagnostic Characteristics
This species can be distinguished from other red paintbrushes in its range by the covering of long, soft hairs (rather than stiff and straight), and by the middle leaf segments that are almost as narrow as the lateral segments.
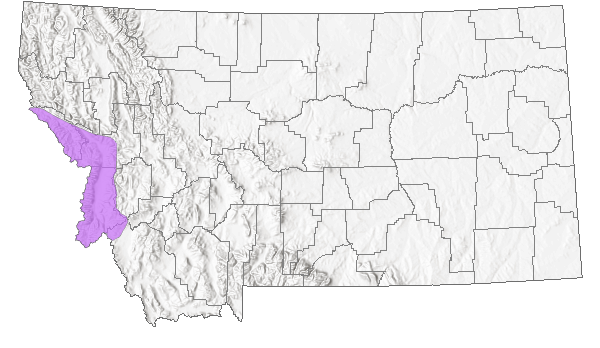
Species Range
Montana Range
Range Descriptions
 Native
Native
Range Comments
Central ID and adjacent southwest MT. Regional endemic.
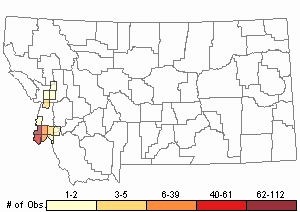
Observations in Montana Natural Heritage Program Database
Number of Observations: 261
(Click on the following maps and charts to see full sized version)
Map Help and Descriptions
Relative Density
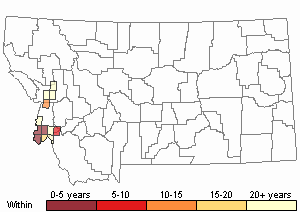
Recency
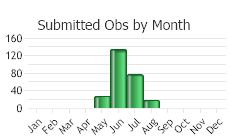
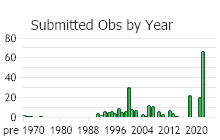
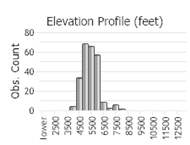 (Observations spanning multiple months or years are excluded from time charts)
(Observations spanning multiple months or years are excluded from time charts)
Habitat
Stony soil of slopes and summits in the montane and subalpine zones.
Ecological Systems Associated with this Species
Ecology
POLLINATORS The following animal species have been reported as pollinators of this plant species or its genus where their geographic ranges overlap:
Bombus appositus,
Bombus bifarius,
Bombus fervidus,
Bombus flavifrons,
Bombus melanopygus,
Bombus sylvicola,
Bombus occidentalis, and
Bombus kirbiellus (Macior 1974, Thorp et al. 1983, Bauer 1983, Mayer et al. 2000, Wilson et al. 2010, Pyke et al. 2012, Koch et al. 2012, Miller-Struttmann and Galen 2014, Williams et al. 2014).
Stewardship Responsibility
Threats or Limiting Factors
STATE THREAT SCORE REASON
Reported threats to Montana’s populations of Coville Indian Paintbrush are impacts due to noxious weeds (MTNHP Threat Assessment 2021). Spotted Knapweed (Centaurea stoebe) is established with some populations, where negative impacts range from moderate to serious.
References
- Literature Cited AboveLegend:
 View Online Publication
View Online Publication Bauer, P.J. 1983. Bumblebee pollination relationships on the Beartooth Plateau tundra of Southern Montana. American Journal of Botany. 70(1): 134-144.
Bauer, P.J. 1983. Bumblebee pollination relationships on the Beartooth Plateau tundra of Southern Montana. American Journal of Botany. 70(1): 134-144. Koch, J., J. Strange, and P. Williams. 2012. Bumble bees of the western United States. Washington, DC: USDA Forest Service, Pollinator Partnership. 143 p.
Koch, J., J. Strange, and P. Williams. 2012. Bumble bees of the western United States. Washington, DC: USDA Forest Service, Pollinator Partnership. 143 p. Macior, L.M. 1974. Pollination ecology of the Front Range of the Colorado Rocky Mountains. Melanderia 15: 1-59.
Macior, L.M. 1974. Pollination ecology of the Front Range of the Colorado Rocky Mountains. Melanderia 15: 1-59. Mayer, D.F., E.R. Miliczky, B.F. Finnigan, and C.A. Johnson. 2000. The bee fauna (Hymenoptera: Apoidea) of southeastern Washington. Journal of the Entomological Society of British Columbia 97: 25-31.
Mayer, D.F., E.R. Miliczky, B.F. Finnigan, and C.A. Johnson. 2000. The bee fauna (Hymenoptera: Apoidea) of southeastern Washington. Journal of the Entomological Society of British Columbia 97: 25-31. Miller-Struttmann, N.E. and C. Galen. 2014. High-altitude multi-taskers: bumble bee food plant use broadens along an altitudinal productivity gradient. Oecologia 176:1033-1045.
Miller-Struttmann, N.E. and C. Galen. 2014. High-altitude multi-taskers: bumble bee food plant use broadens along an altitudinal productivity gradient. Oecologia 176:1033-1045. MTNHP Threat Assessment. 2021. State Threat Score Assignment and Assessment of Reported Threats from 2006 to 2021 for State-listed Vascular Plants. Botany Program, Montana Natural Heritage Program, Helena, Montana.
MTNHP Threat Assessment. 2021. State Threat Score Assignment and Assessment of Reported Threats from 2006 to 2021 for State-listed Vascular Plants. Botany Program, Montana Natural Heritage Program, Helena, Montana. Pyke, G.H., D.W. Inouye, and J.D. Thomson. 2012. Local geographic distributions of bumble bees near Crested Butte, Colorado: competition and community structure revisited. Environmental Entomology 41(6): 1332-1349.
Pyke, G.H., D.W. Inouye, and J.D. Thomson. 2012. Local geographic distributions of bumble bees near Crested Butte, Colorado: competition and community structure revisited. Environmental Entomology 41(6): 1332-1349. Thorp, R.W., D.S. Horning, and L.L. Dunning. 1983. Bumble bees and cuckoo bumble bees of California (Hymenoptera: Apidae). Bulletin of the California Insect Survey 23:1-79.
Thorp, R.W., D.S. Horning, and L.L. Dunning. 1983. Bumble bees and cuckoo bumble bees of California (Hymenoptera: Apidae). Bulletin of the California Insect Survey 23:1-79. Williams, P., R. Thorp, L. Richardson, and S. Colla. 2014. Bumble Bees of North America. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press. 208 p.
Williams, P., R. Thorp, L. Richardson, and S. Colla. 2014. Bumble Bees of North America. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press. 208 p. Wilson, J.S., L.E. Wilson, L.D. Loftis, and T. Griswold. 2010. The montane bee fauna of north central Washington, USA, with floral associations. Western North American Naturalist 70(2): 198-207.
Wilson, J.S., L.E. Wilson, L.D. Loftis, and T. Griswold. 2010. The montane bee fauna of north central Washington, USA, with floral associations. Western North American Naturalist 70(2): 198-207.
- Additional ReferencesLegend:
 View Online Publication
View Online Publication
Do you know of a citation we're missing? Lesica, P., M.T. Lavin, and P.F. Stickney. 2012. Manual of Montana Vascular Plants. Fort Worth, TX: BRIT Press. viii + 771 p.
Lesica, P., M.T. Lavin, and P.F. Stickney. 2012. Manual of Montana Vascular Plants. Fort Worth, TX: BRIT Press. viii + 771 p. Lesica, P., M.T. Lavin, and P.F. Stickney. 2022. Manual of Montana Vascular Plants, Second Edition. Fort Worth, TX: BRIT Press. viii + 779 p.
Lesica, P., M.T. Lavin, and P.F. Stickney. 2022. Manual of Montana Vascular Plants, Second Edition. Fort Worth, TX: BRIT Press. viii + 779 p.
- Web Search Engines for Articles on "Coville Indian Paintbrush"





