View in other NatureServe Network Field Guides
NatureServe
Montana
Utah
Wyoming
Idaho
Wisconsin
British Columbia
South Carolina
Yukon
California
New York
Long-tailed Weasel - Neogale frenata
Other Names:
Mustela frenata
Native Species
Global Rank:
G5
State Rank:
S5
(see State Rank Reason below)
Agency Status
USFWS:
USFS:
BLM:
State Rank Reason (see State Rank above)
Species is common and widely distributed. It may have undergone moderate declines in the past decade and faces no known significant threats.
General Description
Largest and most widely distributed of the three Northern American weasels. Distinguished by its long, slender body and long neck. Longest tail of the North American weasels. During summer fur rich brown on the back and sides with yellowish-white under-parts, black tip on tail, and no whitish line down inside of leg. Acquires a white winter coat. Adult males noticeably larger than females. Total length: 11 to 16.5 inches. Weight: three to 12 ounces.
Diagnostic Characteristics
Short-tailed Weasel has white line down inside of leg and is smaller. Least Weasel does not have black tip on tail and is smaller. American Mink is nearly uniform dark brown. Marten is heavier and much larger.
Species Range
Montana Range
Range Descriptions
 Native
Native
Western Hemisphere Range

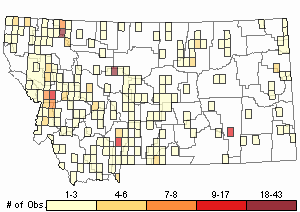
Observations in Montana Natural Heritage Program Database
Number of Observations: 565
(Click on the following maps and charts to see full sized version)
Map Help and Descriptions
Relative Density
Recency
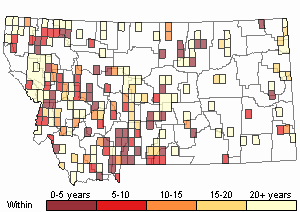
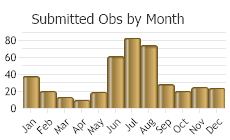
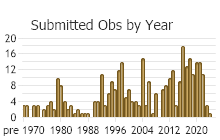
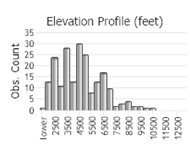 (Observations spanning multiple months or years are excluded from time charts)
(Observations spanning multiple months or years are excluded from time charts)
Migration
Non-migratory.
Habitat
Found in almost all land habitats near water. Has the broadest ecological and geographical range of the North American weasels. Prefers areas with abundant prey. Avoids dense forest, most abundant in late seral ecotones. Primarily nocturnal, but sometimes active during the day. Quite fearless and curious. Mainly terrestrial but can climb and swim well. Nests in old burrows of other animals. Occupies a diverse range of habitats. More prone to open country and forest openings than M. erminea. Common in intermontane valleys and open forests where M. erminea is absent. May occur up to alpine tundra (Hoffmann and Pattie 1968).
National Vegetation Classification System Groups Associated with this Species
Alpine
Alpine - Vegetated
Forest and Woodland
Deciduous Forest and Woodland
Low Elevation - Xeric Forest and Woodland
Montane - Subalpine Forest and Woodland
Shrubland
Arid - Saline Shrubland
Foothills - Montane Shrubland
Sagebrush Shrubland
Grassland
Lowland - Prairie Grassland
Montane - Subalpine Grassland
Sparse and Barren
Sparse and Barren
Wetland and Riparian
Alkaline - Saline Wetlands
Alpine Riparian and Wetland
Peatland
Riparian and Wetland Forest
Riparian Shrubland
Wet Meadow and Marsh
Recently Disturbed or Modified
Harvested Forest
Insect-Killed Forest
Introduced Vegetation
Recently Burned
Human Land Use
Agriculture
Developed
Food Habits
More of a generalist than the Short-tailed and Least Weasels. Feeds mostly on small mammals up to rabbit-sized, but eats birds and other animals as well. Males: rabbits, tree squirrels, and ground squirrels. FeMales: mice and chipmunks. Dietary componenets overlap. Both sexes will occasionally use birds, herptiles, and insects (Jones et al. 1983).
Ecology
Weasels will cache prey. This permits food storage without obesity, facilitating ability to pursue prey in narrow burrows. Males about 10 to 15% larger than females (Svendsen 1982).
Reproductive Characteristics
Mates during summer, 205- to 337-day gestation; delayed implantation; young born during April; litter size four to nine.
Stewardship Responsibility
References
- Literature Cited AboveLegend:
 View Online Publication
View Online Publication Hoffmann, R.S. and D.L. Pattie. 1968. A guide to Montana mammals: identification, habitat, distribution, and abundance. Missoula, MT: University of Montana. 133 p.
Hoffmann, R.S. and D.L. Pattie. 1968. A guide to Montana mammals: identification, habitat, distribution, and abundance. Missoula, MT: University of Montana. 133 p. Jones, J.K., D.M. Armstrong, R.S. Hoffmann and C. Jones. 1983. Mammals of the northern Great Plains. University of Nebraska Press, Lincoln. 379 pp.
Jones, J.K., D.M. Armstrong, R.S. Hoffmann and C. Jones. 1983. Mammals of the northern Great Plains. University of Nebraska Press, Lincoln. 379 pp. Svendsen, G. E. 1982. Weasels. Pp. 613-628 in: Hapman, J. A. and G. A. Feldhamer (eds). Wild mammals of North America. John Hopkins Univ. Press, Baltimore. 1147 pp.
Svendsen, G. E. 1982. Weasels. Pp. 613-628 in: Hapman, J. A. and G. A. Feldhamer (eds). Wild mammals of North America. John Hopkins Univ. Press, Baltimore. 1147 pp.
- Additional ReferencesLegend:
 View Online Publication
View Online Publication
Do you know of a citation we're missing? Anaconda Minerals Company, and Camp, Dresser & McKee. 1981. Anaconda Stillwater Project 6-month environmental baseline report. CDM Project No. 3139. Vol. I Appendix. Jan. 15, 1981.
Anaconda Minerals Company, and Camp, Dresser & McKee. 1981. Anaconda Stillwater Project 6-month environmental baseline report. CDM Project No. 3139. Vol. I Appendix. Jan. 15, 1981. Andersen, K. W., and J. K. Jones, Jr. 1971. Mammals of northwestern South Dakota. Univ. Kan Mus. Nat. Hist. Pub. 19:361-393.
Andersen, K. W., and J. K. Jones, Jr. 1971. Mammals of northwestern South Dakota. Univ. Kan Mus. Nat. Hist. Pub. 19:361-393. Bauer, Delane, 2002, 2002 Four Seasons Wildlife Study. Savage Mine Report, Richland County, Montana.
Bauer, Delane, 2002, 2002 Four Seasons Wildlife Study. Savage Mine Report, Richland County, Montana. Buck, C.L. 1939. Pattern correlation of mammalian teeth as a means of identification. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, Montana: Montana State University. 55 p.
Buck, C.L. 1939. Pattern correlation of mammalian teeth as a means of identification. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, Montana: Montana State University. 55 p. Chapman, J.A., and G.A. Feldhamer. 1982. Wild mammals of North America: biology, management, and economics. Johns Hopkins University Press, Baltimore, Maryland.
Chapman, J.A., and G.A. Feldhamer. 1982. Wild mammals of North America: biology, management, and economics. Johns Hopkins University Press, Baltimore, Maryland. Cross, James, and Richard P. Weckwerth, 1977, Upland Game Bird (and Fur Survey) Inventory. Wildlife Investigations, Region One. W-130-R-8, Job No. II-1, July 1, 1976 - June 30, 1977.
Cross, James, and Richard P. Weckwerth, 1977, Upland Game Bird (and Fur Survey) Inventory. Wildlife Investigations, Region One. W-130-R-8, Job No. II-1, July 1, 1976 - June 30, 1977. Cross, James, and Richard P. Weckwerth, 1978, Upland Game Bird (and Fur Survey) Inventory. Wildlife Investigations, Region One. W-130-R-9, Job No. II-1, July 1, 1977 - June 30, 1978.
Cross, James, and Richard P. Weckwerth, 1978, Upland Game Bird (and Fur Survey) Inventory. Wildlife Investigations, Region One. W-130-R-9, Job No. II-1, July 1, 1977 - June 30, 1978. Cross, James, and Richard P. Weckwerth, 1980, Upland Game Bird (and Fur Survey) Inventory. Wildlife Investigations, Region One. W-130-R-11, Job No. II-1, July 1, 1979 - June 30, 1980.
Cross, James, and Richard P. Weckwerth, 1980, Upland Game Bird (and Fur Survey) Inventory. Wildlife Investigations, Region One. W-130-R-11, Job No. II-1, July 1, 1979 - June 30, 1980. Cross, James, and Richard P. Weckwerth, 1981, Upland Game Bird (and Fur Survey) Inventory. Wildlife Investigations, Region One. W-130-R-12, Job No. II-1, July 1, 1980 - June 30, 1981.
Cross, James, and Richard P. Weckwerth, 1981, Upland Game Bird (and Fur Survey) Inventory. Wildlife Investigations, Region One. W-130-R-12, Job No. II-1, July 1, 1980 - June 30, 1981. Cross, James, and Richard P. Weckwerth, 1983, Upland Game Bird (and Fur Survey) Inventory. Wildlife Investigations, Region One. W-130-R-14, Job No. II-1, July 1, 1982 - June 30, 1983.
Cross, James, and Richard P. Weckwerth, 1983, Upland Game Bird (and Fur Survey) Inventory. Wildlife Investigations, Region One. W-130-R-14, Job No. II-1, July 1, 1982 - June 30, 1983. Deems, E.F., Jr. and D. Pursley (eds). 1978. North American furbearers: their management, research and harvest status in 1976. Int. Assoc. Fish and Wildlife Agencies and University of Maryland. 171 p.
Deems, E.F., Jr. and D. Pursley (eds). 1978. North American furbearers: their management, research and harvest status in 1976. Int. Assoc. Fish and Wildlife Agencies and University of Maryland. 171 p. ECON, Inc. (Ecological Consulting Service), Helena, MT., 1976, Colstrip 10 x 20 Area wildlife and wildlife habitat annual monitoring report, 1976. Proj. 135-85-A. December 31, 1976.
ECON, Inc. (Ecological Consulting Service), Helena, MT., 1976, Colstrip 10 x 20 Area wildlife and wildlife habitat annual monitoring report, 1976. Proj. 135-85-A. December 31, 1976. Econ, Inc. 1988. Wildlife monitoring report, 1987 field season, Big Sky Mine. March 1988. In Peabody Mining and Reclamation Plan Big Sky Mine Area B. Vol. 8, cont., Tab 10 - Wildlife Resources. Appendix 10-1, 1987 Annual Wildlife Report.
Econ, Inc. 1988. Wildlife monitoring report, 1987 field season, Big Sky Mine. March 1988. In Peabody Mining and Reclamation Plan Big Sky Mine Area B. Vol. 8, cont., Tab 10 - Wildlife Resources. Appendix 10-1, 1987 Annual Wildlife Report. ECON, Inc., Helena, MT., 1987, Wildlife and habitat characterization, Paupers Dream Mine Project Site, Lewis & Clark and Jefferson Counties, Montana. June 25, 1987. In Pangea Mining Co., Inc., Paupers Dream Project.
ECON, Inc., Helena, MT., 1987, Wildlife and habitat characterization, Paupers Dream Mine Project Site, Lewis & Clark and Jefferson Counties, Montana. June 25, 1987. In Pangea Mining Co., Inc., Paupers Dream Project. Farmer, Patrick J., and Thomas W. Butts, Western Technology & Eng., Inc., Helena, MT., 1994, McDonald Project Terrestrial Wildlife Study, November 1989 - November 1993. April 1994. In McDonald Gold Project: Wildlife & Fisheries. [#18]. Seven-up Pete Joint Venture, Lincoln, MT. Unpub. No date.
Farmer, Patrick J., and Thomas W. Butts, Western Technology & Eng., Inc., Helena, MT., 1994, McDonald Project Terrestrial Wildlife Study, November 1989 - November 1993. April 1994. In McDonald Gold Project: Wildlife & Fisheries. [#18]. Seven-up Pete Joint Venture, Lincoln, MT. Unpub. No date. Farmer, Patrick. J., et al., Western Technology and Eng., Inc., Helena, MT., 1984, Montana Tunnels Project Baseline Terrestrial Wildlife Study. December 14, 1984. In Application for a Hard Rock Operating Permit, Montana Tunnels Project, Jefferson County, Montana. Vol. 3. Environmental Baseline Reports. (Centennial Minerals, Inc., Hydrometrics, 1984?)
Farmer, Patrick. J., et al., Western Technology and Eng., Inc., Helena, MT., 1984, Montana Tunnels Project Baseline Terrestrial Wildlife Study. December 14, 1984. In Application for a Hard Rock Operating Permit, Montana Tunnels Project, Jefferson County, Montana. Vol. 3. Environmental Baseline Reports. (Centennial Minerals, Inc., Hydrometrics, 1984?) Fitzgerald, B. M. 1977. Weasel predation on a cyclic population of the montane vole (Microtus montanus) in California. J. Anim. Ecol. 46: 367-397.
Fitzgerald, B. M. 1977. Weasel predation on a cyclic population of the montane vole (Microtus montanus) in California. J. Anim. Ecol. 46: 367-397. Fjell, Alan K., 1986, Peabody Coal Company Big Sky Mine, Rosebud County, MT. Wildlife monitoring report: 1985 field season. March 1986.
Fjell, Alan K., 1986, Peabody Coal Company Big Sky Mine, Rosebud County, MT. Wildlife monitoring report: 1985 field season. March 1986. Fjell, Alan K., and Brian R. Mahan, compilers., 1984, Peabody Coal Company Big Sky Mine, Rosebud County, MT. Wildlife monitoring report: 1983 field season. February 1984.
Fjell, Alan K., and Brian R. Mahan, compilers., 1984, Peabody Coal Company Big Sky Mine, Rosebud County, MT. Wildlife monitoring report: 1983 field season. February 1984. Fjell, Alan K., and Brian R. Mahan., 1983, Peabody Coal Company Big Sky Mine, Rosebud County, MT. Wildlife monitoring report: 1982 field season. May 1983.
Fjell, Alan K., and Brian R. Mahan., 1983, Peabody Coal Company Big Sky Mine, Rosebud County, MT. Wildlife monitoring report: 1982 field season. May 1983. Fjell, Alan K., and Brian R. Mahan., 1985, Peabody Coal Company Big Sky Mine, Rosebud County, MT. Wildlife monitoring report: 1984 field season. February 1985.
Fjell, Alan K., and Brian R. Mahan., 1985, Peabody Coal Company Big Sky Mine, Rosebud County, MT. Wildlife monitoring report: 1984 field season. February 1985. Fjell, Alan K., and Brian R. Mahan., 1987, Big Sky Mine, Rosebud County, MT. Wildlife monitoring report: 1986 field season. April 1987.
Fjell, Alan K., and Brian R. Mahan., 1987, Big Sky Mine, Rosebud County, MT. Wildlife monitoring report: 1986 field season. April 1987. Foresman, K.R. 2001. The wild mammals of Montana. American Society of Mammalogists, Special Publication Number 12. Lawrence, KS. 278 pp.
Foresman, K.R. 2001. The wild mammals of Montana. American Society of Mammalogists, Special Publication Number 12. Lawrence, KS. 278 pp. Foresman, K.R. 2012. Mammals of Montana. Second edition. Mountain Press Publishing, Missoula, Montana. 429 pp.
Foresman, K.R. 2012. Mammals of Montana. Second edition. Mountain Press Publishing, Missoula, Montana. 429 pp. Graham, Dean, and Craig Swick., 1977, A Field evaluation of the cyclone seeder for reducing Richardson ground squirrel populations causing damage in central Montana . August 1977.
Graham, Dean, and Craig Swick., 1977, A Field evaluation of the cyclone seeder for reducing Richardson ground squirrel populations causing damage in central Montana . August 1977. Haglund, B.M. 1972. Ecological effects of weather modification, Bangtail Ridge, Bridger Range, Montana: relationships of pocket gophers (Thomomys talpoides) to time of snow melt. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, Montana: Montana State University. 26 p.
Haglund, B.M. 1972. Ecological effects of weather modification, Bangtail Ridge, Bridger Range, Montana: relationships of pocket gophers (Thomomys talpoides) to time of snow melt. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, Montana: Montana State University. 26 p. Haight, C.P. 1937. Some observations on the predator-prey complex in the Gallatin Valley. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, Montana: Montana State University. 58 p.
Haight, C.P. 1937. Some observations on the predator-prey complex in the Gallatin Valley. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, Montana: Montana State University. 58 p. Hanauska-Brown, L., B.A. Maxell, A. Petersen, and S. Story. 2014. Diversity Monitoring in Montana 2008-2010 Final Report. Montana Fish, Wildlife & Parks. Helena, MT. 78 pp.
Hanauska-Brown, L., B.A. Maxell, A. Petersen, and S. Story. 2014. Diversity Monitoring in Montana 2008-2010 Final Report. Montana Fish, Wildlife & Parks. Helena, MT. 78 pp. Harmata, A.R. 1991. Impacts of oil and gas development on raptors associated with Kevin Rim, Montana. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. Unpublished report by the Kevin Rim Raptor Study Group. Prepared for the USDI BLM, Great Falls Resource Area, Great Falls, MT. 106 p.
Harmata, A.R. 1991. Impacts of oil and gas development on raptors associated with Kevin Rim, Montana. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. Unpublished report by the Kevin Rim Raptor Study Group. Prepared for the USDI BLM, Great Falls Resource Area, Great Falls, MT. 106 p. Hatier, K.G. 1995. Effects of helping behaviors on Coyote packs in Yellowstone National Park, Wyoming. M Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 78 p.
Hatier, K.G. 1995. Effects of helping behaviors on Coyote packs in Yellowstone National Park, Wyoming. M Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 78 p. Hendricks, P., S. Lenard, D.M. Stagliano, and B.A. Maxell. 2013. Baseline nongame wildlife surveys on the Fort Peck Indian Reservation. Report to the Assiniboine and Sioux Tribes of the Fort Peck Indian Reservation. Montana Natural Heritage Program, Helena, MT. 83 p.
Hendricks, P., S. Lenard, D.M. Stagliano, and B.A. Maxell. 2013. Baseline nongame wildlife surveys on the Fort Peck Indian Reservation. Report to the Assiniboine and Sioux Tribes of the Fort Peck Indian Reservation. Montana Natural Heritage Program, Helena, MT. 83 p. Hollenbeck, R.R. 1974. Growth rates and movements within a population of Rana pretiosa pretiosa Baird and Girard in south central Montana. Ph.D. Dissertation. Bozeman, Montana: Montana State University. 66 p.
Hollenbeck, R.R. 1974. Growth rates and movements within a population of Rana pretiosa pretiosa Baird and Girard in south central Montana. Ph.D. Dissertation. Bozeman, Montana: Montana State University. 66 p. Johnson, L.J. 1960. Mammal studies on the Lubrecht Forest, Montana: a preliminary report. Proc. Mont. Acad. Sci. 20: 40-47.
Johnson, L.J. 1960. Mammal studies on the Lubrecht Forest, Montana: a preliminary report. Proc. Mont. Acad. Sci. 20: 40-47. Joslin, Gayle, and Heidi B. Youmans. 1999. Effects of recreation on Rocky Mountain wildlife: a review for Montana. [Montana]: Montana Chapter of the Wildlife Society.
Joslin, Gayle, and Heidi B. Youmans. 1999. Effects of recreation on Rocky Mountain wildlife: a review for Montana. [Montana]: Montana Chapter of the Wildlife Society. Keith, L. B. and J. R. Cary 1991. Mustelid, squirrel and porcupine population trends during a snowshoe hare cycle. J. Mammal. 72(2):373-378.
Keith, L. B. and J. R. Cary 1991. Mustelid, squirrel and porcupine population trends during a snowshoe hare cycle. J. Mammal. 72(2):373-378. Key, C.H. 1979. Mammalian utilization of floodplain habitats along the North Fork of the Flathead River in Glacier National Park, Montana. M.S. thesis. University of Montana, Missoula.
Key, C.H. 1979. Mammalian utilization of floodplain habitats along the North Fork of the Flathead River in Glacier National Park, Montana. M.S. thesis. University of Montana, Missoula. King, C. M. 1989. The natural history of weasels and stoats. Comstock Pub. Assoc. Ithaca, NY. 253 pp.
King, C. M. 1989. The natural history of weasels and stoats. Comstock Pub. Assoc. Ithaca, NY. 253 pp. Koplin, J.R. 1962. Competition and niche segregation in the genus Microtus. M.S. thesis. Montana State University. 66 pp.
Koplin, J.R. 1962. Competition and niche segregation in the genus Microtus. M.S. thesis. Montana State University. 66 pp. Lampe, R.P., J.K. Jones Jr., R.S. Hoffmann, and E.C. Birney. 1974. The mammals of Carter County, southeastern Montana. Occa. Pap. Mus. Nat. Hist. Univ. Kan. 25:1-39.
Lampe, R.P., J.K. Jones Jr., R.S. Hoffmann, and E.C. Birney. 1974. The mammals of Carter County, southeastern Montana. Occa. Pap. Mus. Nat. Hist. Univ. Kan. 25:1-39. Matthews, W.L. 1980a. Wibaux-Beach comparison study: Sydney, Glendive and Plevna Study Areas. Bureau of Land Management, Miles City, MT. 50 p.
Matthews, W.L. 1980a. Wibaux-Beach comparison study: Sydney, Glendive and Plevna Study Areas. Bureau of Land Management, Miles City, MT. 50 p. Matthews, W.L. 1981. Broadus-Pumpkin Creek baseline inventory - wildlife. Bureau of Land Management, Miles City, MT. 83 p.
Matthews, W.L. 1981. Broadus-Pumpkin Creek baseline inventory - wildlife. Bureau of Land Management, Miles City, MT. 83 p. Mead, E.M. and J.I. Mead. 1989. Snake Creek burial cave and a review of the Quaternary mustelids of the Great Basin. Great Basin Naturalist 49(2):143-154.
Mead, E.M. and J.I. Mead. 1989. Snake Creek burial cave and a review of the Quaternary mustelids of the Great Basin. Great Basin Naturalist 49(2):143-154. Montana Prairie Dog Working Group. 2002. Conservation plan for black-tailed and white-tailed prairie dogs in Montana. Montana Fish, Wildlife and Parks. Helena MT. 51 pp.
Montana Prairie Dog Working Group. 2002. Conservation plan for black-tailed and white-tailed prairie dogs in Montana. Montana Fish, Wildlife and Parks. Helena MT. 51 pp. Morrison-Maierle Env. Corp., Helena, MT., 1993, Biological assessment and wildlife reconnaissance, Holnam Cement Plant, Trident, Montana. In Application to Amend Operating Permit 00004 for Trident Quarries, Three Forks, Montana. Exhibit DD: Wildlife Reconnaisance Study. June 28, 1996.
Morrison-Maierle Env. Corp., Helena, MT., 1993, Biological assessment and wildlife reconnaissance, Holnam Cement Plant, Trident, Montana. In Application to Amend Operating Permit 00004 for Trident Quarries, Three Forks, Montana. Exhibit DD: Wildlife Reconnaisance Study. June 28, 1996. Newlon, K.R. 2005. Demography of Lewis's Woodpecker, breeding bird densities, and riparian Aspen integrity in a grazed landscape. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 101 p.
Newlon, K.R. 2005. Demography of Lewis's Woodpecker, breeding bird densities, and riparian Aspen integrity in a grazed landscape. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 101 p. Oechsli, L.M. 2000. Ex-urban development in the Rocky Mountain West: consequences for native vegetation, wildlife diversity, and land-use planning in Big Sky, Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Montana State University, Bozeman. 73 p.
Oechsli, L.M. 2000. Ex-urban development in the Rocky Mountain West: consequences for native vegetation, wildlife diversity, and land-use planning in Big Sky, Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Montana State University, Bozeman. 73 p. Pattie, D.L. and N.A. M. Verbeek. 1967. Alpine mammals of the Beartooth Plateau. Northwest Science 41(3): 110-117.
Pattie, D.L. and N.A. M. Verbeek. 1967. Alpine mammals of the Beartooth Plateau. Northwest Science 41(3): 110-117. Purdum, Jeremiah P. 2013. Acceptance of wildlife crossing structures on US Highway 93 Missoula, Montana. M.S. Thesis. University of Montana. Missoula, MT.
Purdum, Jeremiah P. 2013. Acceptance of wildlife crossing structures on US Highway 93 Missoula, Montana. M.S. Thesis. University of Montana. Missoula, MT. Reichel, J.D. 1986. Habitat use by alpine mammals in the Pacific Northwest. Arctic and Alpine Research. 18(1): 111-119.
Reichel, J.D. 1986. Habitat use by alpine mammals in the Pacific Northwest. Arctic and Alpine Research. 18(1): 111-119. Reichel, J.D. and S.G. Beckstrom. 1993. Northern bog lemming survey: 1992. Unpublished report. Montana Natural Heritage Program, Helena, MT. 64 p.
Reichel, J.D. and S.G. Beckstrom. 1993. Northern bog lemming survey: 1992. Unpublished report. Montana Natural Heritage Program, Helena, MT. 64 p. Reid, F. 2006. Peterson Field Guide to Mammals of North America, 4th Edition. Houghton Mifflin Company: Boston and New York, 608 pp.
Reid, F. 2006. Peterson Field Guide to Mammals of North America, 4th Edition. Houghton Mifflin Company: Boston and New York, 608 pp. Runge, W. 1993. The long-tailed weasel in Saskatchewan. Saskatchewan Env. and Res. Manage. WL Tech Rep. 93-2. 28 pp.
Runge, W. 1993. The long-tailed weasel in Saskatchewan. Saskatchewan Env. and Res. Manage. WL Tech Rep. 93-2. 28 pp. Rust, H. J. 1946. Mammals of northern Idaho. J. Mammal. 27(4): 308-327.
Rust, H. J. 1946. Mammals of northern Idaho. J. Mammal. 27(4): 308-327. Sheffield, S. R. and H. H. Thomas. 1997. Mustela frenata. American Society of Mammalogists, Lawrence, KS. Mammalian Species No. 570:1-9.
Sheffield, S. R. and H. H. Thomas. 1997. Mustela frenata. American Society of Mammalogists, Lawrence, KS. Mammalian Species No. 570:1-9. Simms, D.A. 1979. Studies of an ermine population in southern Ontario. Can. J. Zool. 57:504-520.
Simms, D.A. 1979. Studies of an ermine population in southern Ontario. Can. J. Zool. 57:504-520. Sullivan, Daniel, and Monty Sullins., 1986, Field evaluation of chlorophacinone treated bait for management of Columbian ground squirrels. Tech. Rep. 86-2. September 1986.
Sullivan, Daniel, and Monty Sullins., 1986, Field evaluation of chlorophacinone treated bait for management of Columbian ground squirrels. Tech. Rep. 86-2. September 1986. Thompson, L.S. 1981. Circle West wildlife monitoring study: Third annual report. Technical report No. 8. Montana Department of Natural Resources and Conservation. Helena, Montana.
Thompson, L.S. 1981. Circle West wildlife monitoring study: Third annual report. Technical report No. 8. Montana Department of Natural Resources and Conservation. Helena, Montana. Thompson, L.S. 1982. Distribution of Montana amphibians, reptiles, and mammals. Bozeman: Montana Audubon Council. 24 pp.
Thompson, L.S. 1982. Distribution of Montana amphibians, reptiles, and mammals. Bozeman: Montana Audubon Council. 24 pp. Thompson, Richard W., Western Resource Dev. Corp., Boulder, CO., 1996, Wildlife baseline report for the Montana [Montanore] Project, Lincoln and Sanders counties, Montana. In Application for a Hard Rock Operating Permit and Proposed Plan of Operation, Montanore Project, Lincoln and Sanders Counties, Montana. Vol. 5. Stroiazzo, John. Noranda Minerals Corp., Libby, MT. Revised September 1996.
Thompson, Richard W., Western Resource Dev. Corp., Boulder, CO., 1996, Wildlife baseline report for the Montana [Montanore] Project, Lincoln and Sanders counties, Montana. In Application for a Hard Rock Operating Permit and Proposed Plan of Operation, Montanore Project, Lincoln and Sanders Counties, Montana. Vol. 5. Stroiazzo, John. Noranda Minerals Corp., Libby, MT. Revised September 1996. Tschache, O.P. 1970. Effects of ecological changes induced by various sagebrush control techniques on small mammal populations. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 51 p.
Tschache, O.P. 1970. Effects of ecological changes induced by various sagebrush control techniques on small mammal populations. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 51 p. TVX Mineral Hill Mine, Amerikanuak, Inc., Gardiner, MT., 2002, Yearly summary of wildlife observation reports. 1990-2002 Letter reports.
TVX Mineral Hill Mine, Amerikanuak, Inc., Gardiner, MT., 2002, Yearly summary of wildlife observation reports. 1990-2002 Letter reports. Van Horn, R.C. 1993. Ferruginous Hawk and Prairie Falcon reproductive and behavioral responses to human activity near the Kevin Rim, Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, Montana: Montana State University. 86 p.
Van Horn, R.C. 1993. Ferruginous Hawk and Prairie Falcon reproductive and behavioral responses to human activity near the Kevin Rim, Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, Montana: Montana State University. 86 p. Waage, Bruce C., 1996, Western Energy Company Rosebud Mine, Colstrip, Montana: 1995 Annual Wildlife Monitoring Report; December 1, 1994 - November 30, 1995. February 28, 1996.
Waage, Bruce C., 1996, Western Energy Company Rosebud Mine, Colstrip, Montana: 1995 Annual Wildlife Monitoring Report; December 1, 1994 - November 30, 1995. February 28, 1996. Weckwerth, R.P. 1957. The relationship between the marten population and the abundance of small mammals in Glacier National Park. M.S. thesis. University of Montana, Missoula. 76 pp.
Weckwerth, R.P. 1957. The relationship between the marten population and the abundance of small mammals in Glacier National Park. M.S. thesis. University of Montana, Missoula. 76 pp. Western Technology and Engineering, Inc. (WESTECH)., 1991, Wildlife Monitoring and Additional Baseline Inventory: Absaloka Mine Area Annual Report, 1991. Montana SMP 85005 R1. OSMP Montana 0007B. Febr. 25, 1991.
Western Technology and Engineering, Inc. (WESTECH)., 1991, Wildlife Monitoring and Additional Baseline Inventory: Absaloka Mine Area Annual Report, 1991. Montana SMP 85005 R1. OSMP Montana 0007B. Febr. 25, 1991. Western Technology and Engineering, Inc., Helena, MT., 1989, Reconnaissance of terrestrial wildlife resources in the Basin Creek Mine Amendment 5 vicinity, 1988-1989. November 1989. In Basin Creek Mine Permit Amendment No. 5 - Paupers Pit Southwest, Block B and leach Pad No. 3. Basin Creek Mining, Inc. (Pegasus Gold Corp.). For Montana Dept. of State Lands and USFS Deer Lodge NF.
Western Technology and Engineering, Inc., Helena, MT., 1989, Reconnaissance of terrestrial wildlife resources in the Basin Creek Mine Amendment 5 vicinity, 1988-1989. November 1989. In Basin Creek Mine Permit Amendment No. 5 - Paupers Pit Southwest, Block B and leach Pad No. 3. Basin Creek Mining, Inc. (Pegasus Gold Corp.). For Montana Dept. of State Lands and USFS Deer Lodge NF. Zackheim, K. 1973. Exhibit H: Wildlife Study. In Ash Grove Cement Co. files.
Zackheim, K. 1973. Exhibit H: Wildlife Study. In Ash Grove Cement Co. files.
- Web Search Engines for Articles on "Long-tailed Weasel"
- Additional Sources of Information Related to "Mammals"





