View in other NatureServe Network Field Guides
NatureServe
Montana
Utah
Wyoming
Idaho
Wisconsin
British Columbia
South Carolina
Yukon
California
New York
Northern Pocket Gopher - Thomomys talpoides
Native Species
Global Rank:
G5
State Rank:
S5
(see State Rank Reason below)
Agency Status
USFWS:
USFS:
BLM:
External Links
State Rank Reason (see State Rank above)
Species is relatively common within suitable habitat and widely distributed across portions of the state
- Details on Status Ranking and Review
Northern Pocket Gopher (Thomomys talpoides) Conservation Status Review
Review Date = 05/03/2018
Range Extent
ScoreG - 200,000-2,500,000 km squared (about 80,000-1,000,000 square miles)
Comment380,531 square Kilometers from Natural Heritage Program range maps
Long-term Trend
ScoreE - Relatively Stable (±25% change)
CommentHabitat is likely stable within +/- 25% since European settlement
Short-term Trend
ScoreU - Unknown. Short-term trend in population, range, area occupied, and number and condition of occurrences unknown.
CommentNo data on trends available
Threats
ScoreH - Unthreatened. Threats if any, when considered in comparison with natural fluctuation and change, are minimal or very localized, not leading to significant loss or degradation of populations or area even over a few decades’ time. (Severity, scope, and/or immediacy of threat considered Insignificant.)
CommentNo operational threats in the next 15-20 years identified
Intrinsic Vulnerability
ScoreC - Not Intrinsically Vulnerable. Species matures quickly, reproduces frequently, and/or has high fecundity such that populations recover quickly (< 5 years or 2 generations) from decreases in abundance; or species has high dispersal capability such that extirpated populations soon become reestablished through natural recolonization (unaided by humans).
CommentNot Intrinsically Vulnerable. Species matures quickly, reproduces frequently, and/or has a high fecundity such that populations recover quickly (< 5 years or 2 generations) from decreases in abundance. Species has good dispersal capabilities such that e
Environmental Specificity
ScoreD - Broad. Generalist. Broad-scale or diverse (general) habitat(s) or abiotic and/or biotic factors are used or required by the species, with all key requirements common in the generalized range of the species in the area of interest. If the preferred food(s) or breeding/nonbreeding microhabitat(s) become unavailable, the species switches to an alternative with no resulting decline in numbers of individuals or number of breeding attempts.
CommentRequires friable soils for burrowing, but found in a wide diversity of habitats statewide
Raw Conservation Status Score
Score
3.5 + 0 (geographic distribution) + 0.5 (environmental specificity) + 0 (long-term trend) + 1 (threats) = 5
General Description
The Northern Pocket Gopher, so named for its large, external, fur-lined cheek pouches, measures about 8 inches length in total, with a short, nearly hairless tail of 2 1/2 inches. Its weight varies from 2 3/4 to 4 3/5 ounces (Burt and Grossenheider 1976). It has soft reddish-brown upper fur and a dark gray underside. In the eastern areas of its distribution, the upper fur becomes lighter brown with an orangish or yellowish cast (Foresman 2012). The fur can be smoothed forward or backward (Zeveloff and Collett 1988). Black patches surround the small, nearly hidden ears. Well-developed jaw, neck, forearm, and shoulder muscles give this rodent a solid appearance, while narrow hips (Kritzman 1977) and loose skin enable it to turn 180 degrees in its tunnels (Foresman 2012). It is equipped with long curved claws on three digits of its forepaws (Foresman 2012) and sharply curved, always exposed, yellowish incisors for digging and cutting. The feet are whitish and the incisors may be white-tipped. There may also be white markings under the chin (Zeveloff 1988). The Northern Pocket Gopher has 20 teeth with a shallow groove near the inner side of each upper incisor (Burt and Grossenheider 1976). It begins a gradual molting in spring, marked by a moving band of fur which progresses from the blackish nose to base of tail by the end of the summer.
Species Range
Montana Range
Range Descriptions
 Native
Native
Western Hemisphere Range

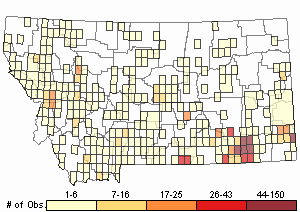
Observations in Montana Natural Heritage Program Database
Number of Observations: 1623
(Click on the following maps and charts to see full sized version)
Map Help and Descriptions
Relative Density
Recency
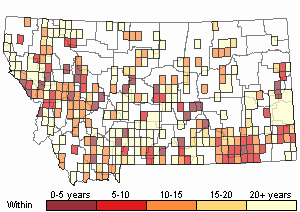
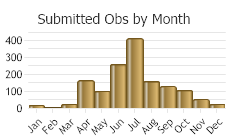
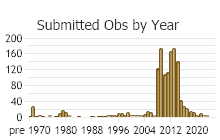
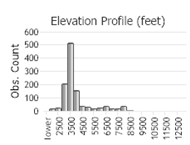 (Observations spanning multiple months or years are excluded from time charts)
(Observations spanning multiple months or years are excluded from time charts)
Migration
Non-migratory.
Habitat
Uses a wide variety of habitats, from cultivated fields and prairie to alpine meadows (Jones et al. 1983). It avoids only dense forests, very shallow, rocky soils, and areas with poor snow cover where the soil frezes over (Hoffman and Pattie 1968).
Ecological Systems Associated with this Species
- Details on Creation and Suggested Uses and Limitations
How Associations Were Made
We associated the use and habitat quality (common or occasional) of each of the 82 ecological systems mapped in Montana for
vertebrate animal species that regularly breed, overwinter, or migrate through the state by:
- Using personal observations and reviewing literature that summarize the breeding, overwintering, or migratory habitat requirements of each species (Dobkin 1992, Hart et al. 1998, Hutto and Young 1999, Maxell 2000, Foresman 2012, Adams 2003, and Werner et al. 2004);
- Evaluating structural characteristics and distribution of each ecological system relative to the species' range and habitat requirements;
- Examining the observation records for each species in the state-wide point observation database associated with each ecological system;
- Calculating the percentage of observations associated with each ecological system relative to the percent of Montana covered by each ecological system to get a measure of "observations versus availability of habitat".
Species that breed in Montana were only evaluated for breeding habitat use, species that only overwinter in Montana were only evaluated for overwintering habitat use, and species that only migrate through Montana were only evaluated for migratory habitat use.
In general, species were listed as associated with an ecological system if structural characteristics of used habitat documented in the literature were present in the ecological system or large numbers of point observations were associated with the ecological system.
However, species were not listed as associated with an ecological system if there was no support in the literature for use of structural characteristics in an ecological system,
even if point observations were associated with that system.
Common versus occasional association with an ecological system was assigned based on the degree to which the structural characteristics of an ecological system matched the preferred structural habitat characteristics for each species as represented in scientific literature.
The percentage of observations associated with each ecological system relative to the percent of Montana covered by each ecological system was also used to guide assignment of common versus occasional association.
If you have any questions or comments on species associations with ecological systems, please contact the Montana Natural Heritage Program's Senior Zoologist.
Suggested Uses and Limitations
Species associations with ecological systems should be used to generate potential lists of species that may occupy broader landscapes for the purposes of landscape-level planning.
These potential lists of species should not be used in place of documented occurrences of species (this information can be requested at:
mtnhp.org/requests) or systematic surveys for species and evaluations of habitat at a local site level by trained biologists.
Users of this information should be aware that the land cover data used to generate species associations is based on imagery from the late 1990s and early 2000s and was only intended to be used at broader landscape scales.
Land cover mapping accuracy is particularly problematic when the systems occur as small patches or where the land cover types have been altered over the past decade.
Thus, particular caution should be used when using the associations in assessments of smaller areas (e.g., evaluations of public land survey sections).
Finally, although a species may be associated with a particular ecological system within its known geographic range, portions of that ecological system may occur outside of the species' known geographic range.
Literature Cited
- Adams, R.A. 2003. Bats of the Rocky Mountain West; natural history, ecology, and conservation. Boulder, CO: University Press of Colorado. 289 p.
- Dobkin, D. S. 1992. Neotropical migrant land birds in the Northern Rockies and Great Plains. USDA Forest Service, Northern Region. Publication No. R1-93-34. Missoula, MT.
- Foresman, K.R. 2012. Mammals of Montana. Second edition. Mountain Press Publishing, Missoula, Montana. 429 pp.
- Hart, M.M., W.A. Williams, P.C. Thornton, K.P. McLaughlin, C.M. Tobalske, B.A. Maxell, D.P. Hendricks, C.R. Peterson, and R.L. Redmond. 1998. Montana atlas of terrestrial vertebrates. Montana Cooperative Wildlife Research Unit, University of Montana, Missoula, MT. 1302 p.
- Hutto, R.L. and J.S. Young. 1999. Habitat relationships of landbirds in the Northern Region, USDA Forest Service, Rocky Mountain Research Station RMRS-GTR-32. 72 p.
- Maxell, B.A. 2000. Management of Montana's amphibians: a review of factors that may present a risk to population viability and accounts on the identification, distribution, taxonomy, habitat use, natural history, and the status and conservation of individual species. Report to U.S. Forest Service Region 1. Missoula, MT: Wildlife Biology Program, University of Montana. 161 p.
- Werner, J.K., B.A. Maxell, P. Hendricks, and D. Flath. 2004. Amphibians and reptiles of Montana. Missoula, MT: Mountain Press Publishing Company. 262 p.
- Commonly Associated with these Ecological Systems
Alpine Systems
Forest and Woodland Systems
Grassland Systems
Human Land Use
Recently Disturbed or Modified
Shrubland, Steppe and Savanna Systems
Wetland and Riparian Systems
- Occasionally Associated with these Ecological Systems
Forest and Woodland Systems
Grassland Systems
Human Land Use
Recently Disturbed or Modified
Sparse and Barren Systems
Food Habits
In addition to the mainstay of underground plant parts, may occasionally use leaves of forbs, but only within close range of a burrow opening (Jones et al. 1983).
Ecology
Pockets are used for transporting food. Lips can be closed behind incisors. Short, sensitive, sparsely-haired tail used for guidance when traveling backwards in burrow. Lower level for nest & storage, upper for foraging (Jones et al. 1983).
Reproductive Characteristics
Young are weaned at 40 days. Dispersal (at 2 months) may be above ground or below ground. Reproductively mature at 1 year (Jones et al. 1983).
Stewardship Responsibility
References
- Literature Cited AboveLegend:
 View Online Publication
View Online Publication Burt, W.H. and R.P. Grossenheider. 1976. A field guide to the mammals. Third edition. Houghton Mifflin Co., Boston. 289 pp.
Burt, W.H. and R.P. Grossenheider. 1976. A field guide to the mammals. Third edition. Houghton Mifflin Co., Boston. 289 pp. Foresman, K.R. 2012. Mammals of Montana. Second edition. Mountain Press Publishing, Missoula, Montana. 429 pp.
Foresman, K.R. 2012. Mammals of Montana. Second edition. Mountain Press Publishing, Missoula, Montana. 429 pp. Hoffmann, R.S. and D.L. Pattie. 1968. A guide to Montana mammals: identification, habitat, distribution, and abundance. Missoula, MT: University of Montana. 133 p.
Hoffmann, R.S. and D.L. Pattie. 1968. A guide to Montana mammals: identification, habitat, distribution, and abundance. Missoula, MT: University of Montana. 133 p. Jones, J.K., D.M. Armstrong, R.S. Hoffmann and C. Jones. 1983. Mammals of the northern Great Plains. University of Nebraska Press, Lincoln. 379 pp.
Jones, J.K., D.M. Armstrong, R.S. Hoffmann and C. Jones. 1983. Mammals of the northern Great Plains. University of Nebraska Press, Lincoln. 379 pp. Kritzman, E.B. 1977. Little mammals of the Pacific Northwest. Pacific Search Press, Seattle, WA.
Kritzman, E.B. 1977. Little mammals of the Pacific Northwest. Pacific Search Press, Seattle, WA. Zeveloff, S.I. and F.R. Collett. 1988. Mammals of the Intermountain west. University of Utah Press, Salt Lake City, Utah.
Zeveloff, S.I. and F.R. Collett. 1988. Mammals of the Intermountain west. University of Utah Press, Salt Lake City, Utah.
- Additional ReferencesLegend:
 View Online Publication
View Online Publication
Do you know of a citation we're missing? [PRESI] Powder River Eagle Studies Incorporated. 1998b. Spring Creek Mine 1997 wildlife monitoring studies. Powder River Eagle Studies Incorporated. Gillete, WY.
[PRESI] Powder River Eagle Studies Incorporated. 1998b. Spring Creek Mine 1997 wildlife monitoring studies. Powder River Eagle Studies Incorporated. Gillete, WY. [WWPC] Washington Water Power Company. 1995. 1994 wildlife report Noxon Rapids and Cabinet Gorge Reservoirs. Washington Water Power Company. Spokane, WA.
[WWPC] Washington Water Power Company. 1995. 1994 wildlife report Noxon Rapids and Cabinet Gorge Reservoirs. Washington Water Power Company. Spokane, WA. Atkinson, E.C. 1992. Ferruginous hawk (Buteo regalis) inventories on the Dillon Resource Area of southwest Montana: 1992. Montana Natural Heritage Program for Bureau of Land Management, Dillon Resource Area. 34 pp.
Atkinson, E.C. 1992. Ferruginous hawk (Buteo regalis) inventories on the Dillon Resource Area of southwest Montana: 1992. Montana Natural Heritage Program for Bureau of Land Management, Dillon Resource Area. 34 pp. Bauer, Delane, 2002, 2002 Four Seasons Wildlife Study. Savage Mine Report, Richland County, Montana.
Bauer, Delane, 2002, 2002 Four Seasons Wildlife Study. Savage Mine Report, Richland County, Montana. Beak Consultants, Inc. 1983. Wildlife. January 1983. In Stillwater Project Environmental Studies. Addendum A, Wildlife. Vol. I. Tech. Report No. 7. 1982.
Beak Consultants, Inc. 1983. Wildlife. January 1983. In Stillwater Project Environmental Studies. Addendum A, Wildlife. Vol. I. Tech. Report No. 7. 1982. Buchanan, B.A. 1972. Ecological effects of weather modification, Bridger Range area, Montana: relationship of soil, vegetation, and microclimate. Ph.D. Dissertation. Montana State University, Bozeman. 130 p.
Buchanan, B.A. 1972. Ecological effects of weather modification, Bridger Range area, Montana: relationship of soil, vegetation, and microclimate. Ph.D. Dissertation. Montana State University, Bozeman. 130 p. Buck, C.L. 1939. Pattern correlation of mammalian teeth as a means of identification. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, Montana: Montana State University. 55 p.
Buck, C.L. 1939. Pattern correlation of mammalian teeth as a means of identification. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, Montana: Montana State University. 55 p. Butts, T.W., Western Technology and R.L. Eng. 1993. Continental Lime Indian Creek Mine, Townsend, MT. Life of Mine Wildlife Reconnaissance. In Life-of-Mine Amendment. Continental Lime, Inc., Indian Creek Mine & Plant. Vol. 2. October 13, 1992.
Butts, T.W., Western Technology and R.L. Eng. 1993. Continental Lime Indian Creek Mine, Townsend, MT. Life of Mine Wildlife Reconnaissance. In Life-of-Mine Amendment. Continental Lime, Inc., Indian Creek Mine & Plant. Vol. 2. October 13, 1992. Conrad, C.C. 1979. Characteristics of Pocket Gopher populations in relation to selected environmental factors in Pelican Valley, Yellowstone National Park. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, Montana: Montana State University. 79 p.
Conrad, C.C. 1979. Characteristics of Pocket Gopher populations in relation to selected environmental factors in Pelican Valley, Yellowstone National Park. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, Montana: Montana State University. 79 p. Craighead, A.C. 2000. Pellet and scat analysis as indicators of present and past habitats. M.Sc. Theses. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 219 p.
Craighead, A.C. 2000. Pellet and scat analysis as indicators of present and past habitats. M.Sc. Theses. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 219 p. Cramer, P.C. 1992. Small mammal diversity and abundance in Douglas Fir old growth forests. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 64 p.
Cramer, P.C. 1992. Small mammal diversity and abundance in Douglas Fir old growth forests. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 64 p. Decker Coal Co., 1981, Wildlife survey. July 7, 1981. In North Decker 5-Year Permit Application. Vol. III. Rule 26.4.304(12-14).
Decker Coal Co., 1981, Wildlife survey. July 7, 1981. In North Decker 5-Year Permit Application. Vol. III. Rule 26.4.304(12-14). Dice, L.R. 1923. Mammal associations and habitats of the Flathead Lake Region, Montana. Ecology 4(3): 247-260.
Dice, L.R. 1923. Mammal associations and habitats of the Flathead Lake Region, Montana. Ecology 4(3): 247-260. Dood, A.R. 1980. Terry Badlands nongame survey and inventory final report. Montana Department of Fish, Wildlife, and Parks and Bureau of Land Management, Helena, MT. 70 pp.
Dood, A.R. 1980. Terry Badlands nongame survey and inventory final report. Montana Department of Fish, Wildlife, and Parks and Bureau of Land Management, Helena, MT. 70 pp. Douglass, Richard J., DMI Ecological Research, Butte, MT., 1995, Small animals potentially living in the proposed Cottonwood Mining Area. August 1995. In Gem River Corporation Application for Operating Permit and Plan of Operations. Marc I Mine, Dry Cottonwood Creek, Deer Lodge County, Montana. Vol. 2, Apps. App. L. No date.
Douglass, Richard J., DMI Ecological Research, Butte, MT., 1995, Small animals potentially living in the proposed Cottonwood Mining Area. August 1995. In Gem River Corporation Application for Operating Permit and Plan of Operations. Marc I Mine, Dry Cottonwood Creek, Deer Lodge County, Montana. Vol. 2, Apps. App. L. No date. ECON, Inc. (Ecological Consulting Service), Helena, MT., 1976, Colstrip 10 x 20 Area wildlife and wildlife habitat annual monitoring report, 1976. Proj. 135-85-A. December 31, 1976.
ECON, Inc. (Ecological Consulting Service), Helena, MT., 1976, Colstrip 10 x 20 Area wildlife and wildlife habitat annual monitoring report, 1976. Proj. 135-85-A. December 31, 1976. Econ, Inc. (Ecological Consulting Service), Helena, MT., 1977, 1977 wildlife and wildlife habitat monitoring study, Peabody Coal Company Big Sky Mine. Proj. 161-85-A. November 30, 1977.
Econ, Inc. (Ecological Consulting Service), Helena, MT., 1977, 1977 wildlife and wildlife habitat monitoring study, Peabody Coal Company Big Sky Mine. Proj. 161-85-A. November 30, 1977. ECON, Inc. (Ecological Consulting Service), Helena, MT., 1977, Colstrip 10 x 20 Area wildlife and wildlife habitat annual monitoring report, 1977. Proj. 164-85-A. December 31, 1977.
ECON, Inc. (Ecological Consulting Service), Helena, MT., 1977, Colstrip 10 x 20 Area wildlife and wildlife habitat annual monitoring report, 1977. Proj. 164-85-A. December 31, 1977. ECON, Inc. (Ecological Consulting Service), Helena, MT., 1979, Annual wildllife report of the Colstrip Area for 1978. Proj. 195-85-A. April 6, 1979.
ECON, Inc. (Ecological Consulting Service), Helena, MT., 1979, Annual wildllife report of the Colstrip Area for 1978. Proj. 195-85-A. April 6, 1979. ECON, Inc. (Ecological Consulting Service), Helena, MT., 1979, Annual wildllife report of the Colstrip Area for 1979, including a special raptor research study. Proj. 216-85-A. March 1, 1980.
ECON, Inc. (Ecological Consulting Service), Helena, MT., 1979, Annual wildllife report of the Colstrip Area for 1979, including a special raptor research study. Proj. 216-85-A. March 1, 1980. Econ, Inc. 1988. Wildlife monitoring report, 1987 field season, Big Sky Mine. March 1988. In Peabody Mining and Reclamation Plan Big Sky Mine Area B. Vol. 8, cont., Tab 10 - Wildlife Resources. Appendix 10-1, 1987 Annual Wildlife Report.
Econ, Inc. 1988. Wildlife monitoring report, 1987 field season, Big Sky Mine. March 1988. In Peabody Mining and Reclamation Plan Big Sky Mine Area B. Vol. 8, cont., Tab 10 - Wildlife Resources. Appendix 10-1, 1987 Annual Wildlife Report. Econ, Inc., Helena, MT., 1978, Peabody Coal Company Big Sky Mine, Rosebud County, MT. Wildlife and wildlife habitat monitoring study. Proj. 190-85-A. December 31, 1978.
Econ, Inc., Helena, MT., 1978, Peabody Coal Company Big Sky Mine, Rosebud County, MT. Wildlife and wildlife habitat monitoring study. Proj. 190-85-A. December 31, 1978. Farmer, Patrick J., and Thomas W. Butts, Western Technology & Eng., Inc., Helena, MT., 1994, McDonald Project Terrestrial Wildlife Study, November 1989 - November 1993. April 1994. In McDonald Gold Project: Wildlife & Fisheries. [#18]. Seven-up Pete Joint Venture, Lincoln, MT. Unpub. No date.
Farmer, Patrick J., and Thomas W. Butts, Western Technology & Eng., Inc., Helena, MT., 1994, McDonald Project Terrestrial Wildlife Study, November 1989 - November 1993. April 1994. In McDonald Gold Project: Wildlife & Fisheries. [#18]. Seven-up Pete Joint Venture, Lincoln, MT. Unpub. No date. Feigley, H.P. 1981. Studies on native small mammals as intermediate hosts of Echinococcus multilocularis. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, Montana: Montana State University. 50 p.
Feigley, H.P. 1981. Studies on native small mammals as intermediate hosts of Echinococcus multilocularis. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, Montana: Montana State University. 50 p. Fjell, Alan K., 1986, Peabody Coal Company Big Sky Mine, Rosebud County, MT. Wildlife monitoring report: 1985 field season. March 1986.
Fjell, Alan K., 1986, Peabody Coal Company Big Sky Mine, Rosebud County, MT. Wildlife monitoring report: 1985 field season. March 1986. Fjell, Alan K., and Brian R. Mahan, compilers., 1984, Peabody Coal Company Big Sky Mine, Rosebud County, MT. Wildlife monitoring report: 1983 field season. February 1984.
Fjell, Alan K., and Brian R. Mahan, compilers., 1984, Peabody Coal Company Big Sky Mine, Rosebud County, MT. Wildlife monitoring report: 1983 field season. February 1984. Fjell, Alan K., and Brian R. Mahan., 1983, Peabody Coal Company Big Sky Mine, Rosebud County, MT. Wildlife monitoring report: 1982 field season. May 1983.
Fjell, Alan K., and Brian R. Mahan., 1983, Peabody Coal Company Big Sky Mine, Rosebud County, MT. Wildlife monitoring report: 1982 field season. May 1983. Fjell, Alan K., and Brian R. Mahan., 1985, Peabody Coal Company Big Sky Mine, Rosebud County, MT. Wildlife monitoring report: 1984 field season. February 1985.
Fjell, Alan K., and Brian R. Mahan., 1985, Peabody Coal Company Big Sky Mine, Rosebud County, MT. Wildlife monitoring report: 1984 field season. February 1985. Fjell, Alan K., and Brian R. Mahan., 1987, Big Sky Mine, Rosebud County, MT. Wildlife monitoring report: 1986 field season. April 1987.
Fjell, Alan K., and Brian R. Mahan., 1987, Big Sky Mine, Rosebud County, MT. Wildlife monitoring report: 1986 field season. April 1987. Foresman, K.R. 2001. The wild mammals of Montana. American Society of Mammalogists, Special Publication Number 12. Lawrence, KS. 278 pp.
Foresman, K.R. 2001. The wild mammals of Montana. American Society of Mammalogists, Special Publication Number 12. Lawrence, KS. 278 pp. Geppert, T. J. 1984. Small mammals of the Shield Trap, East Pryor Mountain, Montana. M.S. thesis. University of Iowa, Iowa City. 45 pp.
Geppert, T. J. 1984. Small mammals of the Shield Trap, East Pryor Mountain, Montana. M.S. thesis. University of Iowa, Iowa City. 45 pp. Haglund, B.M. 1972. Ecological effects of weather modification, Bangtail Ridge, Bridger Range, Montana: relationships of pocket gophers (Thomomys talpoides) to time of snow melt. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, Montana: Montana State University. 26 p.
Haglund, B.M. 1972. Ecological effects of weather modification, Bangtail Ridge, Bridger Range, Montana: relationships of pocket gophers (Thomomys talpoides) to time of snow melt. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, Montana: Montana State University. 26 p. Hanauska-Brown, L., B.A. Maxell, A. Petersen, and S. Story. 2014. Diversity Monitoring in Montana 2008-2010 Final Report. Montana Fish, Wildlife & Parks. Helena, MT. 78 pp.
Hanauska-Brown, L., B.A. Maxell, A. Petersen, and S. Story. 2014. Diversity Monitoring in Montana 2008-2010 Final Report. Montana Fish, Wildlife & Parks. Helena, MT. 78 pp. Harmata, A.R. 1991. Impacts of oil and gas development on raptors associated with Kevin Rim, Montana. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. Unpublished report by the Kevin Rim Raptor Study Group. Prepared for the USDI BLM, Great Falls Resource Area, Great Falls, MT. 106 p.
Harmata, A.R. 1991. Impacts of oil and gas development on raptors associated with Kevin Rim, Montana. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. Unpublished report by the Kevin Rim Raptor Study Group. Prepared for the USDI BLM, Great Falls Resource Area, Great Falls, MT. 106 p. Hatier, K.G. 1995. Effects of helping behaviors on Coyote packs in Yellowstone National Park, Wyoming. M Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 78 p.
Hatier, K.G. 1995. Effects of helping behaviors on Coyote packs in Yellowstone National Park, Wyoming. M Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 78 p. Hayward, G. D. and P. H. Hayward. 1995. Relative abundance and habitat associations of small mammals in the Chamberlain Basin, central Idaho. Northwest Sci. 69(2): 114-125.
Hayward, G. D. and P. H. Hayward. 1995. Relative abundance and habitat associations of small mammals in the Chamberlain Basin, central Idaho. Northwest Sci. 69(2): 114-125. Heath, M.L. 1973. Small mammal populations in clearcuts of various ages in south central Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, Montana: Montana State University. 33 p.
Heath, M.L. 1973. Small mammal populations in clearcuts of various ages in south central Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, Montana: Montana State University. 33 p. Hendricks, P. and M. Roedel. 2001. A faunal survey of the Centennial Valley Sandhills, Beaverhead County, Montana. Report to the U.S. Bureau of Land Management and U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service. Montana Natural Heritage Program, Helena, MT. 44 p.
Hendricks, P. and M. Roedel. 2001. A faunal survey of the Centennial Valley Sandhills, Beaverhead County, Montana. Report to the U.S. Bureau of Land Management and U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service. Montana Natural Heritage Program, Helena, MT. 44 p. Hodgson, J.R. 1970. Ecological distribution of Microtus montanus and Microtus pennsylvanicus in an area of geographic sympatry in southwestern Montana. Ph.D. Dissertation. Bozeman, Montana: Montana State University. 65 p.
Hodgson, J.R. 1970. Ecological distribution of Microtus montanus and Microtus pennsylvanicus in an area of geographic sympatry in southwestern Montana. Ph.D. Dissertation. Bozeman, Montana: Montana State University. 65 p. Hoffmann, R.S., P.L. Wright, and F.E. Newby. 1969. The distribution of some mammals in Montana. I. Mammals other than bats. Journal of Mammalogy 50(3): 579-604.
Hoffmann, R.S., P.L. Wright, and F.E. Newby. 1969. The distribution of some mammals in Montana. I. Mammals other than bats. Journal of Mammalogy 50(3): 579-604. Humphris, Michael., 1990, Wildlife Monitoring Report. Spring Creek Coal Company 1990 Mining Annual Report. Appendix I. April 11, 1990.
Humphris, Michael., 1990, Wildlife Monitoring Report. Spring Creek Coal Company 1990 Mining Annual Report. Appendix I. April 11, 1990. Humphris, Michael., 1993, Wildlife Monitoring Report. Spring Creek Coal Company 1993 Mining Annual Report. Appendix I. April 11, 1993.
Humphris, Michael., 1993, Wildlife Monitoring Report. Spring Creek Coal Company 1993 Mining Annual Report. Appendix I. April 11, 1993. Humphris, Michael., 1994, Wildlife Monitoring Report. Spring Creek Coal Company 1994 Mining Annual Report. Appendix I. April 1994.
Humphris, Michael., 1994, Wildlife Monitoring Report. Spring Creek Coal Company 1994 Mining Annual Report. Appendix I. April 1994. Johnson, L.J. 1960. Mammal studies on the Lubrecht Forest, Montana: a preliminary report. Proc. Mont. Acad. Sci. 20: 40-47.
Johnson, L.J. 1960. Mammal studies on the Lubrecht Forest, Montana: a preliminary report. Proc. Mont. Acad. Sci. 20: 40-47. Joslin, Gayle, and Heidi B. Youmans. 1999. Effects of recreation on Rocky Mountain wildlife: a review for Montana. [Montana]: Montana Chapter of the Wildlife Society.
Joslin, Gayle, and Heidi B. Youmans. 1999. Effects of recreation on Rocky Mountain wildlife: a review for Montana. [Montana]: Montana Chapter of the Wildlife Society. Lampe, R.P., J.K. Jones Jr., R.S. Hoffmann, and E.C. Birney. 1974. The mammals of Carter County, southeastern Montana. Occa. Pap. Mus. Nat. Hist. Univ. Kan. 25:1-39.
Lampe, R.P., J.K. Jones Jr., R.S. Hoffmann, and E.C. Birney. 1974. The mammals of Carter County, southeastern Montana. Occa. Pap. Mus. Nat. Hist. Univ. Kan. 25:1-39. Land & Water Consulting, Inc., Missoula, MT., 2002, Montana Dept. of Transportation Wetland Mitigation Monitoring Report, Year 2002: Creston Site, Creston, Montana. Proj. No. 130091.007. February 2003. In 2002 Wetland Mitigation Monitoring Reports, Vol. I.
Land & Water Consulting, Inc., Missoula, MT., 2002, Montana Dept. of Transportation Wetland Mitigation Monitoring Report, Year 2002: Creston Site, Creston, Montana. Proj. No. 130091.007. February 2003. In 2002 Wetland Mitigation Monitoring Reports, Vol. I. Martin, P.R., K. Dubois and H.B. Youmans. 1981. Terrestrial wildlife inventory in selected coal areas, Powder River resources area final report. Montana Department of Fish, Wildlife and Parks and Bureau of Land Management, Helena, MT. No. YA-553-CTO- 24. 288 p.
Martin, P.R., K. Dubois and H.B. Youmans. 1981. Terrestrial wildlife inventory in selected coal areas, Powder River resources area final report. Montana Department of Fish, Wildlife and Parks and Bureau of Land Management, Helena, MT. No. YA-553-CTO- 24. 288 p. Martin, Steve A., ECON, Inc., Helena, MT., 1982, Flathead Project Wildlife Report, 1981-1982. November 30, 1982.
Martin, Steve A., ECON, Inc., Helena, MT., 1982, Flathead Project Wildlife Report, 1981-1982. November 30, 1982. Matthews, W.L. 1980a. Wibaux-Beach comparison study: Sydney, Glendive and Plevna Study Areas. Bureau of Land Management, Miles City, MT. 50 p.
Matthews, W.L. 1980a. Wibaux-Beach comparison study: Sydney, Glendive and Plevna Study Areas. Bureau of Land Management, Miles City, MT. 50 p. Maxell, B.A. 2016. Flammulated Owl surveys on the Big Timber, Bozeman, Gardiner and Livingston Ranger Districts of the Custer Gallatin National Forest: 2013. Report to Custer Gallatin National Forest. Montana Natural Heritage Program. Helena, MT. 27pp + appendices.
Maxell, B.A. 2016. Flammulated Owl surveys on the Big Timber, Bozeman, Gardiner and Livingston Ranger Districts of the Custer Gallatin National Forest: 2013. Report to Custer Gallatin National Forest. Montana Natural Heritage Program. Helena, MT. 27pp + appendices. Maxell, B.A. 2016. Northern Goshawk surveys on the Beartooth, Ashland, and Sioux Districts of the Custer-Gallatin National Forest: 2012-2014. Montana Natural Heritage Program. Helena, MT. 114pp.
Maxell, B.A. 2016. Northern Goshawk surveys on the Beartooth, Ashland, and Sioux Districts of the Custer-Gallatin National Forest: 2012-2014. Montana Natural Heritage Program. Helena, MT. 114pp. Maxim Technologies, Inc., 2002, Western Energy Company Rosebud Mine, Colstrip, Montana: 2002 Annual Wildlife Monitoring Report; December 1, 2001 - November 30, 2002. Febr. 24, 2002.
Maxim Technologies, Inc., 2002, Western Energy Company Rosebud Mine, Colstrip, Montana: 2002 Annual Wildlife Monitoring Report; December 1, 2001 - November 30, 2002. Febr. 24, 2002. McCaughey, W.W. 1990. Biotic and microsite factors affecting Pinus albicaulis establishment and survival. Ph.D. Dissertation. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 78 p.
McCaughey, W.W. 1990. Biotic and microsite factors affecting Pinus albicaulis establishment and survival. Ph.D. Dissertation. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 78 p. Mealey, S.P. 1975. The natural food habits of free ranging grizzly bears in Yellowstone National Park, 1973-1974. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 158 p.
Mealey, S.P. 1975. The natural food habits of free ranging grizzly bears in Yellowstone National Park, 1973-1974. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 158 p. Mont. Dept. of Agriculture., 198?, Pocket gopher control techniques.
Mont. Dept. of Agriculture., 198?, Pocket gopher control techniques. Mont. Dept. of Agriculture., 1985, Controlling burrowing rodents with burrow fumigants. Inform. Bul. No. 6.
Mont. Dept. of Agriculture., 1985, Controlling burrowing rodents with burrow fumigants. Inform. Bul. No. 6. Montana Prairie Dog Working Group. 2002. Conservation plan for black-tailed and white-tailed prairie dogs in Montana. Montana Fish, Wildlife and Parks. Helena MT. 51 pp.
Montana Prairie Dog Working Group. 2002. Conservation plan for black-tailed and white-tailed prairie dogs in Montana. Montana Fish, Wildlife and Parks. Helena MT. 51 pp. Montana Tunnels Mine, Inc., Jefferson City, Helena, MT., 1988?, Application for an Amendment to the Montana Tunnels Operating Permit for the Prickly Pear Water Supply System, Jefferson County, Montana.
Montana Tunnels Mine, Inc., Jefferson City, Helena, MT., 1988?, Application for an Amendment to the Montana Tunnels Operating Permit for the Prickly Pear Water Supply System, Jefferson County, Montana. OEA Research, Helena, MT., 1982, Beal Mine Wildlife Report. June 17, 1982.
OEA Research, Helena, MT., 1982, Beal Mine Wildlife Report. June 17, 1982. Oechsli, L.M. 2000. Ex-urban development in the Rocky Mountain West: consequences for native vegetation, wildlife diversity, and land-use planning in Big Sky, Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Montana State University, Bozeman. 73 p.
Oechsli, L.M. 2000. Ex-urban development in the Rocky Mountain West: consequences for native vegetation, wildlife diversity, and land-use planning in Big Sky, Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Montana State University, Bozeman. 73 p. Pattie, D.L. and N.A. M. Verbeek. 1967. Alpine mammals of the Beartooth Plateau. Northwest Science 41(3): 110-117.
Pattie, D.L. and N.A. M. Verbeek. 1967. Alpine mammals of the Beartooth Plateau. Northwest Science 41(3): 110-117. Pefaur, J. E., and R. S. Hoffmann. 1975. Studies of small mammal populations at three sites on the Northern Great Plains. Occasional Papers of the Museum of Natural History, University of Kansas, Lawrence. No. 37:1-27.
Pefaur, J. E., and R. S. Hoffmann. 1975. Studies of small mammal populations at three sites on the Northern Great Plains. Occasional Papers of the Museum of Natural History, University of Kansas, Lawrence. No. 37:1-27. Powder River Eagle Studies, Inc., Gillette, WY., 1996, Spring Creek Mine 1995 Wildlife Monitoring Studies. Spring Creek Coal Company 1995-1996 Mining Annual Report. Vol. I, App. I. May 1996.
Powder River Eagle Studies, Inc., Gillette, WY., 1996, Spring Creek Mine 1995 Wildlife Monitoring Studies. Spring Creek Coal Company 1995-1996 Mining Annual Report. Vol. I, App. I. May 1996. Powder River Eagle Studies, Inc., Gillette, WY., 1997, Spring Creek Mine 1996 Wildlife Monitoring Studies. February 1997.
Powder River Eagle Studies, Inc., Gillette, WY., 1997, Spring Creek Mine 1996 Wildlife Monitoring Studies. February 1997. Powder River Eagle Studies, Inc., Gillette, WY., 1999, Spring Creek Mine 1998 Wildlife Monitoring. March 1999.
Powder River Eagle Studies, Inc., Gillette, WY., 1999, Spring Creek Mine 1998 Wildlife Monitoring. March 1999. Reichel, J. D. 1976. Coyote-prey relationships on the National Bison Range. M.S. thesis. University of Montana, Missoula. 86 pp. plus appendices.
Reichel, J. D. 1976. Coyote-prey relationships on the National Bison Range. M.S. thesis. University of Montana, Missoula. 86 pp. plus appendices. Reichel, J.D. 1986. Habitat use by alpine mammals in the Pacific Northwest. Arctic and Alpine Research. 18(1): 111-119.
Reichel, J.D. 1986. Habitat use by alpine mammals in the Pacific Northwest. Arctic and Alpine Research. 18(1): 111-119. Reichel, J.D. 1997. Amphibian and reptile survey in northcentral Montana on the Lewistown District, BLM. Unpublished report.
Reichel, J.D. 1997. Amphibian and reptile survey in northcentral Montana on the Lewistown District, BLM. Unpublished report. Reichel, J.D. and S.G. Beckstrom. 1993. Northern bog lemming survey: 1992. Unpublished report. Montana Natural Heritage Program, Helena, MT. 64 p.
Reichel, J.D. and S.G. Beckstrom. 1993. Northern bog lemming survey: 1992. Unpublished report. Montana Natural Heritage Program, Helena, MT. 64 p. Reichel, J.D., D.L. Genter and E. Atkinson. 1992. Sensitive animal species in the Elkhorn and Big Belt Mountains of the Helena National Forest. Unpublished report to the Helena National Forest. Montana Natural Heritage Program, Helena. 158 p.
Reichel, J.D., D.L. Genter and E. Atkinson. 1992. Sensitive animal species in the Elkhorn and Big Belt Mountains of the Helena National Forest. Unpublished report to the Helena National Forest. Montana Natural Heritage Program, Helena. 158 p. Reid, F. 2006. Peterson Field Guide to Mammals of North America, 4th Edition. Houghton Mifflin Company: Boston and New York, 608 pp.
Reid, F. 2006. Peterson Field Guide to Mammals of North America, 4th Edition. Houghton Mifflin Company: Boston and New York, 608 pp. Rust, H. J. 1946. Mammals of northern Idaho. J. Mammal. 27(4): 308-327.
Rust, H. J. 1946. Mammals of northern Idaho. J. Mammal. 27(4): 308-327. Sawyer, H. E. 1935. Studies on the rodents of Montana. M.A. thesis. University of Montana, Missoula. 111 pp.
Sawyer, H. E. 1935. Studies on the rodents of Montana. M.A. thesis. University of Montana, Missoula. 111 pp. Schleyer, B.O. 1983. Activity patterns of grizzly bears in the Yellowstone ecosystem and their reproductive behavior, predation and the use of carrion. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 130 p.
Schleyer, B.O. 1983. Activity patterns of grizzly bears in the Yellowstone ecosystem and their reproductive behavior, predation and the use of carrion. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 130 p. Scow, K.L. 1981. Ecological distribution of small mammals at Sarpy Creek, Montana, with special consideration of the Deer Mouse, Peromyscus maniculatus. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, Montana: Montana State University. 73 p.
Scow, K.L. 1981. Ecological distribution of small mammals at Sarpy Creek, Montana, with special consideration of the Deer Mouse, Peromyscus maniculatus. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, Montana: Montana State University. 73 p. Spring Creek Coal Company., 1992, Wildlife Monitoring Report. Spring Creek Coal Company 1992 Mining Annual Report. Appendix I.
Spring Creek Coal Company., 1992, Wildlife Monitoring Report. Spring Creek Coal Company 1992 Mining Annual Report. Appendix I. Teipner, C. L., E. O. Garton and L. Nelson. 1983. Pocket gophers in forest ecosystems. USDA, Forest Service, Gen. Tech. Rep. INT-154.
Teipner, C. L., E. O. Garton and L. Nelson. 1983. Pocket gophers in forest ecosystems. USDA, Forest Service, Gen. Tech. Rep. INT-154. Thompson, L.S. 1981. Circle West wildlife monitoring study: Third annual report. Technical report No. 8. Montana Department of Natural Resources and Conservation. Helena, Montana.
Thompson, L.S. 1981. Circle West wildlife monitoring study: Third annual report. Technical report No. 8. Montana Department of Natural Resources and Conservation. Helena, Montana. Thompson, L.S. 1982. Distribution of Montana amphibians, reptiles, and mammals. Bozeman: Montana Audubon Council. 24 pp.
Thompson, L.S. 1982. Distribution of Montana amphibians, reptiles, and mammals. Bozeman: Montana Audubon Council. 24 pp. Thompson, Richard W., Western Resource Dev. Corp., Boulder, CO., 1996, Wildlife baseline report for the Montana [Montanore] Project, Lincoln and Sanders counties, Montana. In Application for a Hard Rock Operating Permit and Proposed Plan of Operation, Montanore Project, Lincoln and Sanders Counties, Montana. Vol. 5. Stroiazzo, John. Noranda Minerals Corp., Libby, MT. Revised September 1996.
Thompson, Richard W., Western Resource Dev. Corp., Boulder, CO., 1996, Wildlife baseline report for the Montana [Montanore] Project, Lincoln and Sanders counties, Montana. In Application for a Hard Rock Operating Permit and Proposed Plan of Operation, Montanore Project, Lincoln and Sanders Counties, Montana. Vol. 5. Stroiazzo, John. Noranda Minerals Corp., Libby, MT. Revised September 1996. Thunderbird Wildlife Consulting, Inc., Gillette, WY., 2003, 2002 wildlife monitoring report: Big Sky Mine. February 2003.
Thunderbird Wildlife Consulting, Inc., Gillette, WY., 2003, 2002 wildlife monitoring report: Big Sky Mine. February 2003. Tryon, C. A., Jr. 1947. The biology of the pocket gopher (Thomomys talpoides) in Montana. Montana State College, Agr. Exp. Sta. Bull. 448, Bozeman. 30 pp.
Tryon, C. A., Jr. 1947. The biology of the pocket gopher (Thomomys talpoides) in Montana. Montana State College, Agr. Exp. Sta. Bull. 448, Bozeman. 30 pp. Tschache, O.P. 1970. Effects of ecological changes induced by various sagebrush control techniques on small mammal populations. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 51 p.
Tschache, O.P. 1970. Effects of ecological changes induced by various sagebrush control techniques on small mammal populations. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 51 p. Urban, Larry, 2002, Biological Resources Report: Wagner Pit Wetland Restoration Site. Proj. No. STPX 56(50) CN 4645. February 23, 2002. In Wgner Pit WS#13 Upper Yellowstone, Yellowstone County. Fin. Dist. 5 AdminDist 5.
Urban, Larry, 2002, Biological Resources Report: Wagner Pit Wetland Restoration Site. Proj. No. STPX 56(50) CN 4645. February 23, 2002. In Wgner Pit WS#13 Upper Yellowstone, Yellowstone County. Fin. Dist. 5 AdminDist 5. Van Horn, R.C. 1993. Ferruginous Hawk and Prairie Falcon reproductive and behavioral responses to human activity near the Kevin Rim, Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, Montana: Montana State University. 86 p.
Van Horn, R.C. 1993. Ferruginous Hawk and Prairie Falcon reproductive and behavioral responses to human activity near the Kevin Rim, Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, Montana: Montana State University. 86 p. Vaughan, T.A. 1967. Food Habits of the Northern Pocket Gopher On Shortgrass Prairie. Am. Midl. Nat. 77:176-189.
Vaughan, T.A. 1967. Food Habits of the Northern Pocket Gopher On Shortgrass Prairie. Am. Midl. Nat. 77:176-189. Verts, B. J. and L. N. Carraway. 1999. Thomomys talpoides. American Society of Mammalogists, Lawrence, KS. Mammalian Species No. 618:1-11.
Verts, B. J. and L. N. Carraway. 1999. Thomomys talpoides. American Society of Mammalogists, Lawrence, KS. Mammalian Species No. 618:1-11. VTN Colorado, Inc. Decker Coal Company., 1975, Draft environmental impact assessment for the proposed North Extension of the West Decker Mine.
VTN Colorado, Inc. Decker Coal Company., 1975, Draft environmental impact assessment for the proposed North Extension of the West Decker Mine. Waage, Bruce C., 1993, Western Energy Company Rosebud Mine, Colstrip, Montana: Annual Wildlife Monitoring Report; 1992 Field Season. December 1993.
Waage, Bruce C., 1993, Western Energy Company Rosebud Mine, Colstrip, Montana: Annual Wildlife Monitoring Report; 1992 Field Season. December 1993. Waage, Bruce C., 1995, Western Energy Company Rosebud Mine, Colstrip, Montana:1994 Annual Wildlife Monitoring Report; December 1, 1993 - November 30, 1994. February 27, 1995.
Waage, Bruce C., 1995, Western Energy Company Rosebud Mine, Colstrip, Montana:1994 Annual Wildlife Monitoring Report; December 1, 1993 - November 30, 1994. February 27, 1995. Waage, Bruce C., 1996, Western Energy Company Rosebud Mine, Colstrip, Montana: 1995 Annual Wildlife Monitoring Report; December 1, 1994 - November 30, 1995. February 28, 1996.
Waage, Bruce C., 1996, Western Energy Company Rosebud Mine, Colstrip, Montana: 1995 Annual Wildlife Monitoring Report; December 1, 1994 - November 30, 1995. February 28, 1996. Waage, Bruce C., 1999, Western Energy Company Rosebud Mine, Colstrip, Montana: 1998 Annual Wildlife Monitoring Report; December 1, 1997 - November 30, 1998 Survey Period. February 24, 1999.
Waage, Bruce C., 1999, Western Energy Company Rosebud Mine, Colstrip, Montana: 1998 Annual Wildlife Monitoring Report; December 1, 1997 - November 30, 1998 Survey Period. February 24, 1999. Waage, Bruce C., 2002, Western Energy Company Rosebud Mine, Colstrip, Montana. 2001 Annual Wildlife Monitoring Report; December 1, 2000 - November 30, 2001. Febr. 26, 2002.
Waage, Bruce C., 2002, Western Energy Company Rosebud Mine, Colstrip, Montana. 2001 Annual Wildlife Monitoring Report; December 1, 2000 - November 30, 2001. Febr. 26, 2002. WESTECH Env. Services, Inc., Helena, MT., 2000, Reconnaissance of Wildlife and Fisheries Resources at the Ruby Garnet Alder Gulch Property. May 24, 2000. In Application for an Operating Permit and Proposed Plan of Operations, Alder Gulch Mine Project, Mad
WESTECH Env. Services, Inc., Helena, MT., 2000, Reconnaissance of Wildlife and Fisheries Resources at the Ruby Garnet Alder Gulch Property. May 24, 2000. In Application for an Operating Permit and Proposed Plan of Operations, Alder Gulch Mine Project, Mad Westech, Inc. [Western Technology and Engineering]. 1989. Reconnaissance of terrestrial wildlife resources in the Pauper's Dream project vicinity, Aug. 1988. Prepared for Hydrometrics, Inc., Helena, MT. 22 pp.
Westech, Inc. [Western Technology and Engineering]. 1989. Reconnaissance of terrestrial wildlife resources in the Pauper's Dream project vicinity, Aug. 1988. Prepared for Hydrometrics, Inc., Helena, MT. 22 pp. Western Energy Co., Colstrip, MT. Unpub., 1983, Western Energy Company's Application for Amendment to Surface Mining Permit NO. 8003, Area B: sections 7, 8, 17,18 T1N R41E, sections 12, 13 T1N R40E, Mining Expansion. March 1983.
Western Energy Co., Colstrip, MT. Unpub., 1983, Western Energy Company's Application for Amendment to Surface Mining Permit NO. 8003, Area B: sections 7, 8, 17,18 T1N R41E, sections 12, 13 T1N R40E, Mining Expansion. March 1983. Western Energy Co., Colstrip, MT., 1981, Western Energy Company's Application for a Surface Mining Permit: Area C - Block 1. Vol. 1. May 1981.
Western Energy Co., Colstrip, MT., 1981, Western Energy Company's Application for a Surface Mining Permit: Area C - Block 1. Vol. 1. May 1981. Western Technology & Engineering, Inc. (WESTECH)., 1991, 1991 Bull Mountains Mine No. 1 Terrestrial Wildlife Monitoring Study. In Meridian Minerals Company Bull Mountains Mine No. 1 Permit Application, Musselshell County, Montana. Vol. 7 of 14: Section 26
Western Technology & Engineering, Inc. (WESTECH)., 1991, 1991 Bull Mountains Mine No. 1 Terrestrial Wildlife Monitoring Study. In Meridian Minerals Company Bull Mountains Mine No. 1 Permit Application, Musselshell County, Montana. Vol. 7 of 14: Section 26 Western Technology and Engineering, Inc. (WESTECH), Helena, MT., 1994, Terrestrial Wildlife Reconnaissance: Interim Report. Golden Sunlight Mines, Inc., Oxide Expansion. February 1994.
Western Technology and Engineering, Inc. (WESTECH), Helena, MT., 1994, Terrestrial Wildlife Reconnaissance: Interim Report. Golden Sunlight Mines, Inc., Oxide Expansion. February 1994. Western Technology and Engineering, Inc. (WESTECH). 1994. Wildlife Monitoring Absaloka Mine Area Annual Report, 1993. Montana SMP 85005. OSMP Montana 0007c. Mar. 12, 1994.
Western Technology and Engineering, Inc. (WESTECH). 1994. Wildlife Monitoring Absaloka Mine Area Annual Report, 1993. Montana SMP 85005. OSMP Montana 0007c. Mar. 12, 1994. Western Technology and Engineering, Inc. (WESTECH)., 1990, Wildlife Monitoring: Absaloka Mine Area Annual Report, 1990. 12/21/89-12/20/90. Montana SMP 85005 R1. OSMP Montana 0007B. Febr. 15, 1991.
Western Technology and Engineering, Inc. (WESTECH)., 1990, Wildlife Monitoring: Absaloka Mine Area Annual Report, 1990. 12/21/89-12/20/90. Montana SMP 85005 R1. OSMP Montana 0007B. Febr. 15, 1991. Western Technology and Engineering, Inc. (WESTECH)., 1991, Wildlife Monitoring and Additional Baseline Inventory: Absaloka Mine Area Annual Report, 1991. Montana SMP 85005 R1. OSMP Montana 0007B. Febr. 25, 1991.
Western Technology and Engineering, Inc. (WESTECH)., 1991, Wildlife Monitoring and Additional Baseline Inventory: Absaloka Mine Area Annual Report, 1991. Montana SMP 85005 R1. OSMP Montana 0007B. Febr. 25, 1991. Western Technology and Engineering, Inc. (WESTECH)., 1994, Wildlife Monitoring Absaloka Mine Area Annual Report, 1994. Montana SMP 85005. OSMP Montana 0007D. Febr. 24, 1994.
Western Technology and Engineering, Inc. (WESTECH)., 1994, Wildlife Monitoring Absaloka Mine Area Annual Report, 1994. Montana SMP 85005. OSMP Montana 0007D. Febr. 24, 1994. Western Technology and Engineering, Inc. (WESTECH)., 1996, Wildlife Monitoring Absaloka Mine Area Annual Report, 1995. Montana SMP 85005. OSMP Montana 0007D. Febr. 23, 1996.
Western Technology and Engineering, Inc. (WESTECH)., 1996, Wildlife Monitoring Absaloka Mine Area Annual Report, 1995. Montana SMP 85005. OSMP Montana 0007D. Febr. 23, 1996. Western Technology and Engineering, Inc. (WESTECH)., 1997, Wildlife Monitoring Absaloka Mine Area Annual Report, 1996. Montana SMP 85005. OSMP Montana 0007D. Mar. 1997.
Western Technology and Engineering, Inc. (WESTECH)., 1997, Wildlife Monitoring Absaloka Mine Area Annual Report, 1996. Montana SMP 85005. OSMP Montana 0007D. Mar. 1997. Western Technology and Engineering, Inc. (WESTECH)., 1999, Wildlife Monitoring Absaloka Mine Area Annual Report, 1998. SMP 85005. OSMP Montana 0007E. April 1999.
Western Technology and Engineering, Inc. (WESTECH)., 1999, Wildlife Monitoring Absaloka Mine Area Annual Report, 1998. SMP 85005. OSMP Montana 0007E. April 1999. Western Technology and Engineering, Inc. (WESTECH)., 2000, Wildlife Monitoring Absaloka Mine Area Annual Report, 1999. Montana SMP 85005. OSMP Montana 0007E. February 2000.
Western Technology and Engineering, Inc. (WESTECH)., 2000, Wildlife Monitoring Absaloka Mine Area Annual Report, 1999. Montana SMP 85005. OSMP Montana 0007E. February 2000. Western Technology and Engineering, Inc. (WESTECH)., 2001, Wildlife Monitoring Absaloka Mine Area Annual Report, 2000. Montana SMP 85005. OSMP Montana 0007E. February 2001.
Western Technology and Engineering, Inc. (WESTECH)., 2001, Wildlife Monitoring Absaloka Mine Area Annual Report, 2000. Montana SMP 85005. OSMP Montana 0007E. February 2001. Western Technology and Engineering, Inc., Helena, MT., 1989, Reconnaissance of terrestrial wildlife resources in the Basin Creek Mine Amendment 5 vicinity, 1988-1989. November 1989. In Basin Creek Mine Permit Amendment No. 5 - Paupers Pit Southwest, Block B and leach Pad No. 3. Basin Creek Mining, Inc. (Pegasus Gold Corp.). For Montana Dept. of State Lands and USFS Deer Lodge NF.
Western Technology and Engineering, Inc., Helena, MT., 1989, Reconnaissance of terrestrial wildlife resources in the Basin Creek Mine Amendment 5 vicinity, 1988-1989. November 1989. In Basin Creek Mine Permit Amendment No. 5 - Paupers Pit Southwest, Block B and leach Pad No. 3. Basin Creek Mining, Inc. (Pegasus Gold Corp.). For Montana Dept. of State Lands and USFS Deer Lodge NF. Western Technology and Engineering, Inc., Helena, MT., 1989, Reconnaissance of the wildlife resources in the vicinity of the Kendall Venture Mine. January 1989. In Kendall Venture North Moccasin Project: Amendment to Operating Permit 00122, Fergus County, Montana. Vol. 2, App. A, Feb., 1989.
Western Technology and Engineering, Inc., Helena, MT., 1989, Reconnaissance of the wildlife resources in the vicinity of the Kendall Venture Mine. January 1989. In Kendall Venture North Moccasin Project: Amendment to Operating Permit 00122, Fergus County, Montana. Vol. 2, App. A, Feb., 1989. Williams, O. 1955. Distribution of mice and shrews in a Colorado montane forest. J. Mammal. 36(2): 221-231.
Williams, O. 1955. Distribution of mice and shrews in a Colorado montane forest. J. Mammal. 36(2): 221-231.
- Web Search Engines for Articles on "Northern Pocket Gopher"
- Additional Sources of Information Related to "Mammals"





