View in other NatureServe Network Field Guides
NatureServe
Montana
Utah
Wyoming
Idaho
Wisconsin
British Columbia
South Carolina
Yukon
California
New York
Short-leaved Cinquefoil - Potentilla brevifolia
State Rank Reason (see State Rank above)
Rare in Montana, where it is currently only from a few collections from the Madison Range. The remote, high-elevation habitat should greatly minimize the potential for any negative impacts to the viability of the species in the state. Accurate estimates of population levels are lacking.
General Description
Perennial from a long-branched rootstock, clothed in old leaves. Stems ascending, glandular, 5–15 cm. Leaf blades cordate-ovate, 10–15 mm long, pinnately divided into 3 to 7 deeply lobed, fan-shaped, glandular-puberulent leaflets. Inflorescence a several-flowered, glandular cyme with ascending branches. Flowers: sepals ovate, 3–4 mm long with shorter, lanceolate bracteoles; petals yellow, 5–6 mm long, retuse. Achenes smooth, 1–1.5 mm long (
Lesica et al. 2012. Manual of Montana Vascular Plants. BRIT Press. Fort Worth, TX).
Phenology
Flowering in August.
Diagnostic Characteristics
Distinguished from other Montana Potentilla by combining perennial mat-forming habit, finely glandular-hairy herbage, short pinnate leaf blades, and a style attached between the middle and top of the ovary.
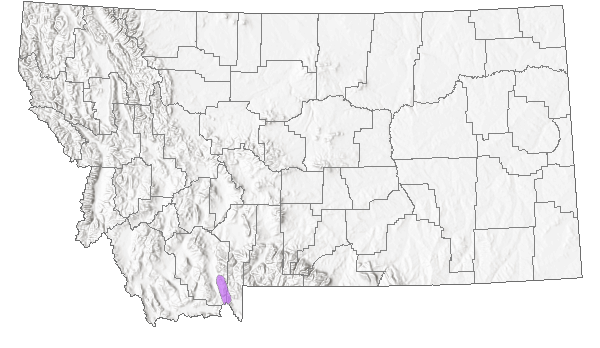
Species Range
Montana Range
Range Descriptions
 Native
Native
Range Comments
OR to southwest MT, south to northwest WY and northeast NV. Regional endemic.
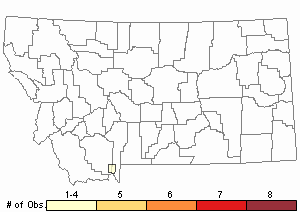
Observations in Montana Natural Heritage Program Database
Number of Observations: 4
(Click on the following maps and charts to see full sized version)
Map Help and Descriptions
Relative Density
Recency
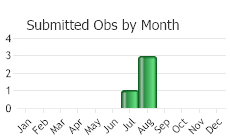
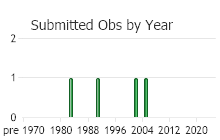
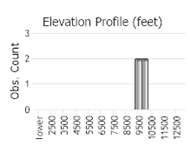 (Observations spanning multiple months or years are excluded from time charts)
(Observations spanning multiple months or years are excluded from time charts)
Habitat
Open, rocky, granite-derived soil and scree slopes in the alpine zone.
National Vegetation Classification System Groups Associated with this Species
Alpine
Alpine - Sparse and Barren
Alpine - Vegetated
Ecology
POLLINATORS The following animal species have been reported as pollinators of this plant species or its genus where their geographic ranges overlap:
Bombus bifarius,
Bombus fervidus,
Bombus frigidus,
Bombus rufocinctus,
Bombus occidentalis,
Bombus pensylvanicus,
Bombus impatiens, and
Bombus flavidus (Thorp et al. 1983, Wilson et al. 2010, Colla and Dumesh 2010, Colla et al. 2011, Koch and Strange 2012, Koch et al. 2012, Williams et al. 2014).
Stewardship Responsibility
Threats or Limiting Factors
STATE THREAT SCORE REASON
Threat impact not assigned because threats are not known (MTNHP Threat Assessment 2021).
References
- Literature Cited AboveLegend:
 View Online Publication
View Online Publication Colla, S., L. Richardson, and P. Williams. 2011. Bumble bees of the eastern United States. Washington, DC: USDA Forest Service, Pollinator Partnership. 103 p.
Colla, S., L. Richardson, and P. Williams. 2011. Bumble bees of the eastern United States. Washington, DC: USDA Forest Service, Pollinator Partnership. 103 p. Colla, S.R. and S. Dumesh. 2010. The bumble bees of southern Ontario: notes on natural history and distribution. Journal of the Entomological Society of Ontario 141:39-68.
Colla, S.R. and S. Dumesh. 2010. The bumble bees of southern Ontario: notes on natural history and distribution. Journal of the Entomological Society of Ontario 141:39-68. Koch, J., J. Strange, and P. Williams. 2012. Bumble bees of the western United States. Washington, DC: USDA Forest Service, Pollinator Partnership. 143 p.
Koch, J., J. Strange, and P. Williams. 2012. Bumble bees of the western United States. Washington, DC: USDA Forest Service, Pollinator Partnership. 143 p. Koch, J.B. and J.P. Strange. 2012. The status of Bombus occidentalis and B. moderatus in Alaska with special focus on Nosema bombi incidence. Northwest Science 86:212-220.
Koch, J.B. and J.P. Strange. 2012. The status of Bombus occidentalis and B. moderatus in Alaska with special focus on Nosema bombi incidence. Northwest Science 86:212-220. Lesica, P., M.T. Lavin, and P.F. Stickney. 2012. Manual of Montana Vascular Plants. Fort Worth, TX: BRIT Press. viii + 771 p.
Lesica, P., M.T. Lavin, and P.F. Stickney. 2012. Manual of Montana Vascular Plants. Fort Worth, TX: BRIT Press. viii + 771 p. MTNHP Threat Assessment. 2021. State Threat Score Assignment and Assessment of Reported Threats from 2006 to 2021 for State-listed Vascular Plants. Botany Program, Montana Natural Heritage Program, Helena, Montana.
MTNHP Threat Assessment. 2021. State Threat Score Assignment and Assessment of Reported Threats from 2006 to 2021 for State-listed Vascular Plants. Botany Program, Montana Natural Heritage Program, Helena, Montana. Thorp, R.W., D.S. Horning, and L.L. Dunning. 1983. Bumble bees and cuckoo bumble bees of California (Hymenoptera: Apidae). Bulletin of the California Insect Survey 23:1-79.
Thorp, R.W., D.S. Horning, and L.L. Dunning. 1983. Bumble bees and cuckoo bumble bees of California (Hymenoptera: Apidae). Bulletin of the California Insect Survey 23:1-79. Williams, P., R. Thorp, L. Richardson, and S. Colla. 2014. Bumble Bees of North America. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press. 208 p.
Williams, P., R. Thorp, L. Richardson, and S. Colla. 2014. Bumble Bees of North America. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press. 208 p. Wilson, J.S., L.E. Wilson, L.D. Loftis, and T. Griswold. 2010. The montane bee fauna of north central Washington, USA, with floral associations. Western North American Naturalist 70(2): 198-207.
Wilson, J.S., L.E. Wilson, L.D. Loftis, and T. Griswold. 2010. The montane bee fauna of north central Washington, USA, with floral associations. Western North American Naturalist 70(2): 198-207.
- Additional ReferencesLegend:
 View Online Publication
View Online Publication
Do you know of a citation we're missing? Lesica, P., M.T. Lavin, and P.F. Stickney. 2022. Manual of Montana Vascular Plants, Second Edition. Fort Worth, TX: BRIT Press. viii + 779 p.
Lesica, P., M.T. Lavin, and P.F. Stickney. 2022. Manual of Montana Vascular Plants, Second Edition. Fort Worth, TX: BRIT Press. viii + 779 p. Simanonok, M. 2018. Plant-pollinator network assembly after wildfire. Ph.D. Dissertation. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 123 p.
Simanonok, M. 2018. Plant-pollinator network assembly after wildfire. Ph.D. Dissertation. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 123 p. Simanonok, M.P. and L.A. Burkle. 2019. Nesting success of wood-cavity-nesting bees declines with increasing time since wildfire. Ecology and Evolution 9:12436-12445.
Simanonok, M.P. and L.A. Burkle. 2019. Nesting success of wood-cavity-nesting bees declines with increasing time since wildfire. Ecology and Evolution 9:12436-12445.
- Web Search Engines for Articles on "Short-leaved Cinquefoil"





