View in other NatureServe Network Field Guides
NatureServe
Montana
Utah
Wyoming
Idaho
Wisconsin
British Columbia
South Carolina
Yukon
California
New York
Hooker's Balsamroot - Balsamorhiza hookeri
Other Names:
Balsamorhiza hispidula, Balsamorhiza hookeri var. hispidula
State Rank Reason (see State Rank above)
Known in Montana only from the vicinity of Monida and within the Mount Haggin WMA.
- Details on Status Ranking and Review
Population Size
Score2 - Small: Generally 2,000-10,000 individuals.
Range Extent
Score2 - Regional or State Endemic or Small Montana Range: Generally restricted to an area <100,000 sq. miles (equivalent to 2/3 the size of Montana or less) or Montana contributes 50% or more of the species’ range or populations OR limited to 2-3 Sub-basins in Montana.
CommentPeripheral and sporadically distributed in southwest Montana.
Area of Occupancy
Score3 - Very Low: Generally occurring in 3 or fewer Subwatersheds (6th Code HUC’s).
Environmental Specificity
Score1 - Moderate: Species is restricted to a specific habitat that is more widely distributed or to several restricted habitats and is typically dependent upon relatively unaltered, good-quality habitat (C Values of 5-7).
Trends
ScoreNA - Rank factor not assessed.
CommentTrends are unknown, though populations are likely stable, experiencing only minor declines or perhaps even expanding.
Threats
Score0-1 - Low to Medium.
Intrinsic Vulnerability
Score0-1 - Low to Moderate Vulnerability.
Raw Conservation Status Score
Score
8 to 10 total points scored out of a possible 16 (Rarity factors and threats only).
General Description
Hooker's Balsamroot is a perennial with a leafless flowering stem 10-40 cm tall, arising from a carrot-like taproot. The basal leaves are 10-40 cm long and pinnately-divided into narrow segments. Foliage is pubescent with coarse, firm hairs. The solitary flower heads resemble those of a sunflower. The narrow involucral bracts are long-hairy, at least on margins. The 10-16 yellow rays are 1.5-3.5 cm long. The achene is glabrous.
Our plants are variety hispidula (Sharp) Cronquist
Phenology
Flowering in late June - early July.
Diagnostic Characteristics
Distinguished from Balsamorhiza incana and B. macrophylla by the rays mostly less than 3 cm long, and foliage with coarse, firm hairs.
Species Range
Montana Range
Range Descriptions
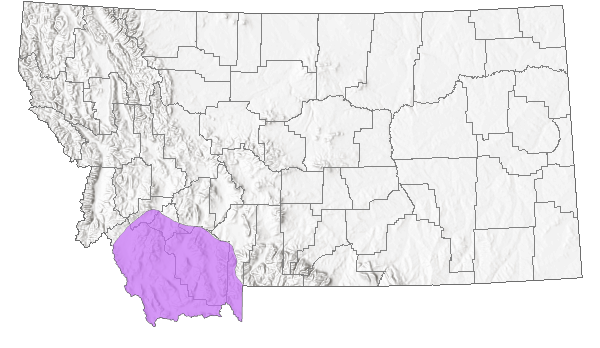
 Native
Native
Range Comments
WA to MT south to CA, AZ and CO (Lesica et al. 2012. Manual of Montana Vascular Plants. BRIT Press. Fort Worth, TX).
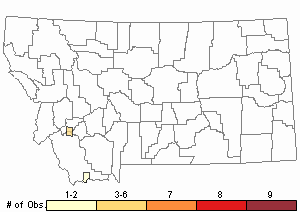
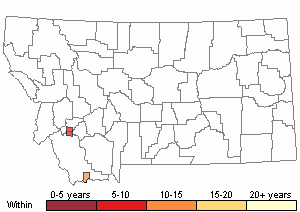
Observations in Montana Natural Heritage Program Database
Number of Observations: 8
(Click on the following maps and charts to see full sized version)
Map Help and Descriptions
Relative Density
Recency
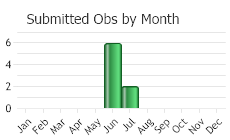
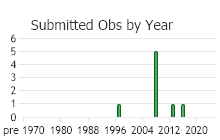
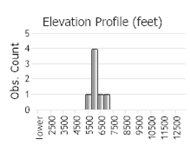 (Observations spanning multiple months or years are excluded from time charts)
(Observations spanning multiple months or years are excluded from time charts)
Habitat
Sagebrush steppe.
National Vegetation Classification System Groups Associated with this Species
Shrubland
Sagebrush Shrubland
Grassland
Montane - Subalpine Grassland
Ecology
POLLINATORS The following animal species have been reported as pollinators of this plant species or its genus where their geographic ranges overlap:
Bombus appositus,
Bombus centralis,
Bombus fervidus,
Bombus nevadensis,
Bombus rufocinctus,
Bombus occidentalis, and
Bombus griseocollis (Thorp et al. 1983, Mayer et al. 2000, Koch et al. 2012).
Stewardship Responsibility
Threats or Limiting Factors
STATE THREAT SCORE REASON
Threat impact not assigned because threats are not known (MTNHP Threat Assessment 2021).
References
- Literature Cited AboveLegend:
 View Online Publication
View Online Publication Koch, J., J. Strange, and P. Williams. 2012. Bumble bees of the western United States. Washington, DC: USDA Forest Service, Pollinator Partnership. 143 p.
Koch, J., J. Strange, and P. Williams. 2012. Bumble bees of the western United States. Washington, DC: USDA Forest Service, Pollinator Partnership. 143 p. Lesica, P., M.T. Lavin, and P.F. Stickney. 2012. Manual of Montana Vascular Plants. Fort Worth, TX: BRIT Press. viii + 771 p.
Lesica, P., M.T. Lavin, and P.F. Stickney. 2012. Manual of Montana Vascular Plants. Fort Worth, TX: BRIT Press. viii + 771 p. Mayer, D.F., E.R. Miliczky, B.F. Finnigan, and C.A. Johnson. 2000. The bee fauna (Hymenoptera: Apoidea) of southeastern Washington. Journal of the Entomological Society of British Columbia 97: 25-31.
Mayer, D.F., E.R. Miliczky, B.F. Finnigan, and C.A. Johnson. 2000. The bee fauna (Hymenoptera: Apoidea) of southeastern Washington. Journal of the Entomological Society of British Columbia 97: 25-31. MTNHP Threat Assessment. 2021. State Threat Score Assignment and Assessment of Reported Threats from 2006 to 2021 for State-listed Vascular Plants. Botany Program, Montana Natural Heritage Program, Helena, Montana.
MTNHP Threat Assessment. 2021. State Threat Score Assignment and Assessment of Reported Threats from 2006 to 2021 for State-listed Vascular Plants. Botany Program, Montana Natural Heritage Program, Helena, Montana. Thorp, R.W., D.S. Horning, and L.L. Dunning. 1983. Bumble bees and cuckoo bumble bees of California (Hymenoptera: Apidae). Bulletin of the California Insect Survey 23:1-79.
Thorp, R.W., D.S. Horning, and L.L. Dunning. 1983. Bumble bees and cuckoo bumble bees of California (Hymenoptera: Apidae). Bulletin of the California Insect Survey 23:1-79.
- Additional ReferencesLegend:
 View Online Publication
View Online Publication
Do you know of a citation we're missing? Lesica, P., M.T. Lavin, and P.F. Stickney. 2022. Manual of Montana Vascular Plants, Second Edition. Fort Worth, TX: BRIT Press. viii + 779 p.
Lesica, P., M.T. Lavin, and P.F. Stickney. 2022. Manual of Montana Vascular Plants, Second Edition. Fort Worth, TX: BRIT Press. viii + 779 p. Lesica, P., P. Husby, and S. V. Cooper. 1998. Noteworthy collections: Montana. Madrono 45:328-330.
Lesica, P., P. Husby, and S. V. Cooper. 1998. Noteworthy collections: Montana. Madrono 45:328-330. Quire, R.L. 2013. The sagebrush steppe of Montana and southeastern Idaho shows evidence of high native plant diversity, stability, and resistance to the detrimental effects of nonnative plant species. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 124 p.
Quire, R.L. 2013. The sagebrush steppe of Montana and southeastern Idaho shows evidence of high native plant diversity, stability, and resistance to the detrimental effects of nonnative plant species. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 124 p.
- Web Search Engines for Articles on "Hooker's Balsamroot"





