View in other NatureServe Network Field Guides
NatureServe
Montana
Utah
Wyoming
Idaho
Wisconsin
British Columbia
South Carolina
Yukon
California
New York
Four-spotted Skimmer - Libellula quadrimaculata
General Description
We do not yet have descriptive information on this species. Please try the buttons above to search for information from other sources.
Species Range
Montana Range
Range Descriptions
 Native
Native
Range Comments
The Four-spotted Skimmer is commonly distributed across North America, from Arizona and New Mexico in the south to Alaska and the Yukon to the north. This species is also cirbumboreal, occurring throughout Europe and northwestern Africa to Asia and Japan (Dunkle 2000, Paulson 2009).
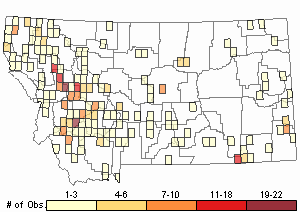
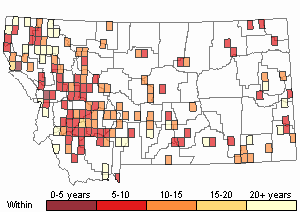
Observations in Montana Natural Heritage Program Database
Number of Observations: 469
(Click on the following maps and charts to see full sized version)
Map Help and Descriptions
Relative Density
Recency
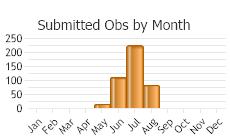
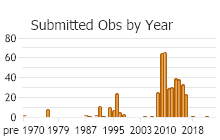
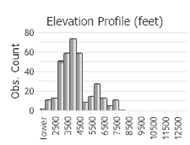 (Observations spanning multiple months or years are excluded from time charts)
(Observations spanning multiple months or years are excluded from time charts)
Migration
Although no records exist regarding the migratory behavior of Four-spotted Skimmers in North America, they do show evidence of cyclical migration events in Europe (Paulson 2009).
Habitat
The preferred habitat of Four-spotted Skimmers is lakes and ponds with emergent vegetation and mud bottoms, fens, bogs, slow streams, and boggy and marshy wetlands. This species tends to select acidic wetland types but they can tolerate saline conditions as well. Four-spotted Skimmers can be seen flying in open areas often a great distance from water (Dunkle 2000, Nikula et al. 2002, Paulson 2009).
National Vegetation Classification System Groups Associated with this Species
Wetland and Riparian
Alkaline - Saline Wetlands
Alpine Riparian and Wetland
Peatland
Riparian and Wetland Forest
Riparian Shrubland
Wet Meadow and Marsh
Food Habits
Larvae feed on a wide variety of aquatic insects, such as mosquito larvae, other aquatic fly larvae, mayfly larvae, and freshwater shrimp. They will also eat very small fish and tadpoles.
Adult- The dragonfly will eat almost any soft-bodied flying insect including mosquitoes, flies, small moths, mayflies, and flying ants or termites.
Reproductive Characteristics
Male Four-spotted Skimmers are highly territorial and fly almost constantly. When they do perch it is often on the ground, which is unusual for Libellulids. Copulation is in flight and is fairly brief, after which the female will either commence oviposition or leave the area. Females oviposit in flight by tapping at the water with the tip of their abdomen, often with the male guarding nearby (Nikula et al. 2000, Paulson 2009).
Stewardship Responsibility
References
- Literature Cited AboveLegend:
 View Online Publication
View Online Publication Dunkle, S.W. 2000. Dragonflies through binoculars: A field guide to dragonflies of North America. New York, NY. Oxford University Press. 266 pp.
Dunkle, S.W. 2000. Dragonflies through binoculars: A field guide to dragonflies of North America. New York, NY. Oxford University Press. 266 pp. Nikula, B., J. Sones, D.W. Stokes, and L.Q. Stokes. 2002. Stokes beginner's guide to dragonflies and damselflies. Boston: Little, Brown. 159 pp.
Nikula, B., J. Sones, D.W. Stokes, and L.Q. Stokes. 2002. Stokes beginner's guide to dragonflies and damselflies. Boston: Little, Brown. 159 pp. Paulson, D.R. 2009. Dragonflies and Damselflies of the West. Princeton University Press, Princeton. 535 pp.
Paulson, D.R. 2009. Dragonflies and Damselflies of the West. Princeton University Press, Princeton. 535 pp.
- Additional ReferencesLegend:
 View Online Publication
View Online Publication
Do you know of a citation we're missing? Nelson, Howard E. 1953. The summer dragonflies of Flathead Valley, Montana. M.A. Thesis. University of Montana. Missoula, MT.
Nelson, Howard E. 1953. The summer dragonflies of Flathead Valley, Montana. M.A. Thesis. University of Montana. Missoula, MT. Sater, S. 2022. The insects of Sevenmile Creek, a pictorial guide to their diversity and ecology. Undergraduate Thesis. Helena, MT: Carroll College. 242 p.
Sater, S. 2022. The insects of Sevenmile Creek, a pictorial guide to their diversity and ecology. Undergraduate Thesis. Helena, MT: Carroll College. 242 p.
- Web Search Engines for Articles on "Four-spotted Skimmer"
- Additional Sources of Information Related to "Insects"





