View in other NatureServe Network Field Guides
NatureServe
Montana
Utah
Wyoming
Idaho
Wisconsin
British Columbia
South Carolina
Yukon
California
New York
Fir Pinwheel - Radiodiscus abietum
General Description
A moderately small shell, diameter to about 6.5 mm, height to about 3.5 mm. The chitonous shell is heliciform of up to 5 3/4 whorls, flattened on the upper surface, rounded on the under surface; color is light chocolate-brown and almost opaque. The inner two whorls have fine spiral striae, visible with a hand lens, that abruptly switch to a series of small and closely-spaced but well-defined axial riblets. The umbilicus is deep and relatively narrow, with almost vertical walls, and about 1.0 mm in diameter. The aperture is crescent-shaped and slightly oblique. Head and tentacles are black (Hendricks 2012, Burke 2013). Internal anatomy is described by Baker (1930) and Pilsbry (1948).
Diagnostic Characteristics
Similar superficially to Discus whitneyi and D. shimekii, but differs in having a combination of minute spiral striations on the first (embryonic) 1.5 whorls that end abruptly where the ribbing begins, a flat spire, a deep and narrow umbilicus, and a crescent-shaped aperture (in contrast to a rounded or ovate aperture).
Species Range
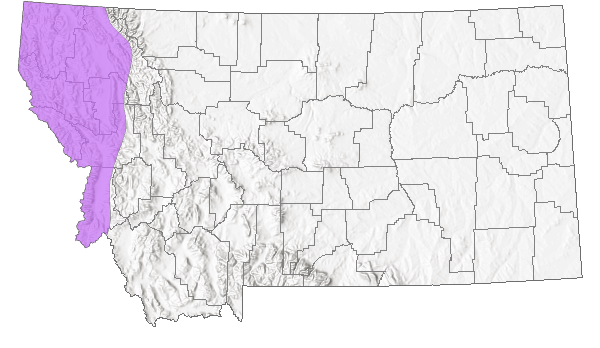
Montana Range
Range Descriptions
 Native
Native
Range Comments
Oregon, Washington, northern Idaho and western Montana (Burke 2013). In Montana, 76 records from seven counties west of the Continental Divide: Flathead (1), Lake (7), Lincoln (20), Mineral (13), Missoula (5), Ravalli (12), Sanders (18). Elevation range is 655 to 1939 m (2150 to 6360 ft). May be fairly common locally; as many as 20 were found at one Ravalli County site in late September (Hendricks 2012). First documented from Montana in 1957 (Brunson and Russell 1967).
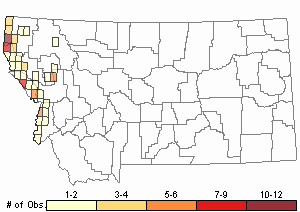
Observations in Montana Natural Heritage Program Database
Number of Observations: 88
(Click on the following maps and charts to see full sized version)
Map Help and Descriptions
Relative Density
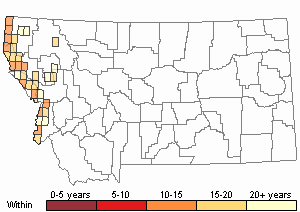
Recency
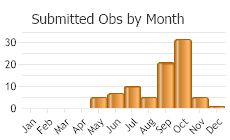
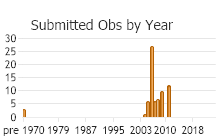
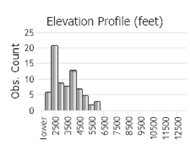 (Observations spanning multiple months or years are excluded from time charts)
(Observations spanning multiple months or years are excluded from time charts)
Migration
Sedentary.
Habitat
Found in a variety mixed conifer forests, but usually in moist mesic sites; canopy species include western redcedar, western hemlock, grand fir, western white pine, Douglas-fir, Engelmann spruce, subalpine fir, western larch, ponderosa pine, lodgepole pine, black cottonwood, water and paper birch, with a secondary canopy including aspen, Pacific yew, and alder. Found under woody debris, rocks, leaf litter, and bryophyte mats (Hendricks 2012).
Reproductive Characteristics
The species is hermaphroditic, based on internal anatomy (Pilsbry 1948). Age/size at reproductive maturity is unknown, but Pilsbry (1948) indicated the type specimen (diameter 4.9 mm, 5 whorls) was immature.
Management
Documented Montana sites are on lands administered by the Confederated Salish and Kootenai Tribes (3 sites), State of Montana (1 site, but bounded closely by the Missoula Ranger District, Lolo National Forest), Superior Ranger District, Lolo National Forest (1 site), Darby Ranger District, Bitterroot National Forest (3 sites), Cabinet Ranger District, Kootenai National Forest (2 sites), Fisher River Ranger District, Kootenai National Forest (1 site), Libby Ranger District, Kootenai National Forest (1 site), and the Rexford Ranger District, Kootenai National Forest (1 site).
Stewardship Responsibility
Threats or Limiting Factors
Logging and grazing over most of the known range are probably the greatest threats, through alteration of appropriate habitat. However, alteration of habitat from fire, highway and road construction, rural home development and land clearing could represent threats, as could fire suppression retardants and chemical methods of weed control.
References
- Literature Cited AboveLegend:
 View Online Publication
View Online Publication Baker, H.B. 1930. New and problematic west American land snails. The Nautilus 43:121-128.
Baker, H.B. 1930. New and problematic west American land snails. The Nautilus 43:121-128. Brunson, R.B. and R.H. Russell. 1967. Radiodiscus, new to molluscan fauna of Montana. Nautilus 81:18-21.
Brunson, R.B. and R.H. Russell. 1967. Radiodiscus, new to molluscan fauna of Montana. Nautilus 81:18-21. Burke, T. E. 2013. Land snails and slugs of the Pacific Northwest. Corvallis, OR: Oregon State University Press. 344 p.
Burke, T. E. 2013. Land snails and slugs of the Pacific Northwest. Corvallis, OR: Oregon State University Press. 344 p. Hendricks, P. 2012. A Guide to the Land Snails and Slugs of Montana. A report to the U.S. Forest Service - Region 1. Montana Natural Heritage Program, Helena, MT. vii + 187 pp. plus appendices.
Hendricks, P. 2012. A Guide to the Land Snails and Slugs of Montana. A report to the U.S. Forest Service - Region 1. Montana Natural Heritage Program, Helena, MT. vii + 187 pp. plus appendices. Pilsbry, H.A. 1948. Land Mollusca of North America (north of Mexico), Volume II Part 2. The Academy of Natural Sciences of Philadelphia Monograph Number 2(2): 521-1113.
Pilsbry, H.A. 1948. Land Mollusca of North America (north of Mexico), Volume II Part 2. The Academy of Natural Sciences of Philadelphia Monograph Number 2(2): 521-1113.
- Additional ReferencesLegend:
 View Online Publication
View Online Publication
Do you know of a citation we're missing? Frest, T.J. and E.J. Johannes. 1995. Interior Columbia Basin mollusk species of special concern. Final report to the Interior Columbia Basin Ecosystem Management Project, Walla Walla, WA. Contract #43-0E00-4-9112. 274 pp. plus appendices.
Frest, T.J. and E.J. Johannes. 1995. Interior Columbia Basin mollusk species of special concern. Final report to the Interior Columbia Basin Ecosystem Management Project, Walla Walla, WA. Contract #43-0E00-4-9112. 274 pp. plus appendices. Frest, T.J. and E.J. Johannes. 2001. An annotated checklist of Idaho land and freshwater mollusks. Journal of the Idaho Academy of Science 36(2):1-51.
Frest, T.J. and E.J. Johannes. 2001. An annotated checklist of Idaho land and freshwater mollusks. Journal of the Idaho Academy of Science 36(2):1-51. Hendricks, P. 2005. Surveys for animal species of concern in northwestern Montana. Unpublished report to the Montana Department of Fish, Wildlife & Parks, Montana Natural Heritage Program, Helena, Montana, May 2005. 53 p.
Hendricks, P. 2005. Surveys for animal species of concern in northwestern Montana. Unpublished report to the Montana Department of Fish, Wildlife & Parks, Montana Natural Heritage Program, Helena, Montana, May 2005. 53 p. Hendricks, P., B.A. Maxell, and S. Lenard. 2006. Land mollusk surveys on USFS Northern Region lands. A report to the USDA Forest Service, Northern Region. Montana Natural Heritage Program, Helena, Montana. 11 pp. plus appendices.
Hendricks, P., B.A. Maxell, and S. Lenard. 2006. Land mollusk surveys on USFS Northern Region lands. A report to the USDA Forest Service, Northern Region. Montana Natural Heritage Program, Helena, Montana. 11 pp. plus appendices. Hendricks, P., B.A. Maxell, S. Lenard, and C. Currier. 2007. Land mollusk surveys on USFS Northern Region lands: 2006. A report to the USDA Forest Service, Northern Region. Montana Natural Heritage Program, Helena, Montana. 11 pp. plus appendices.
Hendricks, P., B.A. Maxell, S. Lenard, and C. Currier. 2007. Land mollusk surveys on USFS Northern Region lands: 2006. A report to the USDA Forest Service, Northern Region. Montana Natural Heritage Program, Helena, Montana. 11 pp. plus appendices. Hendricks, P., B.A. Maxell, S. Lenard, and C. Currier. 2008. Surveys and predicted distribution models for land mollusks on USFS Northern Region Lands: 2007. Report to the USDA Forest Service, Northern Region. Helena, MT: Montana Natural Heritage Program. 12 pp. + appendices.
Hendricks, P., B.A. Maxell, S. Lenard, and C. Currier. 2008. Surveys and predicted distribution models for land mollusks on USFS Northern Region Lands: 2007. Report to the USDA Forest Service, Northern Region. Helena, MT: Montana Natural Heritage Program. 12 pp. + appendices. Smith, A.G. 1943. Mollusks of the Clearwater Mountains, Idaho. Proceedings of the California Academy of Sciences, fourth series, 23:537-554.
Smith, A.G. 1943. Mollusks of the Clearwater Mountains, Idaho. Proceedings of the California Academy of Sciences, fourth series, 23:537-554.
- Web Search Engines for Articles on "Fir Pinwheel"
- Additional Sources of Information Related to "Snails / Slugs"





