View in other NatureServe Network Field Guides
NatureServe
Montana
Utah
Wyoming
Idaho
Wisconsin
British Columbia
South Carolina
Yukon
California
New York
Meadow Grasshopper - Pseudochorthippus curtipennis
Other Names:
Marsh Meadow Grasshopper
General Description
The following comes from Hebard (1928), Brooks (1958), Helfer (1971), Otte (1981), Capinera and Sechrist (1982), Vickery and Kevan (1985), McDaniel (1987), Pfadt (2002), Capinera et al. (2004), and Scott (2010). A small to medium slender grasshopper. The body is brownish dorsally and either brown or green laterally. The abdomen is yellowish with black patches on the side. The wings (tegmina) are grayish or yellowish, broadly rounded at the tip, and variable in length. Generally, female wings are short, covering half to three-fourths of the abdomen. Male wings usually reach to, or slightly beyond the tip.
Phenology
Overwinters in the egg stage. Eggs hatch in June and adults occur from July through September (Capinera et al. 2004, Capinera and Sechrist 1982, Otte 1984, Pfadt 2002, Scott 2010, and Vickery and Kevan 1985).
Diagnostic Characteristics
The following comes from Hebard (1928), Brooks (1958), Helfer (1971), Otte (1981), Capinera and Sechrist (1982), Vickery (1985), McDaniel (1987), Pfadt (2002), Capinera et al. (2004), and Scott (2010). The male body length is 12 mm to 20 mm and females 20 mm to 35 mm. The antennae are long, yellow at the base and merging to black at the tip. Outer face of the hind femur is not banded, but often bears a dark stripe and the knee is black. Hind tibia is yellow or orange.
Easily confused with
Club-horned Grasshopper (
Aeropedellus clavatus), but its filiform antennae distinguish it from that species.
Chorthippis is a large genus worldwide, with 70 to 80 species recognized in Europe and Asia.
C. curtipennis is the only species in North America (Brust et al. 2008).
Species Range
Montana Range
Range Descriptions
 Native
Native
Range Comments
The Meadow Grasshopper occurs over an extraordinary range in North America, ranging from far northern Alaska and Canada, southward to southern California, Arizona, and New Mexico. West to east from the west coast to Newfoundland, and south to the Carolinas. In Montana it has been reported for 29 counties (Capinera et al.2004, Capinera and Sechrist 1982, Otte 1984, Pfadt 2002, Scott 2010, and Vickery and Kevan 1985).
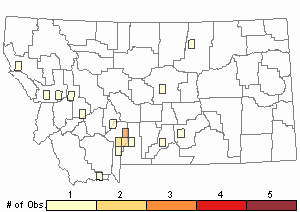
Observations in Montana Natural Heritage Program Database
Number of Observations: 31
(Click on the following maps and charts to see full sized version)
Map Help and Descriptions
Relative Density
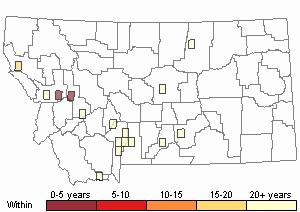
Recency
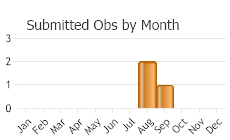
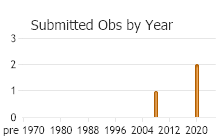
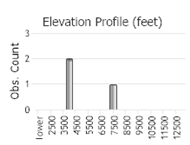 (Observations spanning multiple months or years are excluded from time charts)
(Observations spanning multiple months or years are excluded from time charts)
Habitat
Inhabits areas of tall lush grasses in hayfields, pastures, swales, mountain meadows, edges of marshes, lakes and ponds up to elevations of 11,000 feet. Also occurs in arctic tundra (Capinera et al. 2004, Capinera and Sechrist 1982, Otte 1984, Pfadt 2002, and Vickery and Kevan 1985).
Food Habits
Feeds only on grasses and sedges. Its diet varies with the plant species growing in its habitat, consisting of 16 species of grasses and sedges (Pfadt 2002).
Reproductive Characteristics
The following is taken from Capinera and Sechrist (1982), Otte (1984), Pfadt (2002), and Vickery and Kevan (1985). Males sing (stridulate) to attract females. Females either approach calling males or stridulate in response, causing the males to approach them. After mounting a female, the copulation lasts about 30 minutes. Pods, consisting of 5 to 8 eggs, are laid in or near clumps of grass and sometimes in decaying wood. When eggs hatch, the nymphs pass through 4 instars before reaching the adult stage. There is usually a one-year cycle, but in mountain meadows and higher latitudes incubation may require up to three years before hatching.
Stewardship Responsibility
References
- Literature Cited AboveLegend:
 View Online Publication
View Online Publication Brooks, A.R. 1958. Acridoidea of Southern Alberta, Saskatchewan, and Manitoba (Orthoptera). The Canadian Entomologist (Supplement 9) 90:5-92.
Brooks, A.R. 1958. Acridoidea of Southern Alberta, Saskatchewan, and Manitoba (Orthoptera). The Canadian Entomologist (Supplement 9) 90:5-92. Capinera, J.L. and T.S. Sechrist. 1982. Grasshoppers of Colorado: Identification, Biology, and Management. Fort Collins, CO: Colorado State University Experiment Station, Bulletin 584S. 161 p.
Capinera, J.L. and T.S. Sechrist. 1982. Grasshoppers of Colorado: Identification, Biology, and Management. Fort Collins, CO: Colorado State University Experiment Station, Bulletin 584S. 161 p. Capinera, J.L., R.D. Scott, and T.J. Walker. 2004. Field Guide to Grasshoppers, Katydids, and Crickets of the United States. Ithaca, NY. Cornell University Press.
Capinera, J.L., R.D. Scott, and T.J. Walker. 2004. Field Guide to Grasshoppers, Katydids, and Crickets of the United States. Ithaca, NY. Cornell University Press. Hebard, M. 1928. The Orthoptera of Montana. Proceedings of the Academy of Natural Sciences of Philadelphia, Vol. 80:211-306.
Hebard, M. 1928. The Orthoptera of Montana. Proceedings of the Academy of Natural Sciences of Philadelphia, Vol. 80:211-306. Helfer, J.R. 1971. How to Know the Grasshoppers, Crickets, Cockroaches, and Their Allies. Revised edition (out of print), Mineola, NY: Dover Publications.
Helfer, J.R. 1971. How to Know the Grasshoppers, Crickets, Cockroaches, and Their Allies. Revised edition (out of print), Mineola, NY: Dover Publications. McDaniel, B. 1987. Grasshoppers of South Dakota. Brookings, SD: South Dakota Agricultural Experiment Station, Bulletin TB 89.
McDaniel, B. 1987. Grasshoppers of South Dakota. Brookings, SD: South Dakota Agricultural Experiment Station, Bulletin TB 89. Otte, Daniel. 1981. The North American Grasshoppers. Volume 1. Acrididae (Gomphocerinae and Acridinae). Harvard University Press. 275 pp.
Otte, Daniel. 1981. The North American Grasshoppers. Volume 1. Acrididae (Gomphocerinae and Acridinae). Harvard University Press. 275 pp. Pfadt, R.E. 2002. Field Guide to Common Western Grasshoppers, 3rd edition. Laramie, WY: Wyoming Agricultural Experiment Station, Bulletin 912, modified by S. Schell and S. Schell for electronic publication. Accessed 19 February 2020. http://www.uwyo.edu/entomology/grasshoppers/field-guide/index.html#fieldguidetoc
Pfadt, R.E. 2002. Field Guide to Common Western Grasshoppers, 3rd edition. Laramie, WY: Wyoming Agricultural Experiment Station, Bulletin 912, modified by S. Schell and S. Schell for electronic publication. Accessed 19 February 2020. http://www.uwyo.edu/entomology/grasshoppers/field-guide/index.html#fieldguidetoc Scott, R.D. 2010. Montana Grasshoppers, Katydids, and Crickets A Pictorial Field Guide to the Orthoptera. MagpieMTGraphics, Billings, MT.
Scott, R.D. 2010. Montana Grasshoppers, Katydids, and Crickets A Pictorial Field Guide to the Orthoptera. MagpieMTGraphics, Billings, MT. Vickery, V. R. and D. K. M. Kevan. 1985. The grasshopper, crickets, and related insects of Canada and adjacent regions. Biosystematics Research Institute, Ottawa, Ontario. Publication Number 1777. 918 pp.
Vickery, V. R. and D. K. M. Kevan. 1985. The grasshopper, crickets, and related insects of Canada and adjacent regions. Biosystematics Research Institute, Ottawa, Ontario. Publication Number 1777. 918 pp.
- Additional ReferencesLegend:
 View Online Publication
View Online Publication
Do you know of a citation we're missing? Bland, R.G. 2003. The Orthoptera of Michigan—Biology, Keys, and Descriptions of Grasshoppers, Katydids, and Crickets. East Lansing, MI: Michigan State University Extension, Bulletin E-2815. 221 p.
Bland, R.G. 2003. The Orthoptera of Michigan—Biology, Keys, and Descriptions of Grasshoppers, Katydids, and Crickets. East Lansing, MI: Michigan State University Extension, Bulletin E-2815. 221 p. Henry, J.E. 1969. Protozoan and viral pathogens of grasshoppers. Ph.D. Dissertation. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 153 p.
Henry, J.E. 1969. Protozoan and viral pathogens of grasshoppers. Ph.D. Dissertation. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 153 p. Kirk, K. and C.R. Bomar. 2005. Guide to the grasshoppers of Wisconsin. Madison, WI: Wisconsin Department of Natural Resources, Bureau of Integrated Science Services PUB-SS-1008. 154 p.
Kirk, K. and C.R. Bomar. 2005. Guide to the grasshoppers of Wisconsin. Madison, WI: Wisconsin Department of Natural Resources, Bureau of Integrated Science Services PUB-SS-1008. 154 p. Skinner, K.F. 1995. Plant and grasshopper community composition: indicators & interactions across three spatial scales. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 144 p.
Skinner, K.F. 1995. Plant and grasshopper community composition: indicators & interactions across three spatial scales. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 144 p. Wachter, D.H. 1995. The ecology of selected grasshopper species along an elevational gradient. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, Montana: Montana State University. 59 p.
Wachter, D.H. 1995. The ecology of selected grasshopper species along an elevational gradient. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, Montana: Montana State University. 59 p.
- Web Search Engines for Articles on "Meadow Grasshopper"
- Additional Sources of Information Related to "Insects"





