View in other NatureServe Network Field Guides
NatureServe
Montana
Utah
Wyoming
Idaho
Wisconsin
British Columbia
South Carolina
Yukon
California
New York
Prairie Bluet - Coenagrion angulatum
State Rank Reason (see State Rank above)
The Prairie Bluet damselfly is currently listed as an "S1S3" species of potential concern in Montana because they are potentially at risk because of limited and/or declining numbers, range and/or habitat, even though it may be abundant in some areas. This rank is based on limited collections, but is probably more widespread that the rank implies.
General Description
The Prairie Bluet can be found anywhere in northern and eastern Montana except in the isolated mountains, it is most abundant in June at sun soaked prairie sloughs, marshes and slow streams. Like other Bluets, the Prairie Bluet is a vivid blue with dark markings. Females are less brightly colored. The small prairie bluet (30 mm or ~1in. long) has distinctive patterns that make it relatively easy to identify from other bluets. The blue rings on the abdomen become narrow towards the abdominal tip, which is bright blue. The bottom halves of the bulging eyes are green. A small black crescent shaped marking on the dorsal surface of the second abdominal segment should verify. Females are usually yellowish or greenish. Like all members of its family, the Prairie Bluet is a weak flier and rests horizontally with wings folded over the abdomen.
Phenology
Adults are flying June through August
Diagnostic Characteristics
The small prairie bluet (30 mm or ~1in. long) has distinctive patterns that make it relatively easy to identify from other bluets. The blue rings on the abdomen become narrow towards the abdominal tip, which is bright blue. The bottom halves of the bulging eyes are green. A small black crescent shaped marking on the dorsal surface of the second abdominal segment should verify.
Species Range
Montana Range
Range Descriptions
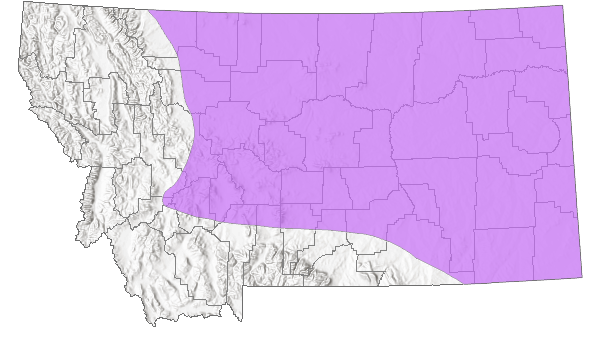
 Native
Native
Range Comments
Known from the northern and central US and Canada prairie region south to Wyoming and east to Iowa. In Montana, it is probably more common than these records indicate, however (Miller and Gustafson 1996).
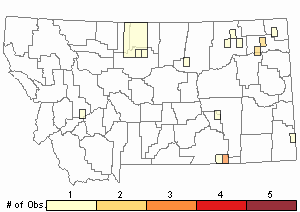
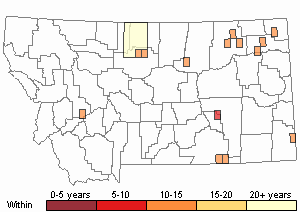
Observations in Montana Natural Heritage Program Database
Number of Observations: 20
(Click on the following maps and charts to see full sized version)
Map Help and Descriptions
Relative Density
Recency
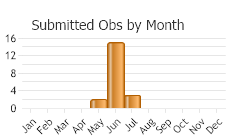
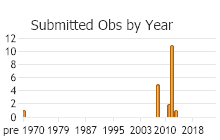
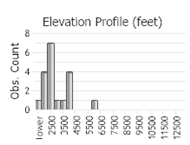 (Observations spanning multiple months or years are excluded from time charts)
(Observations spanning multiple months or years are excluded from time charts)
Habitat
Prairie ponds, sloughs, and marshes as well as slow-flowing streams are the preferred habitats of the Prairie Bluet. Many of these open sunny wetlands can dry out during the summer months or freeze completely in winter (Westfall and May 1996, Acorn 2004, Paulson 2009).
National Vegetation Classification System Groups Associated with this Species
Wetland and Riparian
Alkaline - Saline Wetlands
Peatland
Riparian and Wetland Forest
Riparian Shrubland
Wet Meadow and Marsh
Food Habits
Larvae feed on a wide variety of aquatic insects, such as mosquito larvae, other aquatic fly larvae, mayfly larvae, and freshwater shrimp. Adult- This damselfly will eat almost any soft-bodied flying insect including mosquitoes, flies, small moths, mayflies, and flying ants or termites.
Reproductive Characteristics
Male Prairie Bluets tend to occur more commonly in the grasses along the shoreline, rather than out over open water. Copulation is prolonged and oviposition is usually in tandem with the pair submerging to deposit eggs on emergent plant stems (Paulson 2009).
Interestingly, the larvae halt their growth in the early winter and embed themselves into the ice of the stream or pond. The larvae themselves do not freeze, as their bodies produce a natural antifreeze in their blood which keeps them safe. In the spring, when the ice melts, the larvae continue their development (Acorn 2004, Paulson 2009).
Stewardship Responsibility
Threats or Limiting Factors
The process where Prairie Bluet larvae freeze into stream or pond ice may a limiting factor to the geographic range of this species. This adaptation essentially makes Prairie Bluets solely dependent on habitats that do freeze solid such as those without much snow cover or in areas that are open and windy. These overwintering habitat requirements may be preventing them from expanding their range into more westerly or forested areas where significant snow cover insulates and thereby keeps water temperatures much warmer (Acorn 2004).
References
- Literature Cited AboveLegend:
 View Online Publication
View Online Publication Miller, K.B. and D.L. Gustafson. 1996. Distribution records of the Odonata of Montana. Bulletin of American Odonatology 3(4):75-88.
Miller, K.B. and D.L. Gustafson. 1996. Distribution records of the Odonata of Montana. Bulletin of American Odonatology 3(4):75-88. Westfall, M.J., Jr. and M.L. May. 1996. Damselflies of North America. Scientific Publishers, Gainesville, Florida. 649 pp.
Westfall, M.J., Jr. and M.L. May. 1996. Damselflies of North America. Scientific Publishers, Gainesville, Florida. 649 pp.
- Additional ReferencesLegend:
 View Online Publication
View Online Publication
Do you know of a citation we're missing? Acorn, J. 2004. Damselflies of Alberta: flying neon toothpicks in grass. Edmonton, Alberta: University of Alberta Press. 156 pp.
Acorn, J. 2004. Damselflies of Alberta: flying neon toothpicks in grass. Edmonton, Alberta: University of Alberta Press. 156 pp. Dunkle, S.W. 2000. Dragonflies through binoculars: A field guide to dragonflies of North America. New York, NY. Oxford University Press. 266 pp.
Dunkle, S.W. 2000. Dragonflies through binoculars: A field guide to dragonflies of North America. New York, NY. Oxford University Press. 266 pp. Paulson, D.R. 2009. Dragonflies and Damselflies of the West. Princeton University Press, Princeton. 535 pp.
Paulson, D.R. 2009. Dragonflies and Damselflies of the West. Princeton University Press, Princeton. 535 pp.
- Web Search Engines for Articles on "Prairie Bluet"
- Additional Sources of Information Related to "Insects"





