View in other NatureServe Network Field Guides
NatureServe
Montana
Utah
Wyoming
Idaho
Wisconsin
British Columbia
South Carolina
Yukon
California
New York
Magdalena Alpine - Erebia magdalena
General Description
[From Ferris and Borwn 1981; Scott 1986; Opler and Wright 1999; Glassberg 2001; Guppy and Shepard 2001] Forewing 2.4-2.8 cm. Almost completely black or dark brown on both surfaces (with a green or purple sheen when fresh); sometimes a scattering of white or gray scales near wingtips on undersurface and a faint trace of bands on under hindwings; antennae ringed with gray-white.
Shropshire and Tallamy (2025) provide a list, with synonymies, of 13,055 described native, exotic, and occasional straying Lepidoptera species of North America, north of Mexico; known but undescribed taxa, taxa with unresolved taxonomy, and excluded species are also included. The
main manuscript includes links to supplementary materials, including a reference list for Lepidoptera of North America north of Mexico, and a filterable spreadsheet with information on taxonomy, synonymy, size ranges of species, distribution by state, province, and country with references, and host-plant Family and Genus associations with references.
Phenology
One flight; mostly July (Scott 1986). July to early August (Glassberg 2001); July in British Columbia and Alberta (Guppy and Shepard 2001).
Diagnostic Characteristics
All black or dark-brown wing surfaces are distinctive.
Species Range
Montana Range
Range Descriptions
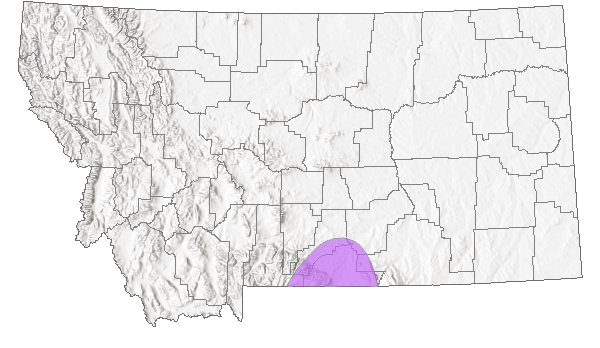
 Native
Native
Range Comments
Occurs in isolated populations in the Rocky Mountains of British Columbia and Alberta, southern Montana and adjacent northwestern Wyoming, northeastern Utah, and Colorado to northern New Mexico (Ferris and Brown 1981; Scott 1986; Opler and Wright 1999; Glassberg 2001; Guppy and Shepard 2001); above treeline to at least 4200 m elevation in Colorado (Brown 1957; Scott and Scott 1978). In Montana prior to 2011, reported only from Carbon County (Kohler 1980; Stanford and Opler 1993), more recently (August 2011) from Park County (FLMNH Lepidipterists' Society database). Rare to uncommon (Glassberg 2001).
Shropshire and Tallamy (2025) provide a link to a supplemental filterable spreadsheet with information on distribution by state, province, and country with references for all Lepidoptera species of North America, north of Mexico.
Migration
Non-migratory.
Habitat
Above treeline in alpine rockslides, boulderfields, ridgetops, usually near vegetation (Scott 1986; Guppy and Shepard 2001). Not described for Montana, but probably similar.
Shropshire and Tallamy (2025) provide a link to a supplemental filterable spreadsheet with information on host-plant Family and Genus associations with references for all Lepidoptera species of North America, north of Mexico.
National Vegetation Classification System Groups Associated with this Species
Alpine
Alpine - Vegetated
Grassland
Montane - Subalpine Grassland
Wetland and Riparian
Alpine Riparian and Wetland
Peatland
Wet Meadow and Marsh
Food Habits
Larval food plants poorly known but probably include Carex (eaten in captivity), Festuca, Juncus, Luzula and Poa (eaten in captivity) (Scott 1986, 1992, 2006). Adults feed on flower nectar, including Dryas, Erigeron, Haplopappus, and Silene (Scott 2014).
Reproductive Characteristics
Limited information. Females lay eggs singly under the edges of rocks and boulders near probable host plants; eggs infrequently deposited directly on Carex. Larvae eat leaves, build no nests, and hibernate initially as L2 or L3 instars, possibly requiring two overwinterings to pupate into adults (Scott and Scott 1978; Scott 1986, 1992, 2006; Guppy and Shepard 2001). Males patrol throughout the day over rockslides, especially depressions in rockslides (Scott 1975b, 1982, 1986).
Stewardship Responsibility
References
- Literature Cited AboveLegend:
 View Online Publication
View Online Publication Brown, F.M. 1957. Colorado Butterflies. Proceedings; Numbers Three through Seven. Denver Museum of Natural History, Denver, Co.
Brown, F.M. 1957. Colorado Butterflies. Proceedings; Numbers Three through Seven. Denver Museum of Natural History, Denver, Co. Ferris, C.D. and F.M. Brown (eds). 1981. Butterflies of the Rocky Mountains. Univ. of Oklahoma Press. Norman. 442 pp.
Ferris, C.D. and F.M. Brown (eds). 1981. Butterflies of the Rocky Mountains. Univ. of Oklahoma Press. Norman. 442 pp. Glassberg, J. 2001. Butterflies through Binoculars: A Field Guide to the Butterflies of Western North America. Oxford University Press.
Glassberg, J. 2001. Butterflies through Binoculars: A Field Guide to the Butterflies of Western North America. Oxford University Press. Guppy, C.S. and J.H. Shepard. 2001. Butterflies of British Columbia: including western Alberta, southern Yukon, the Alaska Panhandle, Washington, northern Oregon, northern Idaho, northwestern Montana. UBC Press (Vancouver, BC) and Royal British Columbia Museum (Victoria, BC). 414 pp.
Guppy, C.S. and J.H. Shepard. 2001. Butterflies of British Columbia: including western Alberta, southern Yukon, the Alaska Panhandle, Washington, northern Oregon, northern Idaho, northwestern Montana. UBC Press (Vancouver, BC) and Royal British Columbia Museum (Victoria, BC). 414 pp. Kohler, S. 1980. Checklist of Montana Butterflies (Rhopalocera). Journal of the Lepidopterists' Society 34(1): 1-19.
Kohler, S. 1980. Checklist of Montana Butterflies (Rhopalocera). Journal of the Lepidopterists' Society 34(1): 1-19. Opler, P.A. and A.B. Wright. 1999. A field guide to western butterflies. Second edition. Peterson Field Guides. Houghton Mifflin Company, Boston, Massachusetts. 540 pp.
Opler, P.A. and A.B. Wright. 1999. A field guide to western butterflies. Second edition. Peterson Field Guides. Houghton Mifflin Company, Boston, Massachusetts. 540 pp. Scott, J.A. 1975b. Mate-locating behavior of western North American butterflies. Journal of Research on the Lepidoptera 14:1-40.
Scott, J.A. 1975b. Mate-locating behavior of western North American butterflies. Journal of Research on the Lepidoptera 14:1-40. Scott, J.A. 1982. Mate-locating behavior of western North American butterflies. II. New observations and morphological adaptations. Journal of Research on the Lepidoptera 21(3): 177-187.
Scott, J.A. 1982. Mate-locating behavior of western North American butterflies. II. New observations and morphological adaptations. Journal of Research on the Lepidoptera 21(3): 177-187. Scott, J.A. 1986. The butterflies of North America: a natural history and field guide. Stanford University Press, Stanford, California.
Scott, J.A. 1986. The butterflies of North America: a natural history and field guide. Stanford University Press, Stanford, California. Scott, J.A. 1992. Hostplant records for butterflies and skippers (mostly from Colorado) 1959-1992, with new life histories and notes on oviposition, immatures, and ecology. Papilio new series #6. 185 p.
Scott, J.A. 1992. Hostplant records for butterflies and skippers (mostly from Colorado) 1959-1992, with new life histories and notes on oviposition, immatures, and ecology. Papilio new series #6. 185 p. Scott, J.A. 2006. Butterfly hostplant records, 1992-2005, with a treatise on the evolution of Erynnis, and a note on new terminology for mate-locating behavior. Papilio new series #14. 74 p.
Scott, J.A. 2006. Butterfly hostplant records, 1992-2005, with a treatise on the evolution of Erynnis, and a note on new terminology for mate-locating behavior. Papilio new series #14. 74 p. Scott, J.A. 2014. Lepidoptera of North America 13. Flower visitation by Colorado butterflies (40,615 records) with a review of the literature on pollination of Colorado plants and butterfly attraction (Lepidoptera: Hersperioidea and Papilionoidea). Contributions of the C.P. Gillette Museum of Arthopod Diversity. Fort Collins, CO: Colorado State University. 190 p.
Scott, J.A. 2014. Lepidoptera of North America 13. Flower visitation by Colorado butterflies (40,615 records) with a review of the literature on pollination of Colorado plants and butterfly attraction (Lepidoptera: Hersperioidea and Papilionoidea). Contributions of the C.P. Gillette Museum of Arthopod Diversity. Fort Collins, CO: Colorado State University. 190 p. Scott, J.A. and G.R. Scott. 1978. Ecology and distribution of the butterflies of southern central Colorado. Journal of Research on the Lepidoptera 17(2): 73-128.
Scott, J.A. and G.R. Scott. 1978. Ecology and distribution of the butterflies of southern central Colorado. Journal of Research on the Lepidoptera 17(2): 73-128. Stanford, R.E. and P.A. Opler. 1993. Atlas of western USA butterflies: including adjacent parts of Canada and Mexico. Unpubl. Report. Denver and Fort Collins, Colorado 275 pp.
Stanford, R.E. and P.A. Opler. 1993. Atlas of western USA butterflies: including adjacent parts of Canada and Mexico. Unpubl. Report. Denver and Fort Collins, Colorado 275 pp.
- Additional ReferencesLegend:
 View Online Publication
View Online Publication
Do you know of a citation we're missing? Allen, T.J., J.P. Brock, and J. Glassberg. 2005. Caterpillars in the field and garden: a field guide to the butterfly caterpillars of North America. Oxford University Press.
Allen, T.J., J.P. Brock, and J. Glassberg. 2005. Caterpillars in the field and garden: a field guide to the butterfly caterpillars of North America. Oxford University Press. Brock, J.P. and K. Kaufman. 2003. Kaufman Field Guide to Butterflies of North America. Houghton Mifflin Company, New York, NY 284 pp.
Brock, J.P. and K. Kaufman. 2003. Kaufman Field Guide to Butterflies of North America. Houghton Mifflin Company, New York, NY 284 pp. Forister, M.L., E.M. Grames, C.A. Halsch, K.J. Burls, C.F. Carroll, K.L. Bell, J.P. Jahner, et al. 2023. Assessing risk for butterflies in the context of climate change, demographic uncertainty, and heterogeneous data sources. Ecological Monographs 93(3):e1584. https://doi.org/10.1002/ecm.1584
Forister, M.L., E.M. Grames, C.A. Halsch, K.J. Burls, C.F. Carroll, K.L. Bell, J.P. Jahner, et al. 2023. Assessing risk for butterflies in the context of climate change, demographic uncertainty, and heterogeneous data sources. Ecological Monographs 93(3):e1584. https://doi.org/10.1002/ecm.1584 Layberry, R.A., P.W. Hall, and J.D. LaFontaine. 1998. The Butterflies of Canada. University of Toronto Press. 280 pp. + color plates.
Layberry, R.A., P.W. Hall, and J.D. LaFontaine. 1998. The Butterflies of Canada. University of Toronto Press. 280 pp. + color plates. Shropshire, K.J. and D.W. Tallamy. 2025. Lepidoptera of North America, north of Mexico: an annotated list containing geographic ranges and host-plant records. Zookeys.1261:101-113.
Shropshire, K.J. and D.W. Tallamy. 2025. Lepidoptera of North America, north of Mexico: an annotated list containing geographic ranges and host-plant records. Zookeys.1261:101-113. Simanonok, M.P., and L.A. Burkle. 2014. Partitioning interaction turnover among alpine pollination networks: Spatial temporal, and environmental patterns. Ecosphere 5(11):149.
Simanonok, M.P., and L.A. Burkle. 2014. Partitioning interaction turnover among alpine pollination networks: Spatial temporal, and environmental patterns. Ecosphere 5(11):149.
- Web Search Engines for Articles on "Magdalena Alpine"
- Additional Sources of Information Related to "Insects"





