View in other NatureServe Network Field Guides
NatureServe
Montana
Utah
Wyoming
Idaho
Wisconsin
British Columbia
South Carolina
Yukon
California
New York
Pacific Fritillary - Boloria epithore
General Description
[From Ferris and Brown 1981; Scott 1986; Opler and Wright 1999; Glassberg 2001; Pyle 2002] Forewing 2.1-2.4 cm. Tip of forewing and hindwing evenly rounded. Uppersurface bright orange with black markings large on basal half of wing, small on outer half, hindwing without black border. Undersurface of hindwing mottled light purplish-brown with postbasal spot row yellow. Above and below on both wings, submarginal row of slightly darkened crescents pointing outward.
Shropshire and Tallamy (2025) provide a list, with synonymies, of 13,055 described native, exotic, and occasional straying Lepidoptera species of North America, north of Mexico; known but undescribed taxa, taxa with unresolved taxonomy, and excluded species are also included. The
main manuscript includes links to supplementary materials, including a reference list for Lepidoptera of North America north of Mexico, and a filterable spreadsheet with information on taxonomy, synonymy, size ranges of species, distribution by state, province, and country with references, and host-plant Family and Genus associations with references.
Phenology
One flight; mid-May to June in the Coast ranges, June to July inland, July to mid-August at higher elevations (Scott 1986). Late May to August (Glassberg 2001). Early May to mid-August in the Oregon Cascades, mid-June to late August in the Wallowa Mountains (Warren 2005); late March to late September in Oregon and Washington (Pyle 2002); early May to early September in British Columbia (Guppy and Shepard 2001).
Diagnostic Characteristics
Best determined by submarginal row of slightly darkened crescents pointing outward above and below on both wings (pointing inward for most other Boloria).
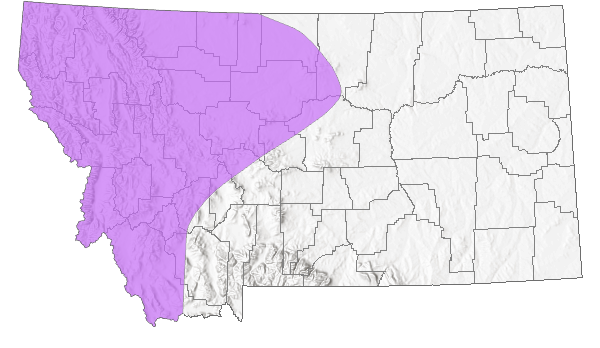
Species Range
Montana Range
Range Descriptions
 Native
Native
Range Comments
Central British Columbia and southwestern Alberta south in the Cascades and Sierra Nevada to central Sierra Nevada, in the Rocky Mountains to central Idaho and western Montana; isolated population in southwestern Yukon (Scott 1986; Opler and Wright 1999; Glassberg 2001; Pyle 2002); to 2440 m elevation in Oregon (Warren 2005), 2170 m elevation in Washington and interior British Columbia (Guppy and Shepard 2001; Pyle 2002). In Montana, reported from all counties west of the continental divide, east to Hill and Blaine counties along the Canadian border (Kohler 1980; Stanford and Opler 1993). Common to abundant (Glassberg 2001).
Shropshire and Tallamy (2025) provide link to a supplemental filterable spreadsheet with information on distribution by state, province, and country with references for all Lepidoptera species of North America, north of Mexico.
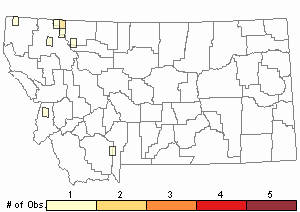
Observations in Montana Natural Heritage Program Database
Number of Observations: 38
(Click on the following maps and charts to see full sized version)
Map Help and Descriptions
Relative Density
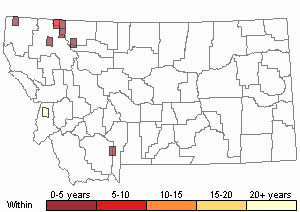
Recency
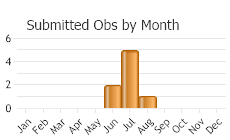
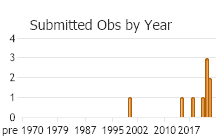
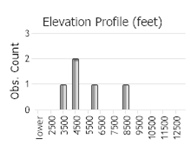 (Observations spanning multiple months or years are excluded from time charts)
(Observations spanning multiple months or years are excluded from time charts)
Migration
Non-migratory.
Habitat
Openings in moist conifer forests, wet meadows, open slopes and hilltops, streamsides, logging roads, rural gardens (Scott 1986; Opler and Wright 1999; Pyle 2002; Warren 2005). In Glacier National Park, Montana reported from montane mesic meadows and above treeline in alpine terrain (Debinski 1993).
Shropshire and Tallamy (2025) provide a link to a supplemental filterable spreadsheet with information on host-plant Family and Genus associations with references for all Lepidoptera species of North America, north of Mexico.
National Vegetation Classification System Groups Associated with this Species
Grassland
Montane - Subalpine Grassland
Wetland and Riparian
Alkaline - Saline Wetlands
Alpine Riparian and Wetland
Peatland
Riparian and Wetland Forest
Riparian Shrubland
Wet Meadow and Marsh
Food Habits
Larval food plants include several species of Viola (Scott 1986; Warren 2005; James and Nunnallee 2011). Adults feed on flower nectar, including Anaphalis, Cirsium, Fragaria, Potentilla, Rubus, and Symphyotrichum (Pyle 2002; James and Nunnallee 2011).
Reproductive Characteristics
Females lay eggs haphazardly and singly on twigs, grass stems, and other inert surfaces, but rarely on host plant (Scott 1986; James and Nunnallee 2011). Eggs hatch in about 4-7 days, develp rapidly (17-18 days) from L1 instar to L4 instar, L4 instars feeds a few days then departs host plant to seek shelter in dead leaves; diapauses (overwinters) as L4 instar. Following termination of diapause in spring L4 develops to L5 instar in 7-24 days (depending on temperature), pupates about 9-12 days later. Larvae not gregarious, build no nest, nocturnal, rest on undersides of host plant leaves (Scott 1986; James and Nunnallee 2011). Males patrol throughout the day in moist meadows and woods in search of females (Scott 1975b, 1986; James and Nunnallee 2011).
Stewardship Responsibility
References
- Literature Cited AboveLegend:
 View Online Publication
View Online Publication Debinski, D. 1993. Butterflies of Glacier National Park, Montana. Occasional Papers of the Museum of Natural History, the University of Kansas, Lawrence, Kansas. No. 159: 1-13.
Debinski, D. 1993. Butterflies of Glacier National Park, Montana. Occasional Papers of the Museum of Natural History, the University of Kansas, Lawrence, Kansas. No. 159: 1-13. Ferris, C.D. and F.M. Brown (eds). 1981. Butterflies of the Rocky Mountains. Univ. of Oklahoma Press. Norman. 442 pp.
Ferris, C.D. and F.M. Brown (eds). 1981. Butterflies of the Rocky Mountains. Univ. of Oklahoma Press. Norman. 442 pp. Glassberg, J. 2001. Butterflies through Binoculars: A Field Guide to the Butterflies of Western North America. Oxford University Press.
Glassberg, J. 2001. Butterflies through Binoculars: A Field Guide to the Butterflies of Western North America. Oxford University Press. Guppy, C.S. and J.H. Shepard. 2001. Butterflies of British Columbia: including western Alberta, southern Yukon, the Alaska Panhandle, Washington, northern Oregon, northern Idaho, northwestern Montana. UBC Press (Vancouver, BC) and Royal British Columbia Museum (Victoria, BC). 414 pp.
Guppy, C.S. and J.H. Shepard. 2001. Butterflies of British Columbia: including western Alberta, southern Yukon, the Alaska Panhandle, Washington, northern Oregon, northern Idaho, northwestern Montana. UBC Press (Vancouver, BC) and Royal British Columbia Museum (Victoria, BC). 414 pp. James, D.G. and D. Nunnallee. 2011. Life histories of Cascadia butterflies. Corvallis, OR: Oregon State University Press. 447 p.
James, D.G. and D. Nunnallee. 2011. Life histories of Cascadia butterflies. Corvallis, OR: Oregon State University Press. 447 p. Kohler, S. 1980. Checklist of Montana Butterflies (Rhopalocera). Journal of the Lepidopterists' Society 34(1): 1-19.
Kohler, S. 1980. Checklist of Montana Butterflies (Rhopalocera). Journal of the Lepidopterists' Society 34(1): 1-19. Opler, P.A. and A.B. Wright. 1999. A field guide to western butterflies. Second edition. Peterson Field Guides. Houghton Mifflin Company, Boston, Massachusetts. 540 pp.
Opler, P.A. and A.B. Wright. 1999. A field guide to western butterflies. Second edition. Peterson Field Guides. Houghton Mifflin Company, Boston, Massachusetts. 540 pp. Opler, P.A., K. Lotts, and T. Naberhaus, coordinators. 2010. Butterflies and moths of North America. Big Sky Institute, Bozeman, MT. Available at: www.butterfliesandmoths.org (Accessed 15 June 2015).
Opler, P.A., K. Lotts, and T. Naberhaus, coordinators. 2010. Butterflies and moths of North America. Big Sky Institute, Bozeman, MT. Available at: www.butterfliesandmoths.org (Accessed 15 June 2015). Pyle, R.M. 2002. The butterflies of Cascadia: a field guide to all the species of Washington, Oregon, and surrounding territories. Seattle Audubon Society, Seattle, Washington. 420 pp.
Pyle, R.M. 2002. The butterflies of Cascadia: a field guide to all the species of Washington, Oregon, and surrounding territories. Seattle Audubon Society, Seattle, Washington. 420 pp. Scott, J.A. 1975b. Mate-locating behavior of western North American butterflies. Journal of Research on the Lepidoptera 14:1-40.
Scott, J.A. 1975b. Mate-locating behavior of western North American butterflies. Journal of Research on the Lepidoptera 14:1-40. Scott, J.A. 1986. The butterflies of North America: a natural history and field guide. Stanford University Press, Stanford, California.
Scott, J.A. 1986. The butterflies of North America: a natural history and field guide. Stanford University Press, Stanford, California. Stanford, R.E. and P.A. Opler. 1993. Atlas of western USA butterflies: including adjacent parts of Canada and Mexico. Unpubl. Report. Denver and Fort Collins, Colorado 275 pp.
Stanford, R.E. and P.A. Opler. 1993. Atlas of western USA butterflies: including adjacent parts of Canada and Mexico. Unpubl. Report. Denver and Fort Collins, Colorado 275 pp. Warren, A.D. 2005. Lepidoptera of North America 6: Butterflies of Oregon, their taxonomy, distribution, and biology. Contributions of the C. P. Gillette Museum of Arthropod Diversity, Colorado State University. Fort Collins, Colorado. 406 pp.
Warren, A.D. 2005. Lepidoptera of North America 6: Butterflies of Oregon, their taxonomy, distribution, and biology. Contributions of the C. P. Gillette Museum of Arthropod Diversity, Colorado State University. Fort Collins, Colorado. 406 pp.
- Additional ReferencesLegend:
 View Online Publication
View Online Publication
Do you know of a citation we're missing? Allen, T.J., J.P. Brock, and J. Glassberg. 2005. Caterpillars in the field and garden: a field guide to the butterfly caterpillars of North America. Oxford University Press.
Allen, T.J., J.P. Brock, and J. Glassberg. 2005. Caterpillars in the field and garden: a field guide to the butterfly caterpillars of North America. Oxford University Press. Brock, J.P. and K. Kaufman. 2003. Kaufman Field Guide to Butterflies of North America. Houghton Mifflin Company, New York, NY 284 pp.
Brock, J.P. and K. Kaufman. 2003. Kaufman Field Guide to Butterflies of North America. Houghton Mifflin Company, New York, NY 284 pp. Forister, M.L., E.M. Grames, C.A. Halsch, K.J. Burls, C.F. Carroll, K.L. Bell, J.P. Jahner, et al. 2023. Assessing risk for butterflies in the context of climate change, demographic uncertainty, and heterogeneous data sources. Ecological Monographs 93(3):e1584. https://doi.org/10.1002/ecm.1584
Forister, M.L., E.M. Grames, C.A. Halsch, K.J. Burls, C.F. Carroll, K.L. Bell, J.P. Jahner, et al. 2023. Assessing risk for butterflies in the context of climate change, demographic uncertainty, and heterogeneous data sources. Ecological Monographs 93(3):e1584. https://doi.org/10.1002/ecm.1584 Layberry, R.A., P.W. Hall, and J.D. LaFontaine. 1998. The Butterflies of Canada. University of Toronto Press. 280 pp. + color plates.
Layberry, R.A., P.W. Hall, and J.D. LaFontaine. 1998. The Butterflies of Canada. University of Toronto Press. 280 pp. + color plates. Shropshire, K.J. and D.W. Tallamy. 2025. Lepidoptera of North America, north of Mexico: an annotated list containing geographic ranges and host-plant records. Zookeys.1261:101-113.
Shropshire, K.J. and D.W. Tallamy. 2025. Lepidoptera of North America, north of Mexico: an annotated list containing geographic ranges and host-plant records. Zookeys.1261:101-113.
- Web Search Engines for Articles on "Pacific Fritillary"
- Additional Sources of Information Related to "Insects"





