View in other NatureServe Network Field Guides
NatureServe
Montana
Utah
Wyoming
Idaho
Wisconsin
British Columbia
South Carolina
Yukon
California
New York
Richardson's Ground Squirrel - Urocitellus richardsonii
Native Species
Global Rank:
G5
State Rank:
S5
(see State Rank Reason below)
Agency Status
USFWS:
USFS:
BLM:
State Rank Reason (see State Rank above)
Species is widely distributed across central and eastern Montana. It faces no known threats and readily uses human-modified habitats.
General Description
The Richardson's Ground Squirrel is a medium-sized ground squirrel of rather uniform coloration. It is buffy yellow to grayish in color. The tail is about one-fourth of the total body length and is blackish to buff with whitish hairs on the outer edges and end. Adults are 7 to 9 inches long and weigh 11 to 18 ounces.
Species Range
Montana Range
Range Descriptions
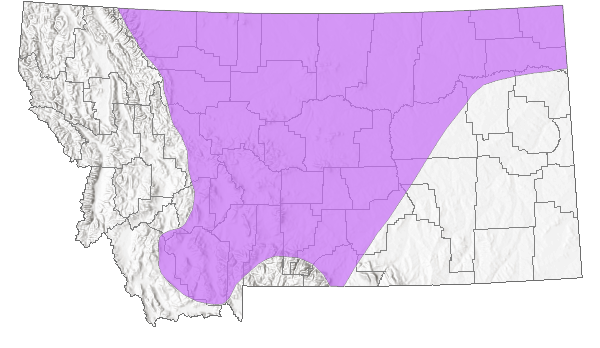
 Native
Native
Western Hemisphere Range

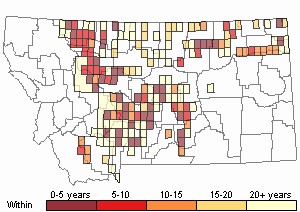
Observations in Montana Natural Heritage Program Database
Number of Observations: 740
(Click on the following maps and charts to see full sized version)
Map Help and Descriptions
Relative Density

Recency
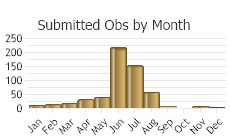
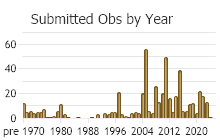
 (Observations spanning multiple months or years are excluded from time charts)
(Observations spanning multiple months or years are excluded from time charts)
Migration
Non-migratory. May exhibit emigration/dispersal movements.
Habitat
Occupies open well-drained land, prairies, and pastures. Can occur on arid shrub-steppe. Less well-adapted to arid shrub-steppe than is S. elegans.
National Vegetation Classification System Groups Associated with this Species
Forest and Woodland
Low Elevation - Xeric Forest and Woodland
Montane - Subalpine Forest and Woodland
Shrubland
Arid - Saline Shrubland
Foothills - Montane Shrubland
Sagebrush Shrubland
Grassland
Lowland - Prairie Grassland
Sparse and Barren
Sparse and Barren
Wetland and Riparian
Alkaline - Saline Wetlands
Peatland
Riparian and Wetland Forest
Riparian Shrubland
Wet Meadow and Marsh
Recently Disturbed or Modified
Introduced Vegetation
Human Land Use
Agriculture
Developed
Food Habits
Primarily herbivorous. Eats leaves, flowers, and seeds of grasses and forbs. Domesticated cereals when available. Stores food in burrow. Will use insects and carrion.
Ecology
Populations of Richardson's Ground Squirrel and Columbian Ground Squirrel are geographically separate from one another from Canada border south to Madison and Beaverhead Counties. Richardson's Ground Squirrel and Columbian Ground Squirrel share the same general distribution and even co-occur at the same locations along with Uinta Ground Squirrel and Wyoming Ground Squirrel in Beaverhead and Madison Counties and possibly in Jefferson and Broadwater Counties.
Reproductive Characteristics
One litter annually, beginning as yearlings. Females typically mate 3 to 5 days after emergence. Most recent studies show gestation to be 22.5 days. Mean litter size at emergence from burrow is minimum 4.9, maximum 8.3.
Stewardship Responsibility
References
- Additional ReferencesLegend:
 View Online Publication
View Online Publication
Do you know of a citation we're missing? Bramblett, R.G., and A.V. Zale. 2002. Montana Prairie Riparian Native Species Report. Montana Cooperative Fishery Research Unit, Montana State University - Bozeman.
Bramblett, R.G., and A.V. Zale. 2002. Montana Prairie Riparian Native Species Report. Montana Cooperative Fishery Research Unit, Montana State University - Bozeman. Buck, C.L. 1939. Pattern correlation of mammalian teeth as a means of identification. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, Montana: Montana State University. 55 p.
Buck, C.L. 1939. Pattern correlation of mammalian teeth as a means of identification. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, Montana: Montana State University. 55 p. Carlsen, T. and R. Northrup. 1992. Canyon Ferry Wildlife Management Area Final Draft Management Plan. March 1992.
Carlsen, T. and R. Northrup. 1992. Canyon Ferry Wildlife Management Area Final Draft Management Plan. March 1992. Clark, T.W. 1970. Richardson's ground squirrel (Spermophilus richardsonii) in the Laramie basin, Wyoming. Great Basin Naturalist 30: 55-70.
Clark, T.W. 1970. Richardson's ground squirrel (Spermophilus richardsonii) in the Laramie basin, Wyoming. Great Basin Naturalist 30: 55-70. Confluence Consulting Inc. 2010. Montana Department of Transportation Wetland Mitigation Monitoring Reports (various sites). MDT Helena, MT.
Confluence Consulting Inc. 2010. Montana Department of Transportation Wetland Mitigation Monitoring Reports (various sites). MDT Helena, MT. Confluence Consulting Inc. 2011. Montana Department of Transportation Wetland Mitigation Monitoring Reports (various sites). MDT Helena, MT.
Confluence Consulting Inc. 2011. Montana Department of Transportation Wetland Mitigation Monitoring Reports (various sites). MDT Helena, MT. Confluence Consulting Inc. 2012. Montana Department of Transportation Wetland Mitigation Monitoring Reports (various sites). MDT Helena, MT.
Confluence Consulting Inc. 2012. Montana Department of Transportation Wetland Mitigation Monitoring Reports (various sites). MDT Helena, MT. Elliott, Joe C. and Hydrometrics, Inc., Helena, MT., 1994, Supplement to wildlife baseline investigation life-of-mine expansion plan: Regal Mine, Barretts Minerals, Inc., Madison County, Montana. August 2000. In Life-of Mine Expansion Plan: Barretts Minerals, Inc., Regal Mine, Madison County, Montana. Vol. 2. App. C: Baseline Wildlife Reconnaissance. December 1999.
Elliott, Joe C. and Hydrometrics, Inc., Helena, MT., 1994, Supplement to wildlife baseline investigation life-of-mine expansion plan: Regal Mine, Barretts Minerals, Inc., Madison County, Montana. August 2000. In Life-of Mine Expansion Plan: Barretts Minerals, Inc., Regal Mine, Madison County, Montana. Vol. 2. App. C: Baseline Wildlife Reconnaissance. December 1999. Eng, R.L. 1976. Wildlife Baseline Study [for West Fork of the Stillwater and Picket Pin drainages]
Eng, R.L. 1976. Wildlife Baseline Study [for West Fork of the Stillwater and Picket Pin drainages] Fagerstone, K.A. 1987. Comparison of Vocalizations between and within Spermophilus Elegans Elegans and S. Richardsonii. Journal of Mammalogy. 68(4): 853-857, 1987.
Fagerstone, K.A. 1987. Comparison of Vocalizations between and within Spermophilus Elegans Elegans and S. Richardsonii. Journal of Mammalogy. 68(4): 853-857, 1987. Feigley, H.P. 1981. Studies on native small mammals as intermediate hosts of Echinococcus multilocularis. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, Montana: Montana State University. 50 p.
Feigley, H.P. 1981. Studies on native small mammals as intermediate hosts of Echinococcus multilocularis. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, Montana: Montana State University. 50 p. Foresman, K.R. 2001. The wild mammals of Montana. American Society of Mammalogists, Special Publication Number 12. Lawrence, KS. 278 pp.
Foresman, K.R. 2001. The wild mammals of Montana. American Society of Mammalogists, Special Publication Number 12. Lawrence, KS. 278 pp. Foresman, K.R. 2012. Mammals of Montana. Second edition. Mountain Press Publishing, Missoula, Montana. 429 pp.
Foresman, K.R. 2012. Mammals of Montana. Second edition. Mountain Press Publishing, Missoula, Montana. 429 pp. Graham, Dean, and Craig Swick., 1977, A Field evaluation of the cyclone seeder for reducing Richardson ground squirrel populations causing damage in central Montana . August 1977.
Graham, Dean, and Craig Swick., 1977, A Field evaluation of the cyclone seeder for reducing Richardson ground squirrel populations causing damage in central Montana . August 1977. Haight, C.P. 1937. Some observations on the predator-prey complex in the Gallatin Valley. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, Montana: Montana State University. 58 p.
Haight, C.P. 1937. Some observations on the predator-prey complex in the Gallatin Valley. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, Montana: Montana State University. 58 p. Hanauska-Brown, L., B.A. Maxell, A. Petersen, and S. Story. 2014. Diversity Monitoring in Montana 2008-2010 Final Report. Montana Fish, Wildlife & Parks. Helena, MT. 78 pp.
Hanauska-Brown, L., B.A. Maxell, A. Petersen, and S. Story. 2014. Diversity Monitoring in Montana 2008-2010 Final Report. Montana Fish, Wildlife & Parks. Helena, MT. 78 pp. Hendricks, P., S. Lenard, D.M. Stagliano, and B.A. Maxell. 2013. Baseline nongame wildlife surveys on the Fort Peck Indian Reservation. Report to the Assiniboine and Sioux Tribes of the Fort Peck Indian Reservation. Montana Natural Heritage Program, Helena, MT. 83 p.
Hendricks, P., S. Lenard, D.M. Stagliano, and B.A. Maxell. 2013. Baseline nongame wildlife surveys on the Fort Peck Indian Reservation. Report to the Assiniboine and Sioux Tribes of the Fort Peck Indian Reservation. Montana Natural Heritage Program, Helena, MT. 83 p. Hoffmann, R.S. and D.L. Pattie. 1968. A guide to Montana mammals: identification, habitat, distribution, and abundance. Missoula, MT: University of Montana. 133 p.
Hoffmann, R.S. and D.L. Pattie. 1968. A guide to Montana mammals: identification, habitat, distribution, and abundance. Missoula, MT: University of Montana. 133 p. Joslin, Gayle, and Heidi B. Youmans. 1999. Effects of recreation on Rocky Mountain wildlife: a review for Montana. [Montana]: Montana Chapter of the Wildlife Society.
Joslin, Gayle, and Heidi B. Youmans. 1999. Effects of recreation on Rocky Mountain wildlife: a review for Montana. [Montana]: Montana Chapter of the Wildlife Society. Koeppl, J.W. and R.S. Hoffman. 1981. Comparative postnatal growth of four ground squirrel species. Journal of Mammalogy. 62(1): 41-57.
Koeppl, J.W. and R.S. Hoffman. 1981. Comparative postnatal growth of four ground squirrel species. Journal of Mammalogy. 62(1): 41-57. Koeppl, J.W., R.S. Hoffmann and C.F. Nadler. 1978. Pattern analysis of acoustical behavior in four species of ground squirrels. Journal of Mammalogy. 59(4): 677-696.
Koeppl, J.W., R.S. Hoffmann and C.F. Nadler. 1978. Pattern analysis of acoustical behavior in four species of ground squirrels. Journal of Mammalogy. 59(4): 677-696. Land & Water Consulting, Inc., Missoula, MT., 2002, Montana Dept. of Transportation Wetland Mitigation Monitoring Report, Year 2001: Johnson - Valier, Valier, Montana. Proj. No. 130091.018. July 2002. In 2001 Wetland Mitigation Monitoring Reports, Vol. I.
Land & Water Consulting, Inc., Missoula, MT., 2002, Montana Dept. of Transportation Wetland Mitigation Monitoring Report, Year 2001: Johnson - Valier, Valier, Montana. Proj. No. 130091.018. July 2002. In 2001 Wetland Mitigation Monitoring Reports, Vol. I. Land & Water Consulting, Inc., Missoula, MT., 2002, Montana Dept. of Transportation Wetland Mitigation Monitoring Report, Year 2001: Ringling - Galt, Ringling, Montana. Proj. No. 130091.015. July 2002. In 2001 Wetland Mitigation Monitoring Reports, Vol. II.
Land & Water Consulting, Inc., Missoula, MT., 2002, Montana Dept. of Transportation Wetland Mitigation Monitoring Report, Year 2001: Ringling - Galt, Ringling, Montana. Proj. No. 130091.015. July 2002. In 2001 Wetland Mitigation Monitoring Reports, Vol. II. Land & Water Consulting, Inc., Missoula, MT., 2002, Montana Dept. of Transportation Wetland Mitigation Monitoring Report, Year 2002: South Fork Smith River, Ringling, Montana. Proj. No. 130091.016. February 2003. In 2002 Wetland Mitigation Monitoring Reports, Vol. II.
Land & Water Consulting, Inc., Missoula, MT., 2002, Montana Dept. of Transportation Wetland Mitigation Monitoring Report, Year 2002: South Fork Smith River, Ringling, Montana. Proj. No. 130091.016. February 2003. In 2002 Wetland Mitigation Monitoring Reports, Vol. II. Michener, Gail R. and James W. Koeppl. 1985. Spermophilus richardsonii. American Society of Mammalogists, Lawrence, KS. Mammalian Species No. 243:1-8.
Michener, Gail R. and James W. Koeppl. 1985. Spermophilus richardsonii. American Society of Mammalogists, Lawrence, KS. Mammalian Species No. 243:1-8. Montana Dept. of Agriculture, Environmental Management Division, Helena, MT. 1885? The Biology and control of the Richardson ground squirrel.
Montana Dept. of Agriculture, Environmental Management Division, Helena, MT. 1885? The Biology and control of the Richardson ground squirrel. Morrison-Maierle Env. Corp., Helena, MT., 1993, Biological assessment and wildlife reconnaissance, Holnam Cement Plant, Trident, Montana. In Application to Amend Operating Permit 00004 for Trident Quarries, Three Forks, Montana. Exhibit DD: Wildlife Reconnaisance Study. June 28, 1996.
Morrison-Maierle Env. Corp., Helena, MT., 1993, Biological assessment and wildlife reconnaissance, Holnam Cement Plant, Trident, Montana. In Application to Amend Operating Permit 00004 for Trident Quarries, Three Forks, Montana. Exhibit DD: Wildlife Reconnaisance Study. June 28, 1996. Mundinger, J.G. 1975. The influence of rest-rotation grazing management on waterfowl production on stock-water reservoirs in Phillips County, Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 100 p.
Mundinger, J.G. 1975. The influence of rest-rotation grazing management on waterfowl production on stock-water reservoirs in Phillips County, Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 100 p. Oechsli, L.M. 2000. Ex-urban development in the Rocky Mountain West: consequences for native vegetation, wildlife diversity, and land-use planning in Big Sky, Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Montana State University, Bozeman. 73 p.
Oechsli, L.M. 2000. Ex-urban development in the Rocky Mountain West: consequences for native vegetation, wildlife diversity, and land-use planning in Big Sky, Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Montana State University, Bozeman. 73 p. Reichel, J.D., D.L. Genter and E. Atkinson. 1992. Sensitive animal species in the Elkhorn and Big Belt Mountains of the Helena National Forest. Unpublished report to the Helena National Forest. Montana Natural Heritage Program, Helena. 158 p.
Reichel, J.D., D.L. Genter and E. Atkinson. 1992. Sensitive animal species in the Elkhorn and Big Belt Mountains of the Helena National Forest. Unpublished report to the Helena National Forest. Montana Natural Heritage Program, Helena. 158 p. Reid, F. 2006. Peterson Field Guide to Mammals of North America, 4th Edition. Houghton Mifflin Company: Boston and New York, 608 pp.
Reid, F. 2006. Peterson Field Guide to Mammals of North America, 4th Edition. Houghton Mifflin Company: Boston and New York, 608 pp. Sawyer, H. E. 1935. Studies on the rodents of Montana. M.A. thesis. University of Montana, Missoula. 111 pp.
Sawyer, H. E. 1935. Studies on the rodents of Montana. M.A. thesis. University of Montana, Missoula. 111 pp. Schladweiler, Philip, and John P. Weigand., 1983, Relationships of endrin and other chlorinated hydrocarbon compounds to wildlife in Montana, 1981-1982. September 1983.
Schladweiler, Philip, and John P. Weigand., 1983, Relationships of endrin and other chlorinated hydrocarbon compounds to wildlife in Montana, 1981-1982. September 1983. Scow, K.L. 1981. Ecological distribution of small mammals at Sarpy Creek, Montana, with special consideration of the Deer Mouse, Peromyscus maniculatus. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, Montana: Montana State University. 73 p.
Scow, K.L. 1981. Ecological distribution of small mammals at Sarpy Creek, Montana, with special consideration of the Deer Mouse, Peromyscus maniculatus. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, Montana: Montana State University. 73 p. Sullins, Monty, 1981, A Field comparison of 0.20, 0.35, and 0.50 percent strychnine grain baits for controlling Richardson ground squirrels. Tech. Rep. 81-3. July 1981.
Sullins, Monty, 1981, A Field comparison of 0.20, 0.35, and 0.50 percent strychnine grain baits for controlling Richardson ground squirrels. Tech. Rep. 81-3. July 1981. Sullivan, Daniel, and Monty Sullins., 1985, Acceptance of various rodenticide baits under field conditions by Columbian and Richardson Ground squirrels. Tech. Rep. 85-05. Sept. 1985.
Sullivan, Daniel, and Monty Sullins., 1985, Acceptance of various rodenticide baits under field conditions by Columbian and Richardson Ground squirrels. Tech. Rep. 85-05. Sept. 1985. Swenson, J.E. 1981. Distribution of Richardson's Ground Squirrel in eastern Montana. Prairie Naturalist. 13(1): 27-30.
Swenson, J.E. 1981. Distribution of Richardson's Ground Squirrel in eastern Montana. Prairie Naturalist. 13(1): 27-30. Urban, Larry, 2002, Biological Resources Report: Wagner Pit Wetland Restoration Site. Proj. No. STPX 56(50) CN 4645. February 23, 2002. In Wgner Pit WS#13 Upper Yellowstone, Yellowstone County. Fin. Dist. 5 AdminDist 5.
Urban, Larry, 2002, Biological Resources Report: Wagner Pit Wetland Restoration Site. Proj. No. STPX 56(50) CN 4645. February 23, 2002. In Wgner Pit WS#13 Upper Yellowstone, Yellowstone County. Fin. Dist. 5 AdminDist 5. Van Horn, R.C. 1993. Ferruginous Hawk and Prairie Falcon reproductive and behavioral responses to human activity near the Kevin Rim, Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, Montana: Montana State University. 86 p.
Van Horn, R.C. 1993. Ferruginous Hawk and Prairie Falcon reproductive and behavioral responses to human activity near the Kevin Rim, Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, Montana: Montana State University. 86 p. Western Technology & Engineering, Inc. (WESTECH)., 1991, 1991 Bull Mountains Mine No. 1 Terrestrial Wildlife Monitoring Study. In Meridian Minerals Company Bull Mountains Mine No. 1 Permit Application, Musselshell County, Montana. Vol. 7 of 14: Section 26
Western Technology & Engineering, Inc. (WESTECH)., 1991, 1991 Bull Mountains Mine No. 1 Terrestrial Wildlife Monitoring Study. In Meridian Minerals Company Bull Mountains Mine No. 1 Permit Application, Musselshell County, Montana. Vol. 7 of 14: Section 26 Zackheim, K. 1973. Exhibit H: Wildlife Study. In Ash Grove Cement Co. files.
Zackheim, K. 1973. Exhibit H: Wildlife Study. In Ash Grove Cement Co. files.
- Web Search Engines for Articles on "Richardson's Ground Squirrel"
- Additional Sources of Information Related to "Mammals"





