View in other NatureServe Network Field Guides
NatureServe
Montana
Utah
Wyoming
Idaho
Wisconsin
British Columbia
South Carolina
Yukon
California
New York
Black Crappie - Pomoxis nigromaculatus
General Description
The black crappie is more widespread across eastern Montana than the white crappie with some scattered populations into central and western Montana. As the name implies, it is darker colored than the white crappie, and has seven or eight dorsal spines instead of the five or six spines found on the white. Crappies are spring-spawning nest-builders like all the other sunfish. Crappies are fun to catch, good to eat, and can weigh up to 3 pounds although 1/2 pound fish are the rule. They are schooling fish and notorious for their love of stumps, debris piles, or other cover. Crappies are spring-spawning nest-builders like all the other sunfish.
Diagnostic Characteristics
Fish from turbid waters may be light colored.
Species Range
Montana Range
Range Descriptions
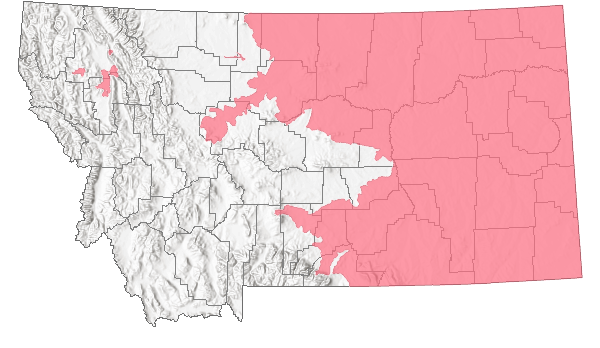
 Non-native
Non-native
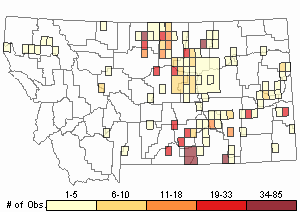
Observations in Montana Natural Heritage Program Database
Number of Observations: 994
(Click on the following maps and charts to see full sized version)
Map Help and Descriptions
Relative Density
Recency
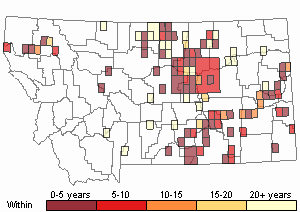
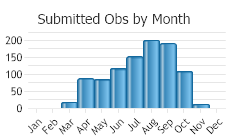
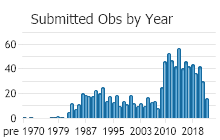
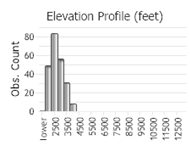 (Observations spanning multiple months or years are excluded from time charts)
(Observations spanning multiple months or years are excluded from time charts)
Habitat
Favors lakes, reservoirs, and relatively large clear streams with sandy to mucky bottoms and aquatic vegetation. Prefers slow portions of streams.
Food Habits
Aquatic insects, crustaceans, and other aquatic invert. Minnows and other small fishes are important in diet of larger individuals.
Ecology
Often found in association with white crappie where collected in southeast Montana.
Reproductive Characteristics
Sexually mature in 2-3 years. Spawns May - June when water temperatures reach 58-64 degrees F., but may spawn later in summer. Incubation: 3-5 days.
Management
The management of this and other native and non-native fish species and their habitats is outlined in Montana Fish, Wildlife and Parks' href="https://fwp.mt.gov/conservation/fisheries-management/statewide-fisheries-management" target="_blank">2023-2026 Statewide Fisheries Management Plane
Useful Links:Central and Eastern Montana Invasive Species TeamMontana Invasive Species websiteAquatic Invasive SpeciesStewardship Responsibility
References
- Literature Cited AboveLegend:
 View Online Publication
View Online Publication Lee, D.S., C.R. Gilbert, C.H. Hocutt, R.E. Jenkins, D. E. McAllister, J. R. Stauffer, Jr. 1980. Atlas of North American freshwater fishes. North Carolina State Musuem of Natural History. 867 p.
Lee, D.S., C.R. Gilbert, C.H. Hocutt, R.E. Jenkins, D. E. McAllister, J. R. Stauffer, Jr. 1980. Atlas of North American freshwater fishes. North Carolina State Musuem of Natural History. 867 p. Scott, W.B. and E.J. Crossman. 1973. Rainbow trout, Kamloops trout, Steelhead trout Salmo gairdneri Richardson. pp. 184-191. In: Freshwater fishes of Canada. Ottawa, Canada: Fisheries Research Board of Canada, Bulletin 184. 966 p.
Scott, W.B. and E.J. Crossman. 1973. Rainbow trout, Kamloops trout, Steelhead trout Salmo gairdneri Richardson. pp. 184-191. In: Freshwater fishes of Canada. Ottawa, Canada: Fisheries Research Board of Canada, Bulletin 184. 966 p.
- Additional ReferencesLegend:
 View Online Publication
View Online Publication
Do you know of a citation we're missing? Dieterman, D.J., M.P. Ruggles, M.L. Wildhaber, and D.L. Galat (eds). 1996. Population structure and habitat use of benthic fishes along the Missouri and Lower Yellowstone Rivers. 1996 Annual report of Missouri River Benthic Fish Study PD-95-5832 to U.S. Army Corps of Engineers and U.S. Bureau of Reclamation. 238 p.
Dieterman, D.J., M.P. Ruggles, M.L. Wildhaber, and D.L. Galat (eds). 1996. Population structure and habitat use of benthic fishes along the Missouri and Lower Yellowstone Rivers. 1996 Annual report of Missouri River Benthic Fish Study PD-95-5832 to U.S. Army Corps of Engineers and U.S. Bureau of Reclamation. 238 p. Duncan, M.B. 2019. Distributions, abundances, and movements of small, nongame fishes in a large Great Plains river network. Ph.D. Dissertation. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 255 p.
Duncan, M.B. 2019. Distributions, abundances, and movements of small, nongame fishes in a large Great Plains river network. Ph.D. Dissertation. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 255 p. Holton, G.D. 1981. Identification of Montana's most common game and sport fishes. Montana Outdoors May/June reprint. 8 p.
Holton, G.D. 1981. Identification of Montana's most common game and sport fishes. Montana Outdoors May/June reprint. 8 p. Joslin, Gayle, and Heidi B. Youmans. 1999. Effects of recreation on Rocky Mountain wildlife: a review for Montana. [Montana]: Montana Chapter of the Wildlife Society.
Joslin, Gayle, and Heidi B. Youmans. 1999. Effects of recreation on Rocky Mountain wildlife: a review for Montana. [Montana]: Montana Chapter of the Wildlife Society. Mullins, M.S. 1991. Biology and predator use of cisco (Coregonus artedi) in Fort Peck Reservoir, Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 68 p.
Mullins, M.S. 1991. Biology and predator use of cisco (Coregonus artedi) in Fort Peck Reservoir, Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 68 p. Penkal, R.F. 1977. Black bass populations of the Tongue River Reservoir, Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 111 p.
Penkal, R.F. 1977. Black bass populations of the Tongue River Reservoir, Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 111 p. Stash, S.W. 2001. Distribution, relative abundance, and habitat associations of Milk River fishes related to irrigation diversion dams. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 82 p.
Stash, S.W. 2001. Distribution, relative abundance, and habitat associations of Milk River fishes related to irrigation diversion dams. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 82 p. Trenka, R.J. 2000. Community structure and habitat associations of fishes of the lower Tongue and Powder Rivers. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 85 p.
Trenka, R.J. 2000. Community structure and habitat associations of fishes of the lower Tongue and Powder Rivers. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 85 p. USDI Bureau of Land Management. No date. Fishes of the Miles city, Montana BLM District. Miles City, MT: Miles City BLM District pamphlet. 12 p.
USDI Bureau of Land Management. No date. Fishes of the Miles city, Montana BLM District. Miles City, MT: Miles City BLM District pamphlet. 12 p. Venditti, D.A. 1994. Diet overlap and habitat utilization of Rainbow Trout and juvenile Walleye in Cooney Reservoir, Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, Montana: Montana State University. 90 p.
Venditti, D.A. 1994. Diet overlap and habitat utilization of Rainbow Trout and juvenile Walleye in Cooney Reservoir, Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, Montana: Montana State University. 90 p. Wollitz, R.E. 1958. The effects of certain commercial toxicants on limnology of 3 cold water ponds near Three Forks, Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 63 p.
Wollitz, R.E. 1958. The effects of certain commercial toxicants on limnology of 3 cold water ponds near Three Forks, Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 63 p. Young, B.A., T.L. Welker, M.L. Wildhaber, C.R. Berry, and D. Scarnecchia (eds). 1997. Population structure and habitat use of benthic fishes along the Missouri and Lower Yellowstone Rivers. 1997 Annual report of Missouri River Benthic Fish Study PD-95-5832 to U.S. Army Corps of Engineers and U.S. Bureau of Reclamation. 207 p.
Young, B.A., T.L. Welker, M.L. Wildhaber, C.R. Berry, and D. Scarnecchia (eds). 1997. Population structure and habitat use of benthic fishes along the Missouri and Lower Yellowstone Rivers. 1997 Annual report of Missouri River Benthic Fish Study PD-95-5832 to U.S. Army Corps of Engineers and U.S. Bureau of Reclamation. 207 p.
- Web Search Engines for Articles on "Black Crappie"
- Additional Sources of Information Related to "Fish"





