View in other NatureServe Network Field Guides
NatureServe
Montana
Utah
Wyoming
Idaho
Wisconsin
British Columbia
South Carolina
Yukon
California
New York
Lesser Yellowlegs - Tringa flavipes
General Description
A medium-sized (length tip of bill to tip of tail: 230 to 250 mm, body mass: 67 to 94g) shorebird, usually recognized by its long, bright-yellow legs, long neck, graceful stride, and distinctive "
tu tu" call. Sexes are similar in plumage and overall size, females have slightly longer wings on average. Breeding plumage: upperparts mottled gray-brown, white, and black. Underparts white with brown streaking on neck and breast and irregular, blackish barring on anterior flanks. Basic plumage: upperparts uniform gray to gray-brown with pale spots. Underparts white with fine gray streaking on neck and breast (Tibbitts and Moskoff 1999).
For a comprehensive review of the conservation status, habitat use, and ecology of this and other Montana bird species, please see
Marks et al. 2016, Birds of Montana.Species Range
Montana Range
Range Descriptions
 Migratory
Migratory
Western Hemisphere Range

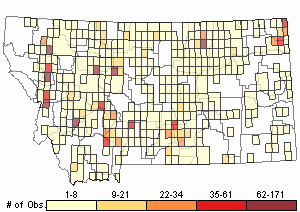
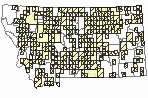
Observations in Montana Natural Heritage Program Database
Number of Observations: 2888
(Click on the following maps and charts to see full sized version)
Map Help and Descriptions
Relative Density
Recency
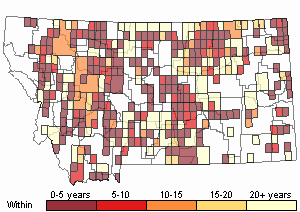
SUMMER (Feb 16 - Dec 14)
Direct Evidence of Breeding
Indirect Evidence of Breeding
No Evidence of Breeding
WINTER (Dec 15 - Feb 15)
Regularly Observed
Not Regularly Observed
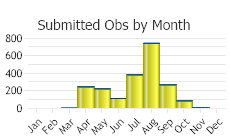
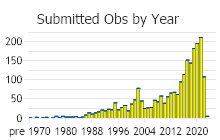
 (Observations spanning multiple months or years are excluded from time charts)
(Observations spanning multiple months or years are excluded from time charts)
Migration
In the Bozeman area, migration periods are from April 28 to May 12 and July 27 to October 10, with peaks around May 4 and September 10 (Skaar 1969).
Habitat
In summer, breeders are conspicuous residents of open woodlands, meadows, and muskegs in the boreal zone from northwestern Alaska to central Quebec. In winter, they frequent a wide variety of wetland types throughout Central and South America (Tibbitts and Moskoff 1999). A migrant. It occurs in high numbers in interior North America. Primary routes are mid-continent, mostly west of Mississippi River in spring and both along Atlantic coast and mid-continent in fall (Tibbitts and Moskoff 1999). During migration, it occurs along mudflats and shallow ponds, often with vegetated shorelines. Sometimes they occur in flooded fields (Johnsgard 1986).
National Vegetation Classification System Groups Associated with this Species
Shrubland
Sagebrush Shrubland
Grassland
Lowland - Prairie Grassland
Wetland and Riparian
Alkaline - Saline Wetlands
Alpine Riparian and Wetland
Peatland
Riparian and Wetland Forest
Riparian Shrubland
Wet Meadow and Marsh
Human Land Use
Agriculture
Developed
Food Habits
Aquatic and terrestrial invertebrates, particularly flies and beetles. Occasionally, small fish and seeds (Tibbitts and Moskoff 1999).
Reproductive Characteristics
Typically nests on dry, mossy ridges or hummocks, next to fallen branches and logs, and underneath low shrubs or small trees. Eggs are ovate pyriform in shape and smoke gray with markings in color. Clutch size usually 4. Montana not included in breeding range (Tibbits and Moskoff 1999).
Stewardship Responsibility
References
- Literature Cited AboveLegend:
 View Online Publication
View Online Publication Johnsgard, P.A. 1986. Birds of the Rocky Mountains: with particular reference to national parks in the northern Rocky Mountain region. Colorado Associated University Press, Boulder, CO.
Johnsgard, P.A. 1986. Birds of the Rocky Mountains: with particular reference to national parks in the northern Rocky Mountain region. Colorado Associated University Press, Boulder, CO. Marks, J.S., P. Hendricks, and D. Casey. 2016. Birds of Montana. Arrington, VA. Buteo Books. 659 pages.
Marks, J.S., P. Hendricks, and D. Casey. 2016. Birds of Montana. Arrington, VA. Buteo Books. 659 pages. Skaar, P.D. 1969. Birds of the Bozeman latilong: a compilation of data concerning the birds which occur between 45 and 46 N. latitude and 111 and 112 W. longitude, with current lists for Idaho, Montana, Wyoming, impinging Montana counties and Yellowstone National Park. Bozeman, MT. 132 p.
Skaar, P.D. 1969. Birds of the Bozeman latilong: a compilation of data concerning the birds which occur between 45 and 46 N. latitude and 111 and 112 W. longitude, with current lists for Idaho, Montana, Wyoming, impinging Montana counties and Yellowstone National Park. Bozeman, MT. 132 p. Tibbitts, T.L. and W. Moskoff. 1999. Lesser Yellowlegs (Tringa flavipes). Species Account Number 427. The Birds of North America Online (A. Poole, Ed.). Ithaca, NY: Cornell Laboratory of Ornithology; Retrieved 3/25/2008 from The Birds of North America Online database
Tibbitts, T.L. and W. Moskoff. 1999. Lesser Yellowlegs (Tringa flavipes). Species Account Number 427. The Birds of North America Online (A. Poole, Ed.). Ithaca, NY: Cornell Laboratory of Ornithology; Retrieved 3/25/2008 from The Birds of North America Online database
- Additional ReferencesLegend:
 View Online Publication
View Online Publication
Do you know of a citation we're missing? American Ornithologists’ Union [AOU]. 1998. Check-list of North American birds, 7th edition. American Ornithologists’ Union, Washington, D.C. 829 p.
American Ornithologists’ Union [AOU]. 1998. Check-list of North American birds, 7th edition. American Ornithologists’ Union, Washington, D.C. 829 p. Cameron, E. S. 1907. The birds of Custer and Dawson counties, Montana. Auk 24(3): 241-270.
Cameron, E. S. 1907. The birds of Custer and Dawson counties, Montana. Auk 24(3): 241-270. Confluence Consulting Inc. 2010. Montana Department of Transportation Wetland Mitigation Monitoring Reports (various sites). MDT Helena, MT.
Confluence Consulting Inc. 2010. Montana Department of Transportation Wetland Mitigation Monitoring Reports (various sites). MDT Helena, MT. Dickson, D.C. 1991. Systematic wildlife observations on the Blackfoot-Clearwater Wildlife Management Area. Montana Department of Fish, Wildlife and Parks. Missoula, MT. 14 pp. plus appendices and photographs.
Dickson, D.C. 1991. Systematic wildlife observations on the Blackfoot-Clearwater Wildlife Management Area. Montana Department of Fish, Wildlife and Parks. Missoula, MT. 14 pp. plus appendices and photographs. Dood, A.R. 1980. Terry Badlands nongame survey and inventory final report. Montana Department of Fish, Wildlife, and Parks and Bureau of Land Management, Helena, MT. 70 pp.
Dood, A.R. 1980. Terry Badlands nongame survey and inventory final report. Montana Department of Fish, Wildlife, and Parks and Bureau of Land Management, Helena, MT. 70 pp. Ehrlich, P., D. Dobkin, and D. Wheye. 1988. The birder’s handbook: a field guide to the natural history of North American birds. Simon and Schuster Inc. New York. 785 pp.
Ehrlich, P., D. Dobkin, and D. Wheye. 1988. The birder’s handbook: a field guide to the natural history of North American birds. Simon and Schuster Inc. New York. 785 pp. Gniadek, S. 1983. Southwest Glendive Wildlife Baseline Inventory. Miles City, Mont: Bureau of Land Management, Miles City District Office. 56 pp with appendices.
Gniadek, S. 1983. Southwest Glendive Wildlife Baseline Inventory. Miles City, Mont: Bureau of Land Management, Miles City District Office. 56 pp with appendices. Hayman, P., J. Marchant, and T. Prater. 1986. Shorebirds: an identification guide to the waders of the world. Houghton Mifflin Co., Boston. 412 pp.
Hayman, P., J. Marchant, and T. Prater. 1986. Shorebirds: an identification guide to the waders of the world. Houghton Mifflin Co., Boston. 412 pp. Hays, R., R.L. Eng, and C.V. Davis (preparers). 1984. A list of Montana birds. Helena, MT: MT Dept. of Fish, Wildlife & Parks.
Hays, R., R.L. Eng, and C.V. Davis (preparers). 1984. A list of Montana birds. Helena, MT: MT Dept. of Fish, Wildlife & Parks. Johnsgard, P. 1981. The Plovers, Sandpipers, and Snipes of the World. University of Nebraska Press, Lincoln, Nebraska. 493 pp.
Johnsgard, P. 1981. The Plovers, Sandpipers, and Snipes of the World. University of Nebraska Press, Lincoln, Nebraska. 493 pp. Johnsgard, P.A. 1992. Birds of the Rocky Mountains with particular reference to national parks in the northern Rocky Mountain region. Lincoln: University of Nebraska Press. xi + 504 pp.
Johnsgard, P.A. 1992. Birds of the Rocky Mountains with particular reference to national parks in the northern Rocky Mountain region. Lincoln: University of Nebraska Press. xi + 504 pp. Joslin, Gayle, and Heidi B. Youmans. 1999. Effects of recreation on Rocky Mountain wildlife: a review for Montana. [Montana]: Montana Chapter of the Wildlife Society.
Joslin, Gayle, and Heidi B. Youmans. 1999. Effects of recreation on Rocky Mountain wildlife: a review for Montana. [Montana]: Montana Chapter of the Wildlife Society. Lenard, S. 2006. Birds of Blaine County, Riparian Point Count Surveys 2005. Report to the Bureau of LandManagement, Havre Field Station, Havre, Montana. Montana Natural Heritage Program, Helena, MT. 16pp.plus appendices.
Lenard, S. 2006. Birds of Blaine County, Riparian Point Count Surveys 2005. Report to the Bureau of LandManagement, Havre Field Station, Havre, Montana. Montana Natural Heritage Program, Helena, MT. 16pp.plus appendices. Lenard, S., J. Carlson, J. Ellis, C. Jones, and C. Tilly. 2003. P. D. Skaar's Montana bird distribution, 6th edition. Montana Audubon, Helena, MT. 144 pp.
Lenard, S., J. Carlson, J. Ellis, C. Jones, and C. Tilly. 2003. P. D. Skaar's Montana bird distribution, 6th edition. Montana Audubon, Helena, MT. 144 pp. Matthews, W.L. 1981. Broadus-Pumpkin Creek baseline inventory - wildlife. Bureau of Land Management, Miles City, MT. 83 p.
Matthews, W.L. 1981. Broadus-Pumpkin Creek baseline inventory - wildlife. Bureau of Land Management, Miles City, MT. 83 p. Montana Bird Distribution Committee. 2012. P.D. Skaar's Montana bird distribution. 7th Edition. Montana Audubon, Helena, Montana. 208 pp. + foldout map.
Montana Bird Distribution Committee. 2012. P.D. Skaar's Montana bird distribution. 7th Edition. Montana Audubon, Helena, Montana. 208 pp. + foldout map. Mora, M. A. 1995. Residues and trends of organochloride pesticide and polychlorinated biphenyls in birds from Texas, 1965-88. Technical Report 14. Washington, D.C.: U.S.D.I. National Biological Service. 26 p.
Mora, M. A. 1995. Residues and trends of organochloride pesticide and polychlorinated biphenyls in birds from Texas, 1965-88. Technical Report 14. Washington, D.C.: U.S.D.I. National Biological Service. 26 p. MT Fish, Wildlife & Parks. No date. Blackfoot-Clearwater Wildlife Management Area checklist.
MT Fish, Wildlife & Parks. No date. Blackfoot-Clearwater Wildlife Management Area checklist. Oechsli, L.M. 2000. Ex-urban development in the Rocky Mountain West: consequences for native vegetation, wildlife diversity, and land-use planning in Big Sky, Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Montana State University, Bozeman. 73 p.
Oechsli, L.M. 2000. Ex-urban development in the Rocky Mountain West: consequences for native vegetation, wildlife diversity, and land-use planning in Big Sky, Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Montana State University, Bozeman. 73 p. Powder River Eagle Studies, Inc., Gillette, WY., 2002, Spring Creek Mine 2001 Wildlife Monitoring. March 2002
Powder River Eagle Studies, Inc., Gillette, WY., 2002, Spring Creek Mine 2001 Wildlife Monitoring. March 2002 Rundquist, V.M. 1973. Avian ecology on stock ponds in two vegetational types in north-central Montana. Ph.D. Dissertation. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 112 p.
Rundquist, V.M. 1973. Avian ecology on stock ponds in two vegetational types in north-central Montana. Ph.D. Dissertation. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 112 p. Sibley, D. 2014. The Sibley guide to birds. Alfred A. Knopf, New York, NY. 598 pp.
Sibley, D. 2014. The Sibley guide to birds. Alfred A. Knopf, New York, NY. 598 pp. Skaar, P. D., D. L. Flath, and L. S. Thompson. 1985. Montana bird distribution. Montana Academy of Sciences Monograph 3(44): ii-69.
Skaar, P. D., D. L. Flath, and L. S. Thompson. 1985. Montana bird distribution. Montana Academy of Sciences Monograph 3(44): ii-69. Skagen, S.K. and F.L. Knopf. 1993. Toward conservation of midcontinental migrations. Conservation Biology 7(3):533-541.
Skagen, S.K. and F.L. Knopf. 1993. Toward conservation of midcontinental migrations. Conservation Biology 7(3):533-541. Swan River National Wildlife Refuge. 1982. Birds of the Swan River NWR. Kalispell, MT: NW MT Fish and Wildlife Center pamphlet.
Swan River National Wildlife Refuge. 1982. Birds of the Swan River NWR. Kalispell, MT: NW MT Fish and Wildlife Center pamphlet. Thompson, L.S. 1981. Circle West wildlife monitoring study: Third annual report. Technical report No. 8. Montana Department of Natural Resources and Conservation. Helena, Montana.
Thompson, L.S. 1981. Circle West wildlife monitoring study: Third annual report. Technical report No. 8. Montana Department of Natural Resources and Conservation. Helena, Montana. Thunderbird Wildlife Consulting, Inc., Gillette, WY., 2003, Spring Creek Mine 2002 Wildlife Monitoring. March 2003.
Thunderbird Wildlife Consulting, Inc., Gillette, WY., 2003, Spring Creek Mine 2002 Wildlife Monitoring. March 2003. U.S. Forest Service. 1991. Forest and rangeland birds of the United States: Natural history and habitat use. U.S. Department of Agriculture, Forest Service Agricultural Handbook 688. 625 pages.
U.S. Forest Service. 1991. Forest and rangeland birds of the United States: Natural history and habitat use. U.S. Department of Agriculture, Forest Service Agricultural Handbook 688. 625 pages. Waage, Bruce C., 1995, Western Energy Company Rosebud Mine, Colstrip, Montana:1994 Annual Wildlife Monitoring Report; December 1, 1993 - November 30, 1994. February 27, 1995.
Waage, Bruce C., 1995, Western Energy Company Rosebud Mine, Colstrip, Montana:1994 Annual Wildlife Monitoring Report; December 1, 1993 - November 30, 1994. February 27, 1995. Waage, Bruce C., 1999, Western Energy Company Rosebud Mine, Colstrip, Montana: 1998 Annual Wildlife Monitoring Report; December 1, 1997 - November 30, 1998 Survey Period. February 24, 1999.
Waage, Bruce C., 1999, Western Energy Company Rosebud Mine, Colstrip, Montana: 1998 Annual Wildlife Monitoring Report; December 1, 1997 - November 30, 1998 Survey Period. February 24, 1999. Waldt, R. 1995. The Pine Butte Swamp Preserve bird list. Choteau, MT: The Nature Conservancy. Updated August 1995.
Waldt, R. 1995. The Pine Butte Swamp Preserve bird list. Choteau, MT: The Nature Conservancy. Updated August 1995. Watts, C.R. and L.C. Eichhorn. 1981. Changes in the birds of central Montana. Proceedings of the Montana Academy of Sciences 40:31-40.
Watts, C.R. and L.C. Eichhorn. 1981. Changes in the birds of central Montana. Proceedings of the Montana Academy of Sciences 40:31-40.
- Web Search Engines for Articles on "Lesser Yellowlegs"
- Additional Sources of Information Related to "Birds"





