View in other NatureServe Network Field Guides
NatureServe
Montana
Utah
Wyoming
Idaho
Wisconsin
British Columbia
South Carolina
Yukon
California
New York
Turkey Vulture - Cathartes aura
Native Species
Global Rank:
G5
State Rank:
S5B
(see State Rank Reason below)
Agency Status
USFWS:
MBTA
USFS:
BLM:
PIF:
External Links
State Rank Reason (see State Rank above)
Species is relatively common within suitable habitat and widely distributed across portions of the state.
General Description
Turkey Vultures are large, black birds. When soaring overhead, the wings have a two-toned gray and black appearance. Turkey vultures often hold their wings in a shallow "V" and rock from side to side when soaring. The head usually appears small in relation to the body. The red color of the head in adults is often hard to see on flying birds. Young birds have a blackish-gray head. Turkey Vultures range in length from 26 to 32 inches and have a wingspan of 68 to 72 inches.
For a comprehensive review of the conservation status, habitat use, and ecology of this and other Montana bird species, please see
Marks et al. 2016, Birds of Montana.Diagnostic Characteristics
Adult Golden Eagles and immature Bald Eagles are slightly larger, usually soar with wings held flat instead of in a "V", and have wings that appear all one shade instead of two-toned. Common Ravens are much smaller and have a wedge-shaped tail.
Species Range
Montana Range
Range Descriptions
 Western Hemisphere Range
Western Hemisphere Range

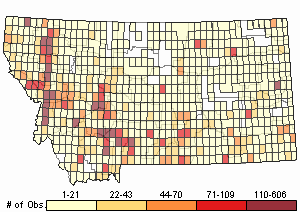
Observations in Montana Natural Heritage Program Database
Number of Observations: 19505
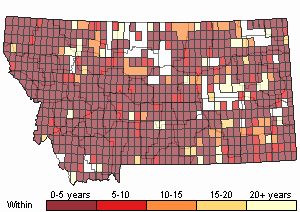
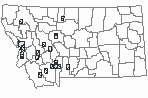
(Click on the following maps and charts to see full sized version)
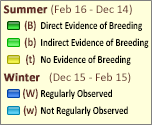
Map Help and Descriptions
Relative Density
Recency
SUMMER (Feb 16 - Dec 14)
Direct Evidence of Breeding
Indirect Evidence of Breeding
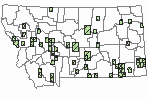
No Evidence of Breeding

WINTER (Dec 15 - Feb 15)
Regularly Observed
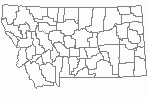
Not Regularly Observed
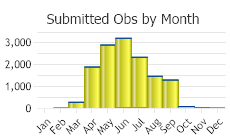
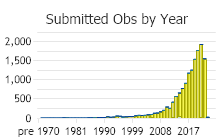
 (Observations spanning multiple months or years are excluded from time charts)
(Observations spanning multiple months or years are excluded from time charts)
Migration
Turkey Vultures often congregate in large roosting and feeding flocks. They migrate to the southern United States and Central America for the winter. In the Bozeman area, no perceptible migration periods or peaks are seen (Skaar 1969).
Habitat
Turkey Vultures forage in a variety of habitats, including grasslands, badlands, open woodlands, and farmlands. Nesting in the northern Rockies is usually done on cliff ledges under overhangs, or in rock crevices, often in river valleys (Johnsgard 1986).
National Vegetation Classification System Groups Associated with this Species
Forest and Woodland
Low Elevation - Xeric Forest and Woodland
Montane - Subalpine Forest and Woodland
Shrubland
Arid - Saline Shrubland
Foothills - Montane Shrubland
Sagebrush Shrubland
Grassland
Lowland - Prairie Grassland
Montane - Subalpine Grassland
Sparse and Barren
Sparse and Barren
Wetland and Riparian
Riparian and Wetland Forest
Riparian Shrubland
Recently Disturbed or Modified
Recently Burned
Human Land Use
Agriculture
Developed
Food Habits
Carrion is the primary food, but they sometimes prey on small mammals.
Ecology
Various reports in the 1870s and 1880s placed the bird as more abundant than it is today (Skaar 1969). Generally found below 8000' at this latitude (Johnsgard 1986).
Reproductive Characteristics
Turkey Vultures nest in caves, large hollow trees, abandoned buildings, and, rarely on the ground or in trees. They do not construct nests, but simply lay their eggs on whatever material is available. Two, or, rarely, three eggs are laid in April or May. Incubation lasts 38 to 41 days. The young, fed by regurgitation, remain in the nest about 8 to 10 weeks.
Stewardship Responsibility
References
- Literature Cited AboveLegend:
 View Online Publication
View Online Publication Johnsgard, P.A. 1986. Birds of the Rocky Mountains: with particular reference to national parks in the northern Rocky Mountain region. Colorado Associated University Press, Boulder, CO.
Johnsgard, P.A. 1986. Birds of the Rocky Mountains: with particular reference to national parks in the northern Rocky Mountain region. Colorado Associated University Press, Boulder, CO. Marks, J.S., P. Hendricks, and D. Casey. 2016. Birds of Montana. Arrington, VA. Buteo Books. 659 pages.
Marks, J.S., P. Hendricks, and D. Casey. 2016. Birds of Montana. Arrington, VA. Buteo Books. 659 pages. Skaar, P.D. 1969. Birds of the Bozeman latilong: a compilation of data concerning the birds which occur between 45 and 46 N. latitude and 111 and 112 W. longitude, with current lists for Idaho, Montana, Wyoming, impinging Montana counties and Yellowstone National Park. Bozeman, MT. 132 p.
Skaar, P.D. 1969. Birds of the Bozeman latilong: a compilation of data concerning the birds which occur between 45 and 46 N. latitude and 111 and 112 W. longitude, with current lists for Idaho, Montana, Wyoming, impinging Montana counties and Yellowstone National Park. Bozeman, MT. 132 p.
- Additional ReferencesLegend:
 View Online Publication
View Online Publication
Do you know of a citation we're missing? [PRESI] Powder River Eagle Studies Incorporated. 1998b. Spring Creek Mine 1997 wildlife monitoring studies. Powder River Eagle Studies Incorporated. Gillete, WY.
[PRESI] Powder River Eagle Studies Incorporated. 1998b. Spring Creek Mine 1997 wildlife monitoring studies. Powder River Eagle Studies Incorporated. Gillete, WY. Allen, G. T. 1979. An assessment of potential conflicts between nesting raptors and human activities in the Long Pines area of southeastern Montana with special emphasis on uranium development. M.S. thesis, Washington State University, Pullman. 109 pp.
Allen, G. T. 1979. An assessment of potential conflicts between nesting raptors and human activities in the Long Pines area of southeastern Montana with special emphasis on uranium development. M.S. thesis, Washington State University, Pullman. 109 pp. American Ornithologists’ Union [AOU]. 1998. Check-list of North American birds, 7th edition. American Ornithologists’ Union, Washington, D.C. 829 p.
American Ornithologists’ Union [AOU]. 1998. Check-list of North American birds, 7th edition. American Ornithologists’ Union, Washington, D.C. 829 p. Becker, D.M. 1977. A survey of breeding raptors on and adjacent to Custer National Forest lands in Carter County, Montana. Unpublished report including 1978 progress report. 107 p.
Becker, D.M. 1977. A survey of breeding raptors on and adjacent to Custer National Forest lands in Carter County, Montana. Unpublished report including 1978 progress report. 107 p. Becker, Dale M., 1980, A Survey of raptors on national forest land in Carter County, Montana. Final Progress Report: 1977-1979.
Becker, Dale M., 1980, A Survey of raptors on national forest land in Carter County, Montana. Final Progress Report: 1977-1979. Bird Conservancy of the Rockies. 2017. Pocket Guide to Northern Prairie Birds. Brighton, CO: Bird Conservancy of the Rockies. 98 p.
Bird Conservancy of the Rockies. 2017. Pocket Guide to Northern Prairie Birds. Brighton, CO: Bird Conservancy of the Rockies. 98 p. Bramblett, R.G., and A.V. Zale. 2002. Montana Prairie Riparian Native Species Report. Montana Cooperative Fishery Research Unit, Montana State University - Bozeman.
Bramblett, R.G., and A.V. Zale. 2002. Montana Prairie Riparian Native Species Report. Montana Cooperative Fishery Research Unit, Montana State University - Bozeman. Cameron, E. S. 1907. The birds of Custer and Dawson counties, Montana. Auk 24(3): 241-270.
Cameron, E. S. 1907. The birds of Custer and Dawson counties, Montana. Auk 24(3): 241-270. Coleman, J. S., and J. D. Fraser. 1989. Habitat use and home ranges of black and turkey vultures. J. Wildl. Manage. 53:782-792.
Coleman, J. S., and J. D. Fraser. 1989. Habitat use and home ranges of black and turkey vultures. J. Wildl. Manage. 53:782-792. Confluence Consulting Inc. 2010. Montana Department of Transportation Wetland Mitigation Monitoring Reports (various sites). MDT Helena, MT.
Confluence Consulting Inc. 2010. Montana Department of Transportation Wetland Mitigation Monitoring Reports (various sites). MDT Helena, MT. Confluence Consulting Inc. 2013. Montana Department of Transportation Wetland Mitigation Monitoring Reports (various sites). MDT Helena, MT.
Confluence Consulting Inc. 2013. Montana Department of Transportation Wetland Mitigation Monitoring Reports (various sites). MDT Helena, MT. Decker Coal Co., 1981, Wildlife survey. July 7, 1981. In North Decker 5-Year Permit Application. Vol. III. Rule 26.4.304(12-14).
Decker Coal Co., 1981, Wildlife survey. July 7, 1981. In North Decker 5-Year Permit Application. Vol. III. Rule 26.4.304(12-14). Dickson, D.C. 1991. Systematic wildlife observations on the Blackfoot-Clearwater Wildlife Management Area. Montana Department of Fish, Wildlife and Parks. Missoula, MT. 14 pp. plus appendices and photographs.
Dickson, D.C. 1991. Systematic wildlife observations on the Blackfoot-Clearwater Wildlife Management Area. Montana Department of Fish, Wildlife and Parks. Missoula, MT. 14 pp. plus appendices and photographs. Dobkin, D. S. 1992. Neotropical migrant landbirds in the Northern Rockies and Great Plains. U.S.D.A. For. Serv. N. Region Publ. R1-93-34. Missoula, Mont.
Dobkin, D. S. 1992. Neotropical migrant landbirds in the Northern Rockies and Great Plains. U.S.D.A. For. Serv. N. Region Publ. R1-93-34. Missoula, Mont. Dood, A.R. 1980. Terry Badlands nongame survey and inventory final report. Montana Department of Fish, Wildlife, and Parks and Bureau of Land Management, Helena, MT. 70 pp.
Dood, A.R. 1980. Terry Badlands nongame survey and inventory final report. Montana Department of Fish, Wildlife, and Parks and Bureau of Land Management, Helena, MT. 70 pp. DuBois, K. and D. Becker. 1987. Identification of Montana's birds of prey. Montana Outdoors Nov/Dec. 20 p.
DuBois, K. and D. Becker. 1987. Identification of Montana's birds of prey. Montana Outdoors Nov/Dec. 20 p. DuBois, K.L. 1979. An inventory of the avifauna in the Long Pines of Southeastern Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 113 p.
DuBois, K.L. 1979. An inventory of the avifauna in the Long Pines of Southeastern Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 113 p. Econ, Inc. 1988. Wildlife monitoring report, 1987 field season, Big Sky Mine. March 1988. In Peabody Mining and Reclamation Plan Big Sky Mine Area B. Vol. 8, cont., Tab 10 - Wildlife Resources. Appendix 10-1, 1987 Annual Wildlife Report.
Econ, Inc. 1988. Wildlife monitoring report, 1987 field season, Big Sky Mine. March 1988. In Peabody Mining and Reclamation Plan Big Sky Mine Area B. Vol. 8, cont., Tab 10 - Wildlife Resources. Appendix 10-1, 1987 Annual Wildlife Report. Ehrlich, P., D. Dobkin, and D. Wheye. 1988. The birder’s handbook: a field guide to the natural history of North American birds. Simon and Schuster Inc. New York. 785 pp.
Ehrlich, P., D. Dobkin, and D. Wheye. 1988. The birder’s handbook: a field guide to the natural history of North American birds. Simon and Schuster Inc. New York. 785 pp. Faanes, C.A. 1983. Breeding birds of wooded draws in western North Dakota. Prairie Nat. 15(4): 173-187.
Faanes, C.A. 1983. Breeding birds of wooded draws in western North Dakota. Prairie Nat. 15(4): 173-187. Garcia and Associates, 2004. Northern Goshawk Surveys for the East Short Pines and the Ekalaka Hills, Sioux Ranger District, Custer National Forest. 8 pp. plus appendices.
Garcia and Associates, 2004. Northern Goshawk Surveys for the East Short Pines and the Ekalaka Hills, Sioux Ranger District, Custer National Forest. 8 pp. plus appendices. Gniadek, S. 1983. Southwest Glendive Wildlife Baseline Inventory. Miles City, Mont: Bureau of Land Management, Miles City District Office. 56 pp with appendices.
Gniadek, S. 1983. Southwest Glendive Wildlife Baseline Inventory. Miles City, Mont: Bureau of Land Management, Miles City District Office. 56 pp with appendices. Hays, R., R.L. Eng, and C.V. Davis (preparers). 1984. A list of Montana birds. Helena, MT: MT Dept. of Fish, Wildlife & Parks.
Hays, R., R.L. Eng, and C.V. Davis (preparers). 1984. A list of Montana birds. Helena, MT: MT Dept. of Fish, Wildlife & Parks. Hejl, S.J., R.L. Hutto, C.R. Preston, and D.M. Finch. 1995. The effects of silvicultural treatments on forest birds in the Rocky Mountains. pp. 220-244 In: T.E. Martin and D.M. Finch (eds). Ecology and Management of Neotropical Migratory Birds. New York, NY: Oxford Univ. Press. 489 p.
Hejl, S.J., R.L. Hutto, C.R. Preston, and D.M. Finch. 1995. The effects of silvicultural treatments on forest birds in the Rocky Mountains. pp. 220-244 In: T.E. Martin and D.M. Finch (eds). Ecology and Management of Neotropical Migratory Birds. New York, NY: Oxford Univ. Press. 489 p. Hendricks, P., G.M. Kudray, S. Lenard, and B.A. Maxell. 2007. A Multi-Scale Analysis Linking Prairie Breeding Birds to Site and Landscape Factors Including USGS GAP Data. Helena, Mont: Montana Natural Heritage Program.
Hendricks, P., G.M. Kudray, S. Lenard, and B.A. Maxell. 2007. A Multi-Scale Analysis Linking Prairie Breeding Birds to Site and Landscape Factors Including USGS GAP Data. Helena, Mont: Montana Natural Heritage Program. Hoffland, John Robert. 1995. A comparison of bird abundance among selectively logged old-growth and mature second-growth Ponderosa Pine. M.S. Thesis. University of Montana. Missoula, MT.
Hoffland, John Robert. 1995. A comparison of bird abundance among selectively logged old-growth and mature second-growth Ponderosa Pine. M.S. Thesis. University of Montana. Missoula, MT. Humphris, Michael., 1990, Wildlife Monitoring Report. Spring Creek Coal Company 1990 Mining Annual Report. Appendix I. April 11, 1990.
Humphris, Michael., 1990, Wildlife Monitoring Report. Spring Creek Coal Company 1990 Mining Annual Report. Appendix I. April 11, 1990. Humphris, Michael., 1991, Wildlife Monitoring Report. Spring Creek Coal Company 1991 Mining Annual Report. Appendix I. April 11, 1991.
Humphris, Michael., 1991, Wildlife Monitoring Report. Spring Creek Coal Company 1991 Mining Annual Report. Appendix I. April 11, 1991. Jackson, J. A. 1983. Nesting phenology, nest site selection, and reproductive success of black and turkey vultures. Pages 245-270 in Wilbur, S. R., and J. A. Jackson, eds. Vulture biology and management. Univ. Calif. Press.
Jackson, J. A. 1983. Nesting phenology, nest site selection, and reproductive success of black and turkey vultures. Pages 245-270 in Wilbur, S. R., and J. A. Jackson, eds. Vulture biology and management. Univ. Calif. Press. Johnsgard, P.A. 1979. Birds of the Great Plains: breeding species and their distribution. University of Nebraska Press, Lincoln. 539 pp.
Johnsgard, P.A. 1979. Birds of the Great Plains: breeding species and their distribution. University of Nebraska Press, Lincoln. 539 pp. Johnsgard, P.A. 1992. Birds of the Rocky Mountains with particular reference to national parks in the northern Rocky Mountain region. Lincoln: University of Nebraska Press. xi + 504 pp.
Johnsgard, P.A. 1992. Birds of the Rocky Mountains with particular reference to national parks in the northern Rocky Mountain region. Lincoln: University of Nebraska Press. xi + 504 pp. Joslin, Gayle, and Heidi B. Youmans. 1999. Effects of recreation on Rocky Mountain wildlife: a review for Montana. [Montana]: Montana Chapter of the Wildlife Society.
Joslin, Gayle, and Heidi B. Youmans. 1999. Effects of recreation on Rocky Mountain wildlife: a review for Montana. [Montana]: Montana Chapter of the Wildlife Society. Kirk, D.A. and M.J. Mossman. 1998. Turkey Vulture (Cathartes aura). Species Account Number 339. The Birds of North America Online (A. Poole, Ed.). Ithaca, NY: Cornell Laboratory of Ornithology; Retrieved 3/25/2008 from The Birds of North America Online database
Kirk, D.A. and M.J. Mossman. 1998. Turkey Vulture (Cathartes aura). Species Account Number 339. The Birds of North America Online (A. Poole, Ed.). Ithaca, NY: Cornell Laboratory of Ornithology; Retrieved 3/25/2008 from The Birds of North America Online database LaVelle, Darlene. 1988. 1988 Nongame surveys in Region 5 and Region 7.' MTFWP. 40pp.
LaVelle, Darlene. 1988. 1988 Nongame surveys in Region 5 and Region 7.' MTFWP. 40pp. Lenard, S. and P. Hendricks. 2005. Birds of selected grassland and riparian plots along the Rocky Mountain Front. Montana Natural Heritage Program for US Fish and Wildlife Service and The Nature Conservancy. 17pp + maps.
Lenard, S. and P. Hendricks. 2005. Birds of selected grassland and riparian plots along the Rocky Mountain Front. Montana Natural Heritage Program for US Fish and Wildlife Service and The Nature Conservancy. 17pp + maps. Lenard, S., J. Carlson, J. Ellis, C. Jones, and C. Tilly. 2003. P. D. Skaar's Montana bird distribution, 6th edition. Montana Audubon, Helena, MT. 144 pp.
Lenard, S., J. Carlson, J. Ellis, C. Jones, and C. Tilly. 2003. P. D. Skaar's Montana bird distribution, 6th edition. Montana Audubon, Helena, MT. 144 pp. Lockhart, J. Michael, 1976, Effects of coal extraction and related development on wildlife populations. Annual progress report; Calendar year 1976. In Decker Coal Company West Pit Permit. Vol. 3. 26.4.304(10-11), 305, 306, and 307. Updated Rules Rewrite, July 1, 1991. Appendix F.
Lockhart, J. Michael, 1976, Effects of coal extraction and related development on wildlife populations. Annual progress report; Calendar year 1976. In Decker Coal Company West Pit Permit. Vol. 3. 26.4.304(10-11), 305, 306, and 307. Updated Rules Rewrite, July 1, 1991. Appendix F. Lockhart, J. Michael, and Terrence P. McEneaney, 1978, Effects of coal extraction and related development on wildlife populations. Annual progress report; Calendar year 1978. In Decker Coal Company West Pit Permit. Vol. 3. 26.4.304(10-11), 305, 306, and 307. Updated Rules Rewrite, July 1, 1991. Appendix F.
Lockhart, J. Michael, and Terrence P. McEneaney, 1978, Effects of coal extraction and related development on wildlife populations. Annual progress report; Calendar year 1978. In Decker Coal Company West Pit Permit. Vol. 3. 26.4.304(10-11), 305, 306, and 307. Updated Rules Rewrite, July 1, 1991. Appendix F. Matthews, W.L. 1980a. Wibaux-Beach comparison study: Sydney, Glendive and Plevna Study Areas. Bureau of Land Management, Miles City, MT. 50 p.
Matthews, W.L. 1980a. Wibaux-Beach comparison study: Sydney, Glendive and Plevna Study Areas. Bureau of Land Management, Miles City, MT. 50 p. Maxell, B.A. 2016. Northern Goshawk surveys on the Beartooth, Ashland, and Sioux Districts of the Custer-Gallatin National Forest: 2012-2014. Montana Natural Heritage Program. Helena, MT. 114pp.
Maxell, B.A. 2016. Northern Goshawk surveys on the Beartooth, Ashland, and Sioux Districts of the Custer-Gallatin National Forest: 2012-2014. Montana Natural Heritage Program. Helena, MT. 114pp. Montana Bird Distribution Committee. 2012. P.D. Skaar's Montana bird distribution. 7th Edition. Montana Audubon, Helena, Montana. 208 pp. + foldout map.
Montana Bird Distribution Committee. 2012. P.D. Skaar's Montana bird distribution. 7th Edition. Montana Audubon, Helena, Montana. 208 pp. + foldout map. Montana Tunnels Mine, Inc., Jefferson City, Helena, MT., 1988?, Application for an Amendment to the Montana Tunnels Operating Permit for the Prickly Pear Water Supply System, Jefferson County, Montana.
Montana Tunnels Mine, Inc., Jefferson City, Helena, MT., 1988?, Application for an Amendment to the Montana Tunnels Operating Permit for the Prickly Pear Water Supply System, Jefferson County, Montana. MT Fish, Wildlife & Parks. No date. Blackfoot-Clearwater Wildlife Management Area checklist.
MT Fish, Wildlife & Parks. No date. Blackfoot-Clearwater Wildlife Management Area checklist. Oechsli, L.M. 2000. Ex-urban development in the Rocky Mountain West: consequences for native vegetation, wildlife diversity, and land-use planning in Big Sky, Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Montana State University, Bozeman. 73 p.
Oechsli, L.M. 2000. Ex-urban development in the Rocky Mountain West: consequences for native vegetation, wildlife diversity, and land-use planning in Big Sky, Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Montana State University, Bozeman. 73 p. Omland, K.S. and E.G. Meyer. 1992. Fall 1991 raptor migration study in the Bozeman, Montana vicinity. Prepared for the Gallatin National Forest, by HawkWatch International, Inc. 31 p.
Omland, K.S. and E.G. Meyer. 1992. Fall 1991 raptor migration study in the Bozeman, Montana vicinity. Prepared for the Gallatin National Forest, by HawkWatch International, Inc. 31 p. Phillips, R.L., A.H. Wheeler, N.C. Forrester, J.M. Lockhart, and T.P. McEneaney. 1990. Nesting ecology of golden eagles and other raptors in southeastern Montana and northern Wyoming. U.S. Fish Wildl. Serv. Tech. Rep. 26:1-13.
Phillips, R.L., A.H. Wheeler, N.C. Forrester, J.M. Lockhart, and T.P. McEneaney. 1990. Nesting ecology of golden eagles and other raptors in southeastern Montana and northern Wyoming. U.S. Fish Wildl. Serv. Tech. Rep. 26:1-13. Pitkin, P. and L. Quattrini. 2017. Pocket Guide to Sagebrush Birds. Bird Conservancy of the Rockies and Point Blue Conservation Science. 68 p.
Pitkin, P. and L. Quattrini. 2017. Pocket Guide to Sagebrush Birds. Bird Conservancy of the Rockies and Point Blue Conservation Science. 68 p. Powder River Eagle Studies, Inc., Gillette, WY., 1995, Big Sky Mine 1994 wildlife monitoring studies. March 1995
Powder River Eagle Studies, Inc., Gillette, WY., 1995, Big Sky Mine 1994 wildlife monitoring studies. March 1995 Powder River Eagle Studies, Inc., Gillette, WY., 1999, Spring Creek Mine 1998 Wildlife Monitoring. March 1999.
Powder River Eagle Studies, Inc., Gillette, WY., 1999, Spring Creek Mine 1998 Wildlife Monitoring. March 1999. Powder River Eagle Studies, Inc., Gillette, WY., 2000, Spring Creek Mine 1999 Wildlife Monitoring. March 2000.
Powder River Eagle Studies, Inc., Gillette, WY., 2000, Spring Creek Mine 1999 Wildlife Monitoring. March 2000. Ralph, J.C., J.R. Sauer, and S. Droege. 1995. Monitoring bird populations by point counts. Gen. Tech. Rep. PSW-GTR-149. Albany, CA: USDA Pacific Southwest Research Station. 181 p.
Ralph, J.C., J.R. Sauer, and S. Droege. 1995. Monitoring bird populations by point counts. Gen. Tech. Rep. PSW-GTR-149. Albany, CA: USDA Pacific Southwest Research Station. 181 p. Restani, M. and A.R. Harmata. 1992. Survey of raptors along the upper Missouri River, Montana. Montana State University. Bozeman, MT. 53 pp plus appendix.
Restani, M. and A.R. Harmata. 1992. Survey of raptors along the upper Missouri River, Montana. Montana State University. Bozeman, MT. 53 pp plus appendix. Richmond, C.W. and F.H. Knowlton. 1894. Birds of south-central Montana. Auk 11:298-308.
Richmond, C.W. and F.H. Knowlton. 1894. Birds of south-central Montana. Auk 11:298-308. Ryder, R.A. 1972. Avian population studies on the Pawnee site, 1968-1971. Fort Collins, CO: Colorado State University. Grassland Biome, U.S. International Biological Program, Tech. Rep. 57 p.
Ryder, R.A. 1972. Avian population studies on the Pawnee site, 1968-1971. Fort Collins, CO: Colorado State University. Grassland Biome, U.S. International Biological Program, Tech. Rep. 57 p. Saab, V. and C. Groves. 1992. Idaho's migratory landbirds, description, habitats & conservation. Nongame Wildlife Leaflet #10. Idaho Department of Fish and Game, UBLM, USFS, USFWS, National Fish and Wildlife Foundation. 16 p.
Saab, V. and C. Groves. 1992. Idaho's migratory landbirds, description, habitats & conservation. Nongame Wildlife Leaflet #10. Idaho Department of Fish and Game, UBLM, USFS, USFWS, National Fish and Wildlife Foundation. 16 p. Salt, W.R. and J.R. Salt. 1976. The birds of Alberta. Hurtig Publishers, Edmonton, Alberta. xv + 498 pp.
Salt, W.R. and J.R. Salt. 1976. The birds of Alberta. Hurtig Publishers, Edmonton, Alberta. xv + 498 pp. Sater, S. 2022. The insects of Sevenmile Creek, a pictorial guide to their diversity and ecology. Undergraduate Thesis. Helena, MT: Carroll College. 242 p.
Sater, S. 2022. The insects of Sevenmile Creek, a pictorial guide to their diversity and ecology. Undergraduate Thesis. Helena, MT: Carroll College. 242 p. Sibley, D. 2014. The Sibley guide to birds. Alfred A. Knopf, New York, NY. 598 pp.
Sibley, D. 2014. The Sibley guide to birds. Alfred A. Knopf, New York, NY. 598 pp. Skaar, P. D., D. L. Flath, and L. S. Thompson. 1985. Montana bird distribution. Montana Academy of Sciences Monograph 3(44): ii-69.
Skaar, P. D., D. L. Flath, and L. S. Thompson. 1985. Montana bird distribution. Montana Academy of Sciences Monograph 3(44): ii-69. Smith, J. 2000. Recap of the fall 2000 migration season, Bridger Mountains. Raptor Watch 15(1):6-10.
Smith, J. 2000. Recap of the fall 2000 migration season, Bridger Mountains. Raptor Watch 15(1):6-10. Stewart, R.E. 1975. Breeding birds of North Dakota. Tri-College Center for Environmental Studies, Fargo, North Dakota. 295 pp.
Stewart, R.E. 1975. Breeding birds of North Dakota. Tri-College Center for Environmental Studies, Fargo, North Dakota. 295 pp. Stewart, R.E. and H.A. Kantrud. 1972. Population estimates of breeding birds in North Dakota. The Auk 89(4):766-788.
Stewart, R.E. and H.A. Kantrud. 1972. Population estimates of breeding birds in North Dakota. The Auk 89(4):766-788. Thomas, J. W. (ed). 1979. Wildlife habitats in managed forests: the Blue Mountains of Oregon and Washington. Agriculture Handbook 553, USDA, Forest Service, Wildlife Management Institute, Washington, DC. 512 pp.
Thomas, J. W. (ed). 1979. Wildlife habitats in managed forests: the Blue Mountains of Oregon and Washington. Agriculture Handbook 553, USDA, Forest Service, Wildlife Management Institute, Washington, DC. 512 pp. Thompson, L.S. 1981. Circle West wildlife monitoring study: Third annual report. Technical report No. 8. Montana Department of Natural Resources and Conservation. Helena, Montana.
Thompson, L.S. 1981. Circle West wildlife monitoring study: Third annual report. Technical report No. 8. Montana Department of Natural Resources and Conservation. Helena, Montana. Thunderbird Wildlife Consulting, Inc., Gillette, WY., 2003, 2002 wildlife monitoring report: Big Sky Mine. February 2003.
Thunderbird Wildlife Consulting, Inc., Gillette, WY., 2003, 2002 wildlife monitoring report: Big Sky Mine. February 2003. U.S. Forest Service. 1991. Forest and rangeland birds of the United States: Natural history and habitat use. U.S. Department of Agriculture, Forest Service Agricultural Handbook 688. 625 pages.
U.S. Forest Service. 1991. Forest and rangeland birds of the United States: Natural history and habitat use. U.S. Department of Agriculture, Forest Service Agricultural Handbook 688. 625 pages. Verner, J., and L.V. Ritter. 1985. A comparison of transects and point counts in oak-pine woodlands of California. The Condor 87:47-68.
Verner, J., and L.V. Ritter. 1985. A comparison of transects and point counts in oak-pine woodlands of California. The Condor 87:47-68. VTN Environmental Sciences, Sheridan, Wyoming for Montana Dept. of State Lands, 1973, Environmental Analysis Decker Coal Company Mine, Decker, Montana.
VTN Environmental Sciences, Sheridan, Wyoming for Montana Dept. of State Lands, 1973, Environmental Analysis Decker Coal Company Mine, Decker, Montana. Waage, B.C. 1984. Western Energy Company Rosebud Mine, Rosebud County, Montana: Annual Wildlife Monitoring Report, 1983 Field Season. June 1984.
Waage, B.C. 1984. Western Energy Company Rosebud Mine, Rosebud County, Montana: Annual Wildlife Monitoring Report, 1983 Field Season. June 1984. Waage, Bruce C., 1991, Western Energy Company Rosebud Mine, Colstrip, Montana: Annual Wildlife Monitoring Report, 1990 Field Season. September 1991.
Waage, Bruce C., 1991, Western Energy Company Rosebud Mine, Colstrip, Montana: Annual Wildlife Monitoring Report, 1990 Field Season. September 1991. Watts, C.R. and L.C. Eichhorn. 1981. Changes in the birds of central Montana. Proceedings of the Montana Academy of Sciences 40:31-40.
Watts, C.R. and L.C. Eichhorn. 1981. Changes in the birds of central Montana. Proceedings of the Montana Academy of Sciences 40:31-40. Western Energy Co., Colstrip, MT., 1981, Western Energy Company Rosebud Mine, Colstrip, Montana: Annual Wildlife Report, 1981.
Western Energy Co., Colstrip, MT., 1981, Western Energy Company Rosebud Mine, Colstrip, Montana: Annual Wildlife Report, 1981. Western Technology and Engineering, Inc. (WESTECH)., 1993, Wildlife Monitoring Asaloka Mine Area Annual Report, 1992. Montana SMP 85005 R1. OSMP Montana 00078. 1993.
Western Technology and Engineering, Inc. (WESTECH)., 1993, Wildlife Monitoring Asaloka Mine Area Annual Report, 1992. Montana SMP 85005 R1. OSMP Montana 00078. 1993. Westmoreland Resources, Inc., Hardin, MT., 1981, 1981 Wildlife Report. April 1982.
Westmoreland Resources, Inc., Hardin, MT., 1981, 1981 Wildlife Report. April 1982. Westmoreland Resources, Inc., Hardin, MT., 1983, 1983 Wildlife Monitoring.
Westmoreland Resources, Inc., Hardin, MT., 1983, 1983 Wildlife Monitoring.
- Web Search Engines for Articles on "Turkey Vulture"
- Additional Sources of Information Related to "Birds"





