View in other NatureServe Network Field Guides
NatureServe
Montana
Utah
Wyoming
Idaho
Wisconsin
British Columbia
South Carolina
Yukon
California
New York
Northern Pintail - Anas acuta
State Rank Reason (see State Rank above)
Species is relatively common within suitable habitat and widely distributed across portions of the state. Populations have been declining since the mid-20th century.
General Description
Medium-sized dabbling duck. Length: adult males 57 to 76 cm, females 51 to 63 cm. Both sexes distinguished from other dabblers by slim profile, long narrow neck, and pointed tail. Sexually dimorphic plumage. Definitive Alternate male readily distinguished from other North American ducks by combination of chocolate brown head, white neck and underparts, and very long central rectrices. Female distinguished from other female ducks by slender proportions, pointed tail, mottled dull brown or bronze (rarely with some green) speculum, and mottled to spotted dark gray to black bill (Austin and Miller 1995).
For a comprehensive review of the conservation status, habitat use, and ecology of this and other Montana bird species, please see
Marks et al. 2016, Birds of Montana.Species Range
Montana Range
Range Descriptions
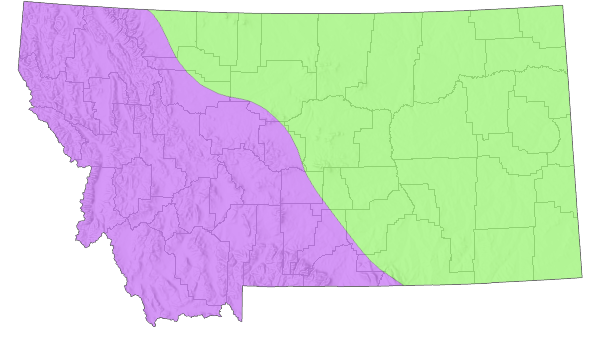 Western Hemisphere Range
Western Hemisphere Range

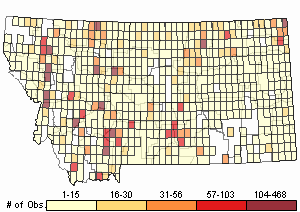
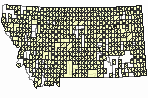
Observations in Montana Natural Heritage Program Database
Number of Observations: 10288
(Click on the following maps and charts to see full sized version)
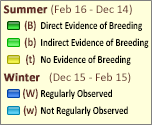
Map Help and Descriptions
Relative Density
Recency
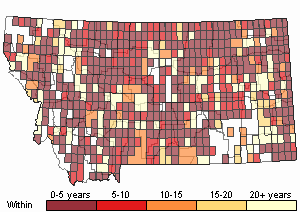
SUMMER (Feb 16 - Dec 14)
Direct Evidence of Breeding
Indirect Evidence of Breeding
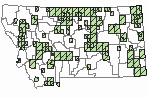
No Evidence of Breeding
WINTER (Dec 15 - Feb 15)
Regularly Observed
Not Regularly Observed
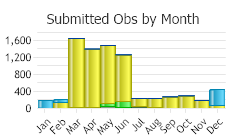
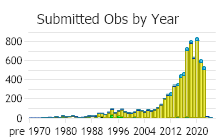
 (Observations spanning multiple months or years are excluded from time charts)
(Observations spanning multiple months or years are excluded from time charts)
Migration
Normal migration periods in the Bozeman area are March 5 to May 5 and September 20 to November 20, with the peak occurring on October 20 (Skaar 1969).
Habitat
Comments on habitat are found in Holm (1984). Typically nest in open country with shallow, seasonal, or intermittent wetlands and low vegetation (Austin and Miller 1995). Summer birds prefer large lakes in the Bozeman area (Skaar 1969). An early fall migrant, the species arrives on wintering areas beginning in August, after wing molt, often forming large roosting and feeding flocks on open, shallow wetlands and flooded agricultural fields (Austin and Miller 1995).
National Vegetation Classification System Groups Associated with this Species
Grassland
Lowland - Prairie Grassland
Wetland and Riparian
Alkaline - Saline Wetlands
Alpine Riparian and Wetland
Peatland
Riparian and Wetland Forest
Riparian Shrubland
Wet Meadow and Marsh
Recently Disturbed or Modified
Introduced Vegetation
Human Land Use
Agriculture
Food Habits
Grain (rice, wheat, corn, barley), moist-soil and aquatic plant seeds, pond weeds, aquatic insects, crustaceans, and snails (Austin and Miller 1995).
Ecology
At Freezeout Lake the major cause of nest failure was skunk predation. Brood movement in southeast Montana tended to be from bare ponds to those with emergent vegetation, from small to larger ponds and to ponds with a lower water loss rate.
Reproductive Characteristics
The species nests from late April through July, with hatchlings observed in May. At Freezeout Lake island nests were more successful (87.5%) than those in other habitats (all types averaged 34.4%). The average clutch size was 9.3; hatching dates were April 20 to July 10.
Stewardship Responsibility
References
- Literature Cited AboveLegend:
 View Online Publication
View Online Publication Austin, J. E., and M. R. Miller. 1995. Northern Pintail (Anas acuta). In The birds of North America, No. 163 (A. Poole and F. Gill, Eds.). Academy of Natural Sciences of Philadelphia and American Ornithologists’ Union. [Revised online 10 November 2014]
Austin, J. E., and M. R. Miller. 1995. Northern Pintail (Anas acuta). In The birds of North America, No. 163 (A. Poole and F. Gill, Eds.). Academy of Natural Sciences of Philadelphia and American Ornithologists’ Union. [Revised online 10 November 2014] Holm, I. 1984. Hatching success of upland nesting ducks in north central Montana in relation to vegetation cover. M.S. thesis, University of Montana, Missoula.
Holm, I. 1984. Hatching success of upland nesting ducks in north central Montana in relation to vegetation cover. M.S. thesis, University of Montana, Missoula. Marks, J.S., P. Hendricks, and D. Casey. 2016. Birds of Montana. Arrington, VA. Buteo Books. 659 pages.
Marks, J.S., P. Hendricks, and D. Casey. 2016. Birds of Montana. Arrington, VA. Buteo Books. 659 pages. Skaar, P.D. 1969. Birds of the Bozeman latilong: a compilation of data concerning the birds which occur between 45 and 46 N. latitude and 111 and 112 W. longitude, with current lists for Idaho, Montana, Wyoming, impinging Montana counties and Yellowstone National Park. Bozeman, MT. 132 p.
Skaar, P.D. 1969. Birds of the Bozeman latilong: a compilation of data concerning the birds which occur between 45 and 46 N. latitude and 111 and 112 W. longitude, with current lists for Idaho, Montana, Wyoming, impinging Montana counties and Yellowstone National Park. Bozeman, MT. 132 p.
- Additional ReferencesLegend:
 View Online Publication
View Online Publication
Do you know of a citation we're missing? [WWPC] Washington Water Power Company. 1995. 1994 wildlife report Noxon Rapids and Cabinet Gorge Reservoirs. Washington Water Power Company. Spokane, WA.
[WWPC] Washington Water Power Company. 1995. 1994 wildlife report Noxon Rapids and Cabinet Gorge Reservoirs. Washington Water Power Company. Spokane, WA. American Ornithologists’ Union [AOU]. 1998. Check-list of North American birds, 7th edition. American Ornithologists’ Union, Washington, D.C. 829 p.
American Ornithologists’ Union [AOU]. 1998. Check-list of North American birds, 7th edition. American Ornithologists’ Union, Washington, D.C. 829 p. Austin, J.E. and M.R. Miller. 1995. Northern Pintail (Anas acuta), in The Birds of North America, No. 163. A. Poole and F. Gill, eds. The Academy of Natural Sciences, Philadelphia and The American Ornithologists Union, Washington, D.C.
Austin, J.E. and M.R. Miller. 1995. Northern Pintail (Anas acuta), in The Birds of North America, No. 163. A. Poole and F. Gill, eds. The Academy of Natural Sciences, Philadelphia and The American Ornithologists Union, Washington, D.C. Banks, R.C. and P.F. Springer. 1994. A century of population trends of waterfowl in western North America. Studies in Avian Biology, No. 15: 134-146.
Banks, R.C. and P.F. Springer. 1994. A century of population trends of waterfowl in western North America. Studies in Avian Biology, No. 15: 134-146. Bayless, S.R. 1992. Duck population responses to water development in north central Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 69 p.
Bayless, S.R. 1992. Duck population responses to water development in north central Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 69 p. Belanger, L. 1988. Use of man-made ponds by dabbling duck broods. J. Wildl. Manage. 52(4): 718-723.
Belanger, L. 1988. Use of man-made ponds by dabbling duck broods. J. Wildl. Manage. 52(4): 718-723. Berg, P.F. 1955. A study of waterfowl broods in Eastern Montana with special reference to movements and the relationship of reservoir fencing to production. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 31 p.
Berg, P.F. 1955. A study of waterfowl broods in Eastern Montana with special reference to movements and the relationship of reservoir fencing to production. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 31 p. Bird Conservancy of the Rockies. 2017. Pocket Guide to Northern Prairie Birds. Brighton, CO: Bird Conservancy of the Rockies. 98 p.
Bird Conservancy of the Rockies. 2017. Pocket Guide to Northern Prairie Birds. Brighton, CO: Bird Conservancy of the Rockies. 98 p. Bramblett, R.G., and A.V. Zale. 2002. Montana Prairie Riparian Native Species Report. Montana Cooperative Fishery Research Unit, Montana State University - Bozeman.
Bramblett, R.G., and A.V. Zale. 2002. Montana Prairie Riparian Native Species Report. Montana Cooperative Fishery Research Unit, Montana State University - Bozeman. Butler, M.A. 1996. The validity of using artificial nests to assess nest-predation rates in prairie nesting ducks. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 82 p.
Butler, M.A. 1996. The validity of using artificial nests to assess nest-predation rates in prairie nesting ducks. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 82 p. Cameron, E. S. 1907. The birds of Custer and Dawson counties, Montana. Auk 24(3): 241-270.
Cameron, E. S. 1907. The birds of Custer and Dawson counties, Montana. Auk 24(3): 241-270. Carlsen, T.L. 1984. Waterfowl nesting on islands in two ponds of the Canyon Ferry Wildlife Management Area, Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 91 p.
Carlsen, T.L. 1984. Waterfowl nesting on islands in two ponds of the Canyon Ferry Wildlife Management Area, Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 91 p. Casagranda, L.G. 1955. A study of beaver-waterfowl relations in the mountainous area of Beaverhead County, Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 33 p.
Casagranda, L.G. 1955. A study of beaver-waterfowl relations in the mountainous area of Beaverhead County, Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 33 p. Casey, D. 2005. Rocky Mountain Front avian inventory. Final report. Prepared for the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service and The Nature Conservancy by the American Bird Conservancy, Kalispell, Montana.
Casey, D. 2005. Rocky Mountain Front avian inventory. Final report. Prepared for the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service and The Nature Conservancy by the American Bird Conservancy, Kalispell, Montana. Confluence Consulting Inc. 2010. Montana Department of Transportation Wetland Mitigation Monitoring Reports (various sites). MDT Helena, MT.
Confluence Consulting Inc. 2010. Montana Department of Transportation Wetland Mitigation Monitoring Reports (various sites). MDT Helena, MT. Confluence Consulting Inc. 2011. Montana Department of Transportation Wetland Mitigation Monitoring Reports (various sites). MDT Helena, MT.
Confluence Consulting Inc. 2011. Montana Department of Transportation Wetland Mitigation Monitoring Reports (various sites). MDT Helena, MT. Confluence Consulting Inc. 2013. Montana Department of Transportation Wetland Mitigation Monitoring Reports (various sites). MDT Helena, MT.
Confluence Consulting Inc. 2013. Montana Department of Transportation Wetland Mitigation Monitoring Reports (various sites). MDT Helena, MT. Cornely, J.E. 1982. Waterfowl production at Malheur National Wildlife Refuge, 1942-1980. Transactions of the 47th North American Wildlife and Natural Resources Conference. pp 559-571.
Cornely, J.E. 1982. Waterfowl production at Malheur National Wildlife Refuge, 1942-1980. Transactions of the 47th North American Wildlife and Natural Resources Conference. pp 559-571. Dickson, D.C. 1991. Systematic wildlife observations on the Blackfoot-Clearwater Wildlife Management Area. Montana Department of Fish, Wildlife and Parks. Missoula, MT. 14 pp. plus appendices and photographs.
Dickson, D.C. 1991. Systematic wildlife observations on the Blackfoot-Clearwater Wildlife Management Area. Montana Department of Fish, Wildlife and Parks. Missoula, MT. 14 pp. plus appendices and photographs. DuBois, K.L. 1979. An inventory of the avifauna in the Long Pines of Southeastern Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 113 p.
DuBois, K.L. 1979. An inventory of the avifauna in the Long Pines of Southeastern Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 113 p. ECON, Inc. (Ecological Consulting Service), Helena, MT., 1975, Colstrip 10 x 20 Area wildlife and wildlife habitat annual monitoring report, 1975. Proj. 71-23-A. December 31, 1975.
ECON, Inc. (Ecological Consulting Service), Helena, MT., 1975, Colstrip 10 x 20 Area wildlife and wildlife habitat annual monitoring report, 1975. Proj. 71-23-A. December 31, 1975. ECON, Inc. (Ecological Consulting Service), Helena, MT., 1977, Colstrip 10 x 20 Area wildlife and wildlife habitat annual monitoring report, 1977. Proj. 164-85-A. December 31, 1977.
ECON, Inc. (Ecological Consulting Service), Helena, MT., 1977, Colstrip 10 x 20 Area wildlife and wildlife habitat annual monitoring report, 1977. Proj. 164-85-A. December 31, 1977. ECON, Inc. (Ecological Consulting Service), Helena, MT., 1979, Annual wildllife report of the Colstrip Area for 1978. Proj. 195-85-A. April 6, 1979.
ECON, Inc. (Ecological Consulting Service), Helena, MT., 1979, Annual wildllife report of the Colstrip Area for 1978. Proj. 195-85-A. April 6, 1979. ECON, Inc. (Ecological Consulting Service), Helena, MT., 1979, Annual wildllife report of the Colstrip Area for 1979, including a special raptor research study. Proj. 216-85-A. March 1, 1980.
ECON, Inc. (Ecological Consulting Service), Helena, MT., 1979, Annual wildllife report of the Colstrip Area for 1979, including a special raptor research study. Proj. 216-85-A. March 1, 1980. ECON, Inc. (Ecological Consulting Service), Helena, MT., 1979, Area B four-section wildlife report. August 3, 1979.
ECON, Inc. (Ecological Consulting Service), Helena, MT., 1979, Area B four-section wildlife report. August 3, 1979. Ehrlich, P., D. Dobkin, and D. Wheye. 1988. The birder’s handbook: a field guide to the natural history of North American birds. Simon and Schuster Inc. New York. 785 pp.
Ehrlich, P., D. Dobkin, and D. Wheye. 1988. The birder’s handbook: a field guide to the natural history of North American birds. Simon and Schuster Inc. New York. 785 pp. Ellig, L.J. 1953. Waterfowl relationships to Greenfields Lake, Teton County, Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 49 p.
Ellig, L.J. 1953. Waterfowl relationships to Greenfields Lake, Teton County, Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 49 p. Fields, S.P. 2011. Factors influencing the density and distribution of breeding waterfowl in north-central Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 112 p.
Fields, S.P. 2011. Factors influencing the density and distribution of breeding waterfowl in north-central Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 112 p. Forman, Kurt J., 1993. Influence of skunk removal on nest success and breeding populations of upland nesting ducks. M.S. Thesis. University of Montana. Missoula, MT.
Forman, Kurt J., 1993. Influence of skunk removal on nest success and breeding populations of upland nesting ducks. M.S. Thesis. University of Montana. Missoula, MT. Gjersing, F.M. 1971. A study of waterfowl production on two rest rotation grazing units in northcentral Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 42 p.
Gjersing, F.M. 1971. A study of waterfowl production on two rest rotation grazing units in northcentral Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 42 p. Gjersing, F.M. 1975. Waterfowl production in relation to rest-rotation grazing. Journal of Range Management 28:37-42.
Gjersing, F.M. 1975. Waterfowl production in relation to rest-rotation grazing. Journal of Range Management 28:37-42. Gniadek, S. 1983. Southwest Glendive Wildlife Baseline Inventory. Miles City, Mont: Bureau of Land Management, Miles City District Office. 56 pp with appendices.
Gniadek, S. 1983. Southwest Glendive Wildlife Baseline Inventory. Miles City, Mont: Bureau of Land Management, Miles City District Office. 56 pp with appendices. Goodell, J. 2012. Morse Land Company Breeding Bird Inventory And Analysis. High Desert Museum. Bend, OR. 42 pp + Appendices.
Goodell, J. 2012. Morse Land Company Breeding Bird Inventory And Analysis. High Desert Museum. Bend, OR. 42 pp + Appendices. Hall, Nathan E. 1995. Effects of Striped Skunk removal on duck nest success in the Mission Valley, Montana. M.S. Thesis. University of Montana. Missoula, MT.
Hall, Nathan E. 1995. Effects of Striped Skunk removal on duck nest success in the Mission Valley, Montana. M.S. Thesis. University of Montana. Missoula, MT. Harmata, A.R. 1991. Impacts of oil and gas development on raptors associated with Kevin Rim, Montana. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. Unpublished report by the Kevin Rim Raptor Study Group. Prepared for the USDI BLM, Great Falls Resource Area, Great Falls, MT. 106 p.
Harmata, A.R. 1991. Impacts of oil and gas development on raptors associated with Kevin Rim, Montana. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. Unpublished report by the Kevin Rim Raptor Study Group. Prepared for the USDI BLM, Great Falls Resource Area, Great Falls, MT. 106 p. Hays, R., R.L. Eng, and C.V. Davis (preparers). 1984. A list of Montana birds. Helena, MT: MT Dept. of Fish, Wildlife & Parks.
Hays, R., R.L. Eng, and C.V. Davis (preparers). 1984. A list of Montana birds. Helena, MT: MT Dept. of Fish, Wildlife & Parks. Hendricks, P, S. Lenard, and C. Currier. 2012. Grassland Bird Surveys in North Valley County and Northwest Phillips County, Montana: 2011 Summary. Report to the USDI Bureau of Land Management. Montana Natural Heritage Program. Helena, MT. 7pp.
Hendricks, P, S. Lenard, and C. Currier. 2012. Grassland Bird Surveys in North Valley County and Northwest Phillips County, Montana: 2011 Summary. Report to the USDI Bureau of Land Management. Montana Natural Heritage Program. Helena, MT. 7pp. Hendricks, P., S. Lenard, D.M. Stagliano, and B.A. Maxell. 2013. Baseline nongame wildlife surveys on the Fort Peck Indian Reservation. Report to the Assiniboine and Sioux Tribes of the Fort Peck Indian Reservation. Montana Natural Heritage Program, Helena, MT. 83 p.
Hendricks, P., S. Lenard, D.M. Stagliano, and B.A. Maxell. 2013. Baseline nongame wildlife surveys on the Fort Peck Indian Reservation. Report to the Assiniboine and Sioux Tribes of the Fort Peck Indian Reservation. Montana Natural Heritage Program, Helena, MT. 83 p. Holm, J.W. 1984. Nest success and cover relationships of upland-nesting ducks in northcentral Montana. M.S. thesis. University of Montana. Missoula. 35 pp.
Holm, J.W. 1984. Nest success and cover relationships of upland-nesting ducks in northcentral Montana. M.S. thesis. University of Montana. Missoula. 35 pp. Hudson, M.S. 1980. Waterfowl production on three age-classes of stock ponds in north central Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 45 p.
Hudson, M.S. 1980. Waterfowl production on three age-classes of stock ponds in north central Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 45 p. Johnsgard, P.A. 1975. Waterfowl of North America. Bloomington, IN: Indiana University Press. 575 p.
Johnsgard, P.A. 1975. Waterfowl of North America. Bloomington, IN: Indiana University Press. 575 p. Johnsgard, P.A. 1979. Birds of the Great Plains: breeding species and their distribution. University of Nebraska Press, Lincoln. 539 pp.
Johnsgard, P.A. 1979. Birds of the Great Plains: breeding species and their distribution. University of Nebraska Press, Lincoln. 539 pp. Johnsgard, P.A. 1992. Birds of the Rocky Mountains with particular reference to national parks in the northern Rocky Mountain region. Lincoln: University of Nebraska Press. xi + 504 pp.
Johnsgard, P.A. 1992. Birds of the Rocky Mountains with particular reference to national parks in the northern Rocky Mountain region. Lincoln: University of Nebraska Press. xi + 504 pp. Johnson, D.H. and J.W. Grier. 1988. Determinants of breeding and distributions of ducks. Wildl. Monogr. 100: 1-37.
Johnson, D.H. and J.W. Grier. 1988. Determinants of breeding and distributions of ducks. Wildl. Monogr. 100: 1-37. Johnson, K.M. 1990. Aquatic vegetation, salinity, aquatic invertebrates, and duck brood use at Bowdoin National Wildlife Refuge, Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 77 p.
Johnson, K.M. 1990. Aquatic vegetation, salinity, aquatic invertebrates, and duck brood use at Bowdoin National Wildlife Refuge, Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 77 p. Joslin, Gayle, and Heidi B. Youmans. 1999. Effects of recreation on Rocky Mountain wildlife: a review for Montana. [Montana]: Montana Chapter of the Wildlife Society.
Joslin, Gayle, and Heidi B. Youmans. 1999. Effects of recreation on Rocky Mountain wildlife: a review for Montana. [Montana]: Montana Chapter of the Wildlife Society. Klett, A.T., T.L. Shaiffer, and D.H. Johnson. 1988. Duck nest success in the Prairie Pothole Region. J. Wildl. Manage. 52(3): 431-440.
Klett, A.T., T.L. Shaiffer, and D.H. Johnson. 1988. Duck nest success in the Prairie Pothole Region. J. Wildl. Manage. 52(3): 431-440. Knight, R.R. 1960. Vegetative characteristics of two water areas in Teton County, Montana, in relation to waterfowl usage. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 38 p.
Knight, R.R. 1960. Vegetative characteristics of two water areas in Teton County, Montana, in relation to waterfowl usage. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 38 p. Knight, R.R. 1965. Vegetative characteristics and waterfowl usage of a Montana water area. J. Wildl. Manage. 29(4):782-788.
Knight, R.R. 1965. Vegetative characteristics and waterfowl usage of a Montana water area. J. Wildl. Manage. 29(4):782-788. Lambing, J. H., D. A. Nimick, J. R. Knapton, and D. U. Palawski. 1994. Physical, chemical, and biological data for detailed study of the Sun River Irrigation Project, Freezout Lake Wildlife Management Area, and Benton Lake National Wildlife Refuge, west-central Montana, 1990-92, with selected data for 1987-89. Open-File Report 94-120, U.S. Geological Survey, Helena, Montana.
Lambing, J. H., D. A. Nimick, J. R. Knapton, and D. U. Palawski. 1994. Physical, chemical, and biological data for detailed study of the Sun River Irrigation Project, Freezout Lake Wildlife Management Area, and Benton Lake National Wildlife Refuge, west-central Montana, 1990-92, with selected data for 1987-89. Open-File Report 94-120, U.S. Geological Survey, Helena, Montana. Lenard, S. 2006. Birds of Blaine County, Riparian Point Count Surveys 2005. Report to the Bureau of LandManagement, Havre Field Station, Havre, Montana. Montana Natural Heritage Program, Helena, MT. 16pp.plus appendices.
Lenard, S. 2006. Birds of Blaine County, Riparian Point Count Surveys 2005. Report to the Bureau of LandManagement, Havre Field Station, Havre, Montana. Montana Natural Heritage Program, Helena, MT. 16pp.plus appendices. Lenard, S., Compiler. 2005. Surveys for Animal Species of Concern in Sage and Grassland Landscapes in Montana. An unpublished report to the Montana Department of Fish, Wildlife & Parks, State Wildlife Grants Program. Montana Natural Heritage Program, Helena, Montana. 63pp.
Lenard, S., Compiler. 2005. Surveys for Animal Species of Concern in Sage and Grassland Landscapes in Montana. An unpublished report to the Montana Department of Fish, Wildlife & Parks, State Wildlife Grants Program. Montana Natural Heritage Program, Helena, Montana. 63pp. Lenard, S., J. Carlson, J. Ellis, C. Jones, and C. Tilly. 2003. P. D. Skaar's Montana bird distribution, 6th edition. Montana Audubon, Helena, MT. 144 pp.
Lenard, S., J. Carlson, J. Ellis, C. Jones, and C. Tilly. 2003. P. D. Skaar's Montana bird distribution, 6th edition. Montana Audubon, Helena, MT. 144 pp. Lokemoen, J.T. 1993. Increasing waterfowl nesting success on islands and peninsulas. Ch. 13.2.11 In: Waterfowl Management Handbook. Fish and Wildlife Service Leaflet. 7 p.
Lokemoen, J.T. 1993. Increasing waterfowl nesting success on islands and peninsulas. Ch. 13.2.11 In: Waterfowl Management Handbook. Fish and Wildlife Service Leaflet. 7 p. Lokemoen, J.T., and R.O. Woodward. 1992. Nesting waterfowl and water birds on natural islands in the Dakotas and Montana. Wildlife Society Bulletin 20:163-171.
Lokemoen, J.T., and R.O. Woodward. 1992. Nesting waterfowl and water birds on natural islands in the Dakotas and Montana. Wildlife Society Bulletin 20:163-171. Lorang, K.D. 1979. Waterfowl and hunter use of Freezeout Lake Game Management Area. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, Montana: Montana State University. 79 p.
Lorang, K.D. 1979. Waterfowl and hunter use of Freezeout Lake Game Management Area. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, Montana: Montana State University. 79 p. Matthews, W.L. 1981. Broadus-Pumpkin Creek baseline inventory - wildlife. Bureau of Land Management, Miles City, MT. 83 p.
Matthews, W.L. 1981. Broadus-Pumpkin Creek baseline inventory - wildlife. Bureau of Land Management, Miles City, MT. 83 p. McCarthy, J.J. 1973. Response of nesting Canada geese (Branta canadensis) to islands in stockdams in northcentral Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 36 p.
McCarthy, J.J. 1973. Response of nesting Canada geese (Branta canadensis) to islands in stockdams in northcentral Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 36 p. Miller, M.G. 1980. The influence of habitat features on waterfowl productivity on stock reservoirs in south Valley County, Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 43 p.
Miller, M.G. 1980. The influence of habitat features on waterfowl productivity on stock reservoirs in south Valley County, Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 43 p. Montana Bird Distribution Committee. 2012. P.D. Skaar's Montana bird distribution. 7th Edition. Montana Audubon, Helena, Montana. 208 pp. + foldout map.
Montana Bird Distribution Committee. 2012. P.D. Skaar's Montana bird distribution. 7th Edition. Montana Audubon, Helena, Montana. 208 pp. + foldout map. Mora, M. A. 1995. Residues and trends of organochloride pesticide and polychlorinated biphenyls in birds from Texas, 1965-88. Technical Report 14. Washington, D.C.: U.S.D.I. National Biological Service. 26 p.
Mora, M. A. 1995. Residues and trends of organochloride pesticide and polychlorinated biphenyls in birds from Texas, 1965-88. Technical Report 14. Washington, D.C.: U.S.D.I. National Biological Service. 26 p. MT Fish, Wildlife & Parks. No date. Blackfoot-Clearwater Wildlife Management Area checklist.
MT Fish, Wildlife & Parks. No date. Blackfoot-Clearwater Wildlife Management Area checklist. Mundinger, J.G. 1975. The influence of rest-rotation grazing management on waterfowl production on stock-water reservoirs in Phillips County, Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 100 p.
Mundinger, J.G. 1975. The influence of rest-rotation grazing management on waterfowl production on stock-water reservoirs in Phillips County, Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 100 p. Oechsli, L.M. 2000. Ex-urban development in the Rocky Mountain West: consequences for native vegetation, wildlife diversity, and land-use planning in Big Sky, Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Montana State University, Bozeman. 73 p.
Oechsli, L.M. 2000. Ex-urban development in the Rocky Mountain West: consequences for native vegetation, wildlife diversity, and land-use planning in Big Sky, Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Montana State University, Bozeman. 73 p. Palawski, D.U., et al., 1991, Contaminant biomonitoring at the Benton Lake National Wildlife Refuge in 1988.
Palawski, D.U., et al., 1991, Contaminant biomonitoring at the Benton Lake National Wildlife Refuge in 1988. Palmer, R.S. 1962. Handbook of North American birds. Volume 1. Loons through flamingos. Yale University Press, New Haven. 567 pp.
Palmer, R.S. 1962. Handbook of North American birds. Volume 1. Loons through flamingos. Yale University Press, New Haven. 567 pp. Perkins, A. E. H. 2003. Habitat use, reproductive biology, and nest-site selection of ground-nesting birds at Freezout Lake WMA in central Montana. M.S. thesis, University of Montana, Missoula.
Perkins, A. E. H. 2003. Habitat use, reproductive biology, and nest-site selection of ground-nesting birds at Freezout Lake WMA in central Montana. M.S. thesis, University of Montana, Missoula. Raveling, D.G. and M.E. Heitmeyer. 1989. Relationships of population size and recruitement of pintails to habitat conditions at harvest. J. Wildl. Manage. 53(4): 1088-1103.
Raveling, D.G. and M.E. Heitmeyer. 1989. Relationships of population size and recruitement of pintails to habitat conditions at harvest. J. Wildl. Manage. 53(4): 1088-1103. Rhodes, O.E., Jr., L.M. Smith and M.H. Smith. 1991. Conservation and genetic resources in waterfowl. Trans. N. Amer. Wildl. & Nat. Res. Conf. 56:462-472.
Rhodes, O.E., Jr., L.M. Smith and M.H. Smith. 1991. Conservation and genetic resources in waterfowl. Trans. N. Amer. Wildl. & Nat. Res. Conf. 56:462-472. Rogers, R.R and A. Rogers. 1995. A survey of nesting ferruginous hawks (Buteo regalis) on public lands in Petroleum and Fergus counties, Montana. Prepared for the USDI Bureau of Land Management, Judith Resource Area. 17 p.
Rogers, R.R and A. Rogers. 1995. A survey of nesting ferruginous hawks (Buteo regalis) on public lands in Petroleum and Fergus counties, Montana. Prepared for the USDI Bureau of Land Management, Judith Resource Area. 17 p. Rundquist, V.M. 1973. Avian ecology on stock ponds in two vegetational types in north-central Montana. Ph.D. Dissertation. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 112 p.
Rundquist, V.M. 1973. Avian ecology on stock ponds in two vegetational types in north-central Montana. Ph.D. Dissertation. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 112 p. Saunders, A.A. 1914. The birds of Teton and northern Lewis & Clark counties, Montana. Condor 16:124-144.
Saunders, A.A. 1914. The birds of Teton and northern Lewis & Clark counties, Montana. Condor 16:124-144. Schladweiler, Philip, and John P. Weigand., 1983, Relationships of endrin and other chlorinated hydrocarbon compounds to wildlife in Montana, 1981-1982. September 1983.
Schladweiler, Philip, and John P. Weigand., 1983, Relationships of endrin and other chlorinated hydrocarbon compounds to wildlife in Montana, 1981-1982. September 1983. Sibley, D. 2014. The Sibley guide to birds. Alfred A. Knopf, New York, NY. 598 pp.
Sibley, D. 2014. The Sibley guide to birds. Alfred A. Knopf, New York, NY. 598 pp. Skaar, P. D., D. L. Flath, and L. S. Thompson. 1985. Montana bird distribution. Montana Academy of Sciences Monograph 3(44): ii-69.
Skaar, P. D., D. L. Flath, and L. S. Thompson. 1985. Montana bird distribution. Montana Academy of Sciences Monograph 3(44): ii-69. Smith, R.H. 1952. A study of waterfowl production on artificial reservoirs in eastern Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, Montana: Montana State University. 43 p.
Smith, R.H. 1952. A study of waterfowl production on artificial reservoirs in eastern Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, Montana: Montana State University. 43 p. Stewart, R. E., and H. A. Kantrud. 1973. Ecological distribution of breeding waterfowl populations in North Dakota. Journal of Wildlife Management 37(1):39-50.
Stewart, R. E., and H. A. Kantrud. 1973. Ecological distribution of breeding waterfowl populations in North Dakota. Journal of Wildlife Management 37(1):39-50. Stewart, R.E. and H.A. Kantrud. 1972. Population estimates of breeding birds in North Dakota. The Auk 89(4):766-788.
Stewart, R.E. and H.A. Kantrud. 1972. Population estimates of breeding birds in North Dakota. The Auk 89(4):766-788. Stewart, R.E. and H.A. Kantrud. 1974. Breeding waterfowl populations in the Prairie Pothole Region of North Dakota. Condor 76: 70-79.
Stewart, R.E. and H.A. Kantrud. 1974. Breeding waterfowl populations in the Prairie Pothole Region of North Dakota. Condor 76: 70-79. Swan River National Wildlife Refuge. 1982. Birds of the Swan River NWR. Kalispell, MT: NW MT Fish and Wildlife Center pamphlet.
Swan River National Wildlife Refuge. 1982. Birds of the Swan River NWR. Kalispell, MT: NW MT Fish and Wildlife Center pamphlet. Thompson, L.S. 1978. Species abundance and habitat relations of an insular montane avifauna. Condor 80(1):1-14.
Thompson, L.S. 1978. Species abundance and habitat relations of an insular montane avifauna. Condor 80(1):1-14. Thompson, L.S. 1981. Circle West wildlife monitoring study: Third annual report. Technical report No. 8. Montana Department of Natural Resources and Conservation. Helena, Montana.
Thompson, L.S. 1981. Circle West wildlife monitoring study: Third annual report. Technical report No. 8. Montana Department of Natural Resources and Conservation. Helena, Montana. TRC Environmental Corporation. 2009. Results of the 2008 grassland bird displacement study at the Judith Gap wind energy project, Wheatland County, Montana. Judith Gap Energy LLC. Chicago, IL. 24 pp + appendices.
TRC Environmental Corporation. 2009. Results of the 2008 grassland bird displacement study at the Judith Gap wind energy project, Wheatland County, Montana. Judith Gap Energy LLC. Chicago, IL. 24 pp + appendices. U.S. Forest Service. 1991. Forest and rangeland birds of the United States: Natural history and habitat use. U.S. Department of Agriculture, Forest Service Agricultural Handbook 688. 625 pages.
U.S. Forest Service. 1991. Forest and rangeland birds of the United States: Natural history and habitat use. U.S. Department of Agriculture, Forest Service Agricultural Handbook 688. 625 pages. USDI Fish and Wildlife Service., 1961, A Detailed report on fish and wildlife resources affected by McNamara Dam and Reservoir, Blackfoot River Project, Montana. June 1961.
USDI Fish and Wildlife Service., 1961, A Detailed report on fish and wildlife resources affected by McNamara Dam and Reservoir, Blackfoot River Project, Montana. June 1961. Waldt, R. 1995. The Pine Butte Swamp Preserve bird list. Choteau, MT: The Nature Conservancy. Updated August 1995.
Waldt, R. 1995. The Pine Butte Swamp Preserve bird list. Choteau, MT: The Nature Conservancy. Updated August 1995. Watts, C.R. and L.C. Eichhorn. 1981. Changes in the birds of central Montana. Proceedings of the Montana Academy of Sciences 40:31-40.
Watts, C.R. and L.C. Eichhorn. 1981. Changes in the birds of central Montana. Proceedings of the Montana Academy of Sciences 40:31-40. Western Energy Co., Colstrip, MT., 1980, Western Energy Company Rosebud Mine, Colstrip, Montana: Annual Wildlife Report, 1980.
Western Energy Co., Colstrip, MT., 1980, Western Energy Company Rosebud Mine, Colstrip, Montana: Annual Wildlife Report, 1980. Western Energy Co., Colstrip, MT., 1981, Western Energy Company Rosebud Mine, Colstrip, Montana: Annual Wildlife Report, 1981.
Western Energy Co., Colstrip, MT., 1981, Western Energy Company Rosebud Mine, Colstrip, Montana: Annual Wildlife Report, 1981.
- Web Search Engines for Articles on "Northern Pintail"
- Additional Sources of Information Related to "Birds"





