View in other NatureServe Network Field Guides
NatureServe
Montana
Utah
Wyoming
Idaho
Wisconsin
British Columbia
South Carolina
Yukon
California
New York
Leafy Spurge Hawkmoth - Hyles euphorbiae
General Description
The forewing upperside of the Spurge Hawkmoth (Hyles euphorbiae) is pale yellow-gray to lavender-gray, with a dark brown spot at the center of the costa and at the wing base, and a dark brown band running from the wing tip to the inner margin. The costal and outer margins may be dusted with pink or gray. The hindwing upperside is black with a pale greenish outer margin and a pinkish brown median band which becomes white at the inner margin. The wing span is about 64 -77 mm (Opler et al. 2010).
The larvae are also conspicuously colored, with a pronounced tail or "horn" near the rear end. Young larvae are variously patterned with green, yellow, and black. Older larvae have a distinctive red, black, and yellow pattern with a double row of white spots on each side and white speckles (Balaban and Balaban 2005).
Phenology
Adult Spurge Hawkmoths are present beginning in early to mid-summer (Batra 1983). The females lay eggs singly or in small clusters on spurge leaves. (Opler et al. 2010). After hatching, larvae consume leafy spurge leaves and flowers. Mature larvae enter the soil to pupate. There are one or two generations per year, with soil-inhabiting pupae as the overwintering stage (Batra 1983).
Diagnostic Characteristics
The larvae of the Bedstraw Hawkmoth (H. gallii) are somewhat similar. However, the Bedstraw Hawkmoth has a single row of spots, and the Spurge Hawksmoth has a double row of spots (Balaban and Balaban 2005).
Species Range
Montana Range
Range Descriptions
 Non-native
Non-native
Range Comments
Populations of the Spurge Hawkmoth are present in several western states, including Montana, Idaho, and Oregon. The Spurge Hawkmoth was the first classical biological agent released against leafy spurge in the United States, with approval for introduction granted in 1965 (Batra 1983).
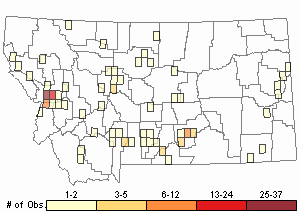
Observations in Montana Natural Heritage Program Database
Number of Observations: 220
(Click on the following maps and charts to see full sized version)
Map Help and Descriptions
Relative Density
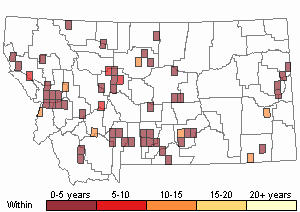
Recency
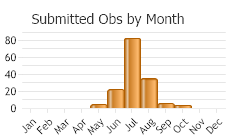
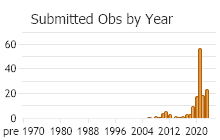
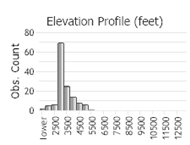 (Observations spanning multiple months or years are excluded from time charts)
(Observations spanning multiple months or years are excluded from time charts)
Habitat
Disturbed meadows and valleys with dense stands of leafy spurge (Opler et al. 2010).
Food Habits
The larvae feed on various species of
Euphorbia in the spurge family Euphorbiaceae. Adults feed on flower nectar (Opler et al. 2010).
Management
Stewardship Responsibility
References
- Literature Cited AboveLegend:
 View Online Publication
View Online Publication Batra, S.W.T. 1983. Establishment of Hyles euphorbiae (L.) (Lepidoptera: Sphingidae) in the United States for Control of the Weedy Spurges Euphorbia esula L. and E. cyparissias L. Journal of the New York Entomological Society, 91(4), 304–311.
Batra, S.W.T. 1983. Establishment of Hyles euphorbiae (L.) (Lepidoptera: Sphingidae) in the United States for Control of the Weedy Spurges Euphorbia esula L. and E. cyparissias L. Journal of the New York Entomological Society, 91(4), 304–311. Opler, P.A., K. Lotts, and T. Naberhaus, coordinators. 2010. Butterflies and moths of North America. Big Sky Institute, Bozeman, MT. Available at: www.butterfliesandmoths.org (Accessed 15 June 2015).
Opler, P.A., K. Lotts, and T. Naberhaus, coordinators. 2010. Butterflies and moths of North America. Big Sky Institute, Bozeman, MT. Available at: www.butterfliesandmoths.org (Accessed 15 June 2015).
- Additional ReferencesLegend:
 View Online Publication
View Online Publication
Do you know of a citation we're missing? Sater, S. 2022. The insects of Sevenmile Creek, a pictorial guide to their diversity and ecology. Undergraduate Thesis. Helena, MT: Carroll College. 242 p.
Sater, S. 2022. The insects of Sevenmile Creek, a pictorial guide to their diversity and ecology. Undergraduate Thesis. Helena, MT: Carroll College. 242 p.
- Web Search Engines for Articles on "Leafy Spurge Hawkmoth"
- Additional Sources of Information Related to "Insects"





