View in other NatureServe Network Field Guides
NatureServe
Montana
Utah
Wyoming
Idaho
Wisconsin
British Columbia
South Carolina
Yukon
California
New York
Eastern Cottontail - Sylvilagus floridanus
Native Species
Global Rank:
G5
State Rank:
SU
(see State Rank Reason below)
Agency Status
USFWS:
USFS:
BLM:
FWP SWAP:
SGIN
External Links
State Rank Reason (see State Rank above)
Species is known to be present in eastern Montana along the border with the Dakotas and is possibly expanding into areas further west. Identification of this species is challenging and data on range and area occupied are likely inaccurate
General Description
We do not yet have descriptive information on this species. Please try the buttons above to search for information from other sources.
Species Range
Montana Range
Range Descriptions
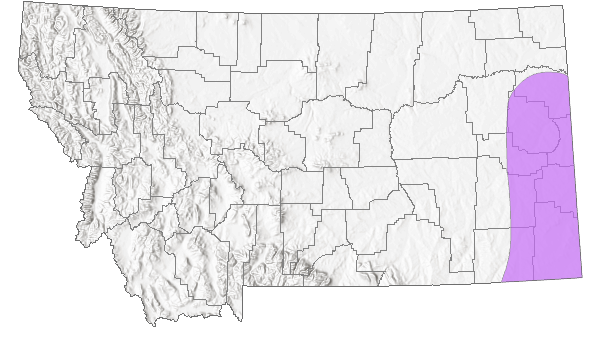
 Native
Native
Western Hemisphere Range

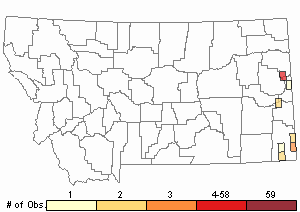
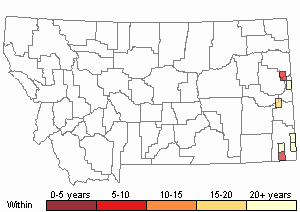
Observations in Montana Natural Heritage Program Database
Number of Observations: 81
(Click on the following maps and charts to see full sized version)
Map Help and Descriptions
Relative Density
Recency
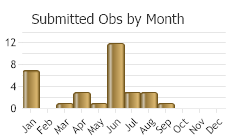
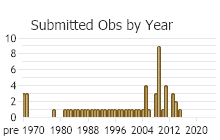
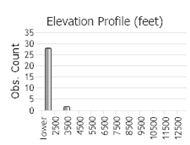 (Observations spanning multiple months or years are excluded from time charts)
(Observations spanning multiple months or years are excluded from time charts)
Migration
The Eastern Cottontail is non-migratory.
Habitat
Eastern Cottontails can be found in riparian habitats and brushy thickets.
National Vegetation Classification System Groups Associated with this Species
Forest and Woodland
Deciduous Forest and Woodland
Low Elevation - Xeric Forest and Woodland
Shrubland
Sagebrush Shrubland
Grassland
Lowland - Prairie Grassland
Sparse and Barren
Sparse and Barren
Wetland and Riparian
Alkaline - Saline Wetlands
Peatland
Riparian and Wetland Forest
Riparian Shrubland
Wet Meadow and Marsh
Human Land Use
Agriculture
Developed
Food Habits
Eastern Cottontails practice coprophagy (reingestion of fecal pellets) as do other Leporidae. Sylvilagus floridanus excretes 2 types of pellets. Soft, greenish pellets are reingested and then completely digested providing vitamin supplementation.
Ecology
Sylvilagus floridanus has been reported to be completely allopatric with Sylvilagus nuttalli (Hall & Kelson 1951). The two species have similar habitat preferences. Their situation in eastern Montana is not clear.
Reproductive Characteristics
Eastern Cottontails breed March through September, with induced ovulation. Litters are of 1 to 9 young, with an average of 4 to 5. Females may breed during their first year, males rarely do. The young are born in an elliptical nest lined with vegetation and fur.
Stewardship Responsibility
References
- Literature Cited AboveLegend:
 View Online Publication
View Online Publication Hall, E.R. and K.R. Kelson. 1951. A new subspecies of Microtus montanus from Montana and comments on Microtus canicaudus Miller. University of Kansas Publications, Museum of Natural History 5 (7):73-79.
Hall, E.R. and K.R. Kelson. 1951. A new subspecies of Microtus montanus from Montana and comments on Microtus canicaudus Miller. University of Kansas Publications, Museum of Natural History 5 (7):73-79.
- Additional ReferencesLegend:
 View Online Publication
View Online Publication
Do you know of a citation we're missing? Bauer, Delane, 2002, 2002 Four Seasons Wildlife Study. Savage Mine Report, Richland County, Montana.
Bauer, Delane, 2002, 2002 Four Seasons Wildlife Study. Savage Mine Report, Richland County, Montana. Bergeron, D.J. and R.W. Seabloom. 1981. Habitat partitioning by eastern and desert cottontails in southwest North Dakota. Prairie Naturalist. 13: 105-110.
Bergeron, D.J. and R.W. Seabloom. 1981. Habitat partitioning by eastern and desert cottontails in southwest North Dakota. Prairie Naturalist. 13: 105-110. Chapman, J. A., J. G. Hockman, and M. M. Ojeda. 1980. Sylvilagus floridanus. Mamm. Species 136:1-8.
Chapman, J. A., J. G. Hockman, and M. M. Ojeda. 1980. Sylvilagus floridanus. Mamm. Species 136:1-8. Foresman, K.R. 2001. The wild mammals of Montana. American Society of Mammalogists, Special Publication Number 12. Lawrence, KS. 278 pp.
Foresman, K.R. 2001. The wild mammals of Montana. American Society of Mammalogists, Special Publication Number 12. Lawrence, KS. 278 pp. Foresman, K.R. 2012. Mammals of Montana. Second edition. Mountain Press Publishing, Missoula, Montana. 429 pp.
Foresman, K.R. 2012. Mammals of Montana. Second edition. Mountain Press Publishing, Missoula, Montana. 429 pp. Hoffmann, R.S. and D.L. Pattie. 1968. A guide to Montana mammals: identification, habitat, distribution, and abundance. Missoula, MT: University of Montana. 133 p.
Hoffmann, R.S. and D.L. Pattie. 1968. A guide to Montana mammals: identification, habitat, distribution, and abundance. Missoula, MT: University of Montana. 133 p. Joslin, Gayle, and Heidi B. Youmans. 1999. Effects of recreation on Rocky Mountain wildlife: a review for Montana. [Montana]: Montana Chapter of the Wildlife Society.
Joslin, Gayle, and Heidi B. Youmans. 1999. Effects of recreation on Rocky Mountain wildlife: a review for Montana. [Montana]: Montana Chapter of the Wildlife Society. Lampe, R.P., J.K. Jones Jr., R.S. Hoffmann, and E.C. Birney. 1974. The mammals of Carter County, southeastern Montana. Occa. Pap. Mus. Nat. Hist. Univ. Kan. 25:1-39.
Lampe, R.P., J.K. Jones Jr., R.S. Hoffmann, and E.C. Birney. 1974. The mammals of Carter County, southeastern Montana. Occa. Pap. Mus. Nat. Hist. Univ. Kan. 25:1-39. Land & Water Consulting, Inc., Missoula, MT., 2002, Montana Dept. of Transportation Wetland Mitigation Monitoring Report, Year 2001: Big Spring Creek, Lewistown, Montana. Proj. No. 130091.029. July 2002. In 2001 Wetland Mitigation Monitoring Reports, Vol. I.
Land & Water Consulting, Inc., Missoula, MT., 2002, Montana Dept. of Transportation Wetland Mitigation Monitoring Report, Year 2001: Big Spring Creek, Lewistown, Montana. Proj. No. 130091.029. July 2002. In 2001 Wetland Mitigation Monitoring Reports, Vol. I. Reid, F. 2006. Peterson Field Guide to Mammals of North America, 4th Edition. Houghton Mifflin Company: Boston and New York, 608 pp.
Reid, F. 2006. Peterson Field Guide to Mammals of North America, 4th Edition. Houghton Mifflin Company: Boston and New York, 608 pp. Schladweiler, Philip, and John P. Weigand., 1983, Relationships of endrin and other chlorinated hydrocarbon compounds to wildlife in Montana, 1981-1982. September 1983.
Schladweiler, Philip, and John P. Weigand., 1983, Relationships of endrin and other chlorinated hydrocarbon compounds to wildlife in Montana, 1981-1982. September 1983.
- Web Search Engines for Articles on "Eastern Cottontail"
- Additional Sources of Information Related to "Mammals"





