View in other NatureServe Network Field Guides
NatureServe
Montana
Utah
Wyoming
Idaho
Wisconsin
British Columbia
South Carolina
Yukon
California
New York
Northern Bog Violet - Viola nephrophylla
Other Names:
Viola pratincola, Viola nephrophylla var. cognata
Native Species
Global Rank:
G5
State Rank:
S3S4
(see State Rank Reason below)
C-value:
8
Agency Status
USFWS:
USFS:
BLM:
State Rank Reason (see State Rank above)
Numerous collections from Montana at MONTU, particularly from west of the continental divide. Though widespread in western Montana in appropriate habitat, usually not abundant.
General Description
Plants glabrous, without rhizomes or stolons. Stems lacking; peduncles 5–20 cm. Leaf blades 2–5 cm wide, broadly cordate with crenate margins; stipules narrow. Flowers 12–25 mm long, blue; the lower 3 petals white at the base, bearded; spur 2–3 mm long; style glabrous. Capsule 6–8 mm long (
Lesica et al. 2012. Manual of Montana Vascular Plants. BRIT Press. Fort Worth, TX)..
Diagnostic Characteristics
Viola species exhibit great phenotypic variation. Leaf and stem sizes usually increase a lot between early spring and late summer (Little in FNA 2015). Stem, leaf, and flower sizes vary with environmental factors, such as aspect, light, soil moisture, and other soil properties (Little in FNA 2015). Hybridization among the blue-flowered, acaulescent Violets in eastern North America is well documented (Little in FNA 2015).
Viola affinis and many of the Viola nephrophylla herbarium specimens across their range were considered to essentially be the same taxon (Little in FNA 2015). However, in a taxonomic revision of the 'blue-flowered, acaulescent Violets' McKinney (1992) maintained the separation of Viola affinis and Viola nephrophylla. Viola affinis (and the synonym of Viola sororia var. affinis) is considered to occur in North America in Ontario, Minnesota, and eastward (Little in FNA 2015). Specimens collected in Montana and annotated to Viola sororia var. affinis are referred back to what was often their original identification as Viola nephrophylla.
Viola nephrophylla - Northern Bog Violet [Source is Lesica et al. 2012 unless otherwise noted.]
*Stems: Acaulescent without stolons and rhizomes. Rhizomes present (Little in FNA 2015).
*Inflorescence: Peduncles 5-20 cm long, usually glabrous.
*Leaves: Blades 2–5 cm wide, broadly cordate with dentate margins.
*Stipules: Narrow. Margins entire or with a border of hairs and apex acute (Little in FNA 2015).
*Flowers: Deep blue or violet, 12–25 mm long. Lower 3 petals bearded and with a white base. Sepals ovate and without cilia on the margins. Spur 2–3 mm long. Spur 1-2 mm (Little in FNA 2015). Style tip glabrous.
*Fruit: Capsule 6-8 mm long.
*Habitat: Wet, organic soil of meadows, marshes, and fens.
Species Range
Montana Range
Range Descriptions
 Native
Native
Range Comments
BC to NL south to CA, NM, MN and NY (Lesica et al. 2012. Manual of Montana Vascular Plants. BRIT Press. Fort Worth, TX).
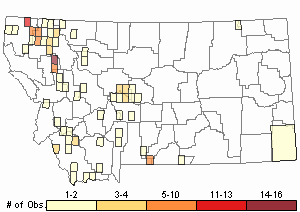
Observations in Montana Natural Heritage Program Database
Number of Observations: 147
(Click on the following maps and charts to see full sized version)
Map Help and Descriptions
Relative Density
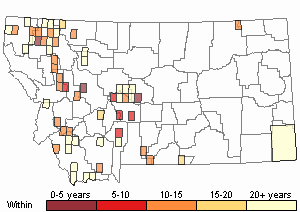
Recency
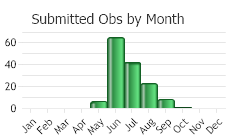
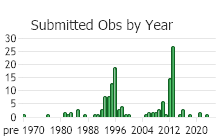
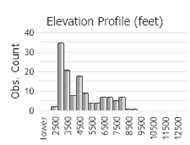 (Observations spanning multiple months or years are excluded from time charts)
(Observations spanning multiple months or years are excluded from time charts)
Habitat
Ecology
POLLINATORS The following animal species have been reported as pollinators of this plant species or its genus where their geographic ranges overlap:
Bombus vagans,
Bombus pensylvanicus,
Bombus bimaculatus,
Bombus griseocollis, and
Bombus impatiens (Colla and Dumesh 2010, Williams et al. 2014).
Stewardship Responsibility
References
- Literature Cited AboveLegend:
 View Online Publication
View Online Publication Colla, S.R. and S. Dumesh. 2010. The bumble bees of southern Ontario: notes on natural history and distribution. Journal of the Entomological Society of Ontario 141:39-68.
Colla, S.R. and S. Dumesh. 2010. The bumble bees of southern Ontario: notes on natural history and distribution. Journal of the Entomological Society of Ontario 141:39-68. Flora of North America Editorial Committee, eds. 2015. Flora of North America north of Mexico, Volume 6. Magnoliophyta: Cucurbitaceae to Droseraceae. Oxford University Press, Inc. New York.
Flora of North America Editorial Committee, eds. 2015. Flora of North America north of Mexico, Volume 6. Magnoliophyta: Cucurbitaceae to Droseraceae. Oxford University Press, Inc. New York. Hitchcock, C.L. and A. Cronquist. 2018. Flora of the Pacific Northwest: An Illustrated Manual. Second Edition. Giblin, D.E., B.S. Legler, P.F. Zika, and R.G. Olmstead (eds). Seattle, WA: University of Washington Press in Association with Burke Museum of Natural History and Culture. 882 p.
Hitchcock, C.L. and A. Cronquist. 2018. Flora of the Pacific Northwest: An Illustrated Manual. Second Edition. Giblin, D.E., B.S. Legler, P.F. Zika, and R.G. Olmstead (eds). Seattle, WA: University of Washington Press in Association with Burke Museum of Natural History and Culture. 882 p. Lesica, P., M.T. Lavin, and P.F. Stickney. 2012. Manual of Montana Vascular Plants. Fort Worth, TX: BRIT Press. viii + 771 p.
Lesica, P., M.T. Lavin, and P.F. Stickney. 2012. Manual of Montana Vascular Plants. Fort Worth, TX: BRIT Press. viii + 771 p. Williams, P., R. Thorp, L. Richardson, and S. Colla. 2014. Bumble Bees of North America. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press. 208 p.
Williams, P., R. Thorp, L. Richardson, and S. Colla. 2014. Bumble Bees of North America. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press. 208 p.
- Additional ReferencesLegend:
 View Online Publication
View Online Publication
Do you know of a citation we're missing? Culver, D.R. 1994. Floristic analysis of the Centennial Region, Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Montana State University, Bozeman. 199 pp.
Culver, D.R. 1994. Floristic analysis of the Centennial Region, Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Montana State University, Bozeman. 199 pp. Lesica, P., M.T. Lavin, and P.F. Stickney. 2022. Manual of Montana Vascular Plants, Second Edition. Fort Worth, TX: BRIT Press. viii + 779 p.
Lesica, P., M.T. Lavin, and P.F. Stickney. 2022. Manual of Montana Vascular Plants, Second Edition. Fort Worth, TX: BRIT Press. viii + 779 p. Simanonok, M. 2018. Plant-pollinator network assembly after wildfire. Ph.D. Dissertation. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 123 p.
Simanonok, M. 2018. Plant-pollinator network assembly after wildfire. Ph.D. Dissertation. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 123 p. Simanonok, M.P. and L.A. Burkle. 2019. Nesting success of wood-cavity-nesting bees declines with increasing time since wildfire. Ecology and Evolution 9:12436-12445.
Simanonok, M.P. and L.A. Burkle. 2019. Nesting success of wood-cavity-nesting bees declines with increasing time since wildfire. Ecology and Evolution 9:12436-12445.
- Web Search Engines for Articles on "Northern Bog Violet"





