View in other NatureServe Network Field Guides
NatureServe
Montana
Utah
Wyoming
Idaho
Wisconsin
British Columbia
South Carolina
Yukon
California
New York
Hybrid White Willow - Salix x fragilis
Other Names:
Brittle Willow, Crack Willow,
Salix ×rubens, Salix fragilis, Salix alba × Salix euxina
General Description
Tree or large shrub to 25 m. Twigs tan, pubescent. Leaf blades 3–10 cm long, narrowly lanceolate with serrate margins, glabrous to sparsely hairy, glaucous below. Female catkins 2–8 cm long, emerging with the leaves on leafy branchlets 1–3 cm long; scales pale, long-hairy, deciduous. Capsules 3–5 mm long, glabrous; stipes 0.5–1 mm long; styles ca. 0.5 mm long (
Lesica et al. 2012. Manual of Montana Vascular Plants. BRIT Press. Fort Worth, TX).
Diagnostic Characteristics
The identity of our common, naturalized tree willow has been the source of taxonomic and nomenclatural confusion. It is now believed to be a hybrid between Salix alba x Salix euxina. The name Salix euxina was published in 2009 for the one parent species that had previously been known as Salix fragilis. At that time, it was also decided that the name Salix fragilis should be used for the hybrid taxa and not the parent species. The name Salix x rubens has sometimes been applied to these hybrids (Dorn 2010, Argus 2010).
Species Range
Montana Range
Range Descriptions
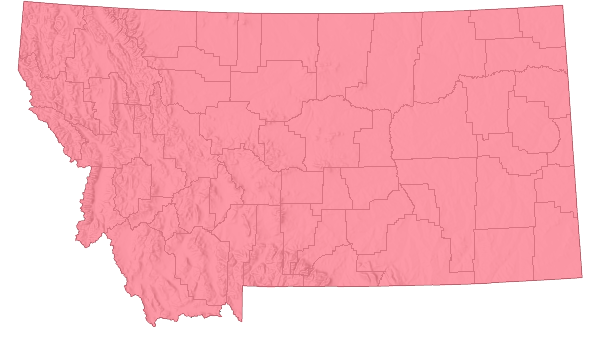
 Non-native
Non-native
Range Comments
Introduced to much of temperate North America; native to Eurasia and cultivated as an ornamental or for wildlife habitat (Lesica et al. 2012. Manual of Montana Vascular Plants. BRIT Press. Fort Worth, TX).
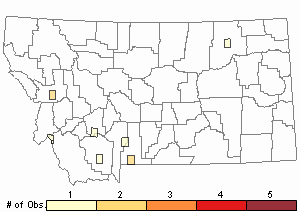
Observations in Montana Natural Heritage Program Database
Number of Observations: 10
(Click on the following maps and charts to see full sized version)
Map Help and Descriptions
Relative Density
Recency
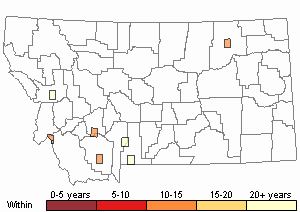
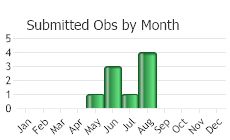
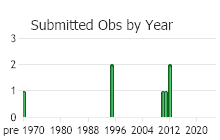
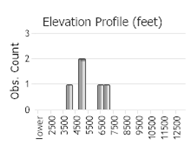 (Observations spanning multiple months or years are excluded from time charts)
(Observations spanning multiple months or years are excluded from time charts)
Habitat
Ecology
POLLINATORS The following animal species have been reported as pollinators of this plant species or its genus where their geographic ranges overlap:
Bombus vagans,
Bombus bifarius,
Bombus fervidus,
Bombus frigidus,
Bombus huntii,
Bombus melanopygus,
Bombus ternarius,
Bombus terricola,
Bombus sitkensis,
Bombus occidentalis,
Bombus pensylvanicus,
Bombus bimaculatus,
Bombus griseocollis,
Bombus impatiens, and
Bombus suckleyi (Plath 1934, Macior 1968, Heinrich 1976, Thorp et al. 1983, Colla and Dumesh 2010, Colla et al. 2011, Koch et al. 2012, Williams et al. 2014).
Management
Stewardship Responsibility
References
- Literature Cited AboveLegend:
 View Online Publication
View Online Publication Colla, S., L. Richardson, and P. Williams. 2011. Bumble bees of the eastern United States. Washington, DC: USDA Forest Service, Pollinator Partnership. 103 p.
Colla, S., L. Richardson, and P. Williams. 2011. Bumble bees of the eastern United States. Washington, DC: USDA Forest Service, Pollinator Partnership. 103 p. Colla, S.R. and S. Dumesh. 2010. The bumble bees of southern Ontario: notes on natural history and distribution. Journal of the Entomological Society of Ontario 141:39-68.
Colla, S.R. and S. Dumesh. 2010. The bumble bees of southern Ontario: notes on natural history and distribution. Journal of the Entomological Society of Ontario 141:39-68. Koch, J., J. Strange, and P. Williams. 2012. Bumble bees of the western United States. Washington, DC: USDA Forest Service, Pollinator Partnership. 143 p.
Koch, J., J. Strange, and P. Williams. 2012. Bumble bees of the western United States. Washington, DC: USDA Forest Service, Pollinator Partnership. 143 p. Lesica, P., M.T. Lavin, and P.F. Stickney. 2012. Manual of Montana Vascular Plants. Fort Worth, TX: BRIT Press. viii + 771 p.
Lesica, P., M.T. Lavin, and P.F. Stickney. 2012. Manual of Montana Vascular Plants. Fort Worth, TX: BRIT Press. viii + 771 p. Macior, L.M. 1968. Bombus (Hymenoptera, Apidae) queen foraging in relation to vernal pollination in Wisconsin. Ecology 49:20-25.
Macior, L.M. 1968. Bombus (Hymenoptera, Apidae) queen foraging in relation to vernal pollination in Wisconsin. Ecology 49:20-25. Plath, O.E. 1934. Bumblebees and their ways. New York, NY: Macmillan Company. 201 p.
Plath, O.E. 1934. Bumblebees and their ways. New York, NY: Macmillan Company. 201 p. Thorp, R.W., D.S. Horning, and L.L. Dunning. 1983. Bumble bees and cuckoo bumble bees of California (Hymenoptera: Apidae). Bulletin of the California Insect Survey 23:1-79.
Thorp, R.W., D.S. Horning, and L.L. Dunning. 1983. Bumble bees and cuckoo bumble bees of California (Hymenoptera: Apidae). Bulletin of the California Insect Survey 23:1-79. Williams, P., R. Thorp, L. Richardson, and S. Colla. 2014. Bumble Bees of North America. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press. 208 p.
Williams, P., R. Thorp, L. Richardson, and S. Colla. 2014. Bumble Bees of North America. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press. 208 p.
- Additional ReferencesLegend:
 View Online Publication
View Online Publication
Do you know of a citation we're missing? Argus, G. 2010. Salix. In: Flora of North America Editorial Committee, eds. 1993+. Flora of North America North of Mexico. 16+ vols. New York and Oxford. Vol. 7.
Argus, G. 2010. Salix. In: Flora of North America Editorial Committee, eds. 1993+. Flora of North America North of Mexico. 16+ vols. New York and Oxford. Vol. 7. Culver, D.R. 1994. Floristic analysis of the Centennial Region, Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Montana State University, Bozeman. 199 pp.
Culver, D.R. 1994. Floristic analysis of the Centennial Region, Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Montana State University, Bozeman. 199 pp. Dorn, R.D. 2010. The genus Salix in North America north of Mexico. 59 pp.
Dorn, R.D. 2010. The genus Salix in North America north of Mexico. 59 pp. Lesica, P., M.T. Lavin, and P.F. Stickney. 2022. Manual of Montana Vascular Plants, Second Edition. Fort Worth, TX: BRIT Press. viii + 779 p.
Lesica, P., M.T. Lavin, and P.F. Stickney. 2022. Manual of Montana Vascular Plants, Second Edition. Fort Worth, TX: BRIT Press. viii + 779 p. Little, E.L., Jr. 1979. Checklist of United States trees (native and naturalized). Agriculture Handbook No. 541. U.S. Forest Service, Washington, D.C. 375 pp.
Little, E.L., Jr. 1979. Checklist of United States trees (native and naturalized). Agriculture Handbook No. 541. U.S. Forest Service, Washington, D.C. 375 pp.
- Web Search Engines for Articles on "Hybrid White Willow"





