View in other NatureServe Network Field Guides
NatureServe
Montana
Utah
Wyoming
Idaho
Wisconsin
British Columbia
South Carolina
Yukon
California
New York
Glaucous Gentian - Gentiana glauca
State Rank Reason (see State Rank above)
Rare in Montana, where it is has been documented only from Glacier National Park. Current population levels and trends are unknown, though it was described as locally common at the collection sites. Its high-elevation habitat is inaccessible, and there are no obvious threats. Additional sites are likely to be documented if surveys were to be conducted.
General Description
Glaucous Gentian is a glabrous, perennial herb. Its stems are 3-10 cm high and arise from rosettes that arise from creeping rhizomes. The fleshy rosette leaves are egg-shaped and 1-2 cm long, while stem leaves of fertile rosettes are opposite and smaller. 3-5 crowded, short-stalked flowers arise from the axils of the upper leaves, or bracts. The tubular, blue corollas are 1-2 cm long and have 5 erect lobes with unfringed plaits between the lobes on the insides. The 5-lobed calyx is ca. 4-7 mm long, and the 5 stamens are attached to the inside of the corolla tube. The fruit is a stalked, short, tubular, many-seeded capsule.
Phenology
Flowering in late July-early August.
Diagnostic Characteristics
Gentiana prostrata has creeping stems but bears only one flower per stem. Gentiana calycosa has flowers greater than 2 cm long. Gentianella propinqua has a slender taproot.
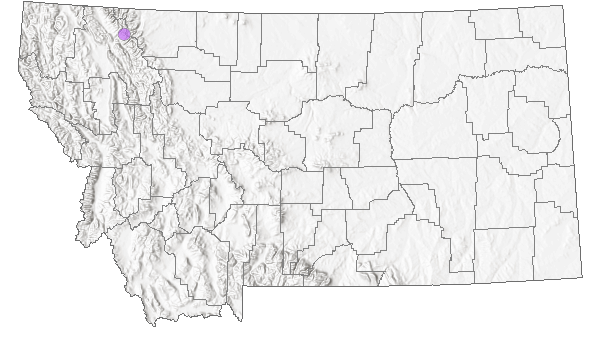
Species Range
Montana Range
Range Descriptions
 Native
Native
Range Comments
AK south to WA and nw. MT. Peripheral.
Observations in Montana Natural Heritage Program Database
Number of Observations: 3
(Click on the following maps and charts to see full sized version)
Map Help and Descriptions
Relative Density
Recency
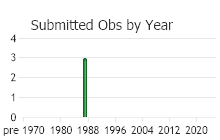
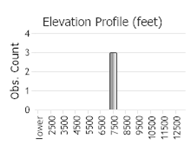 (Observations spanning multiple months or years are excluded from time charts)
(Observations spanning multiple months or years are excluded from time charts)
Habitat
Wet, boggy tundra in the alpine zone.
National Vegetation Classification System Groups Associated with this Species
Alpine
Alpine - Vegetated
Wetland and Riparian
Alpine Riparian and Wetland
Wet Meadow and Marsh
Ecology
POLLINATORS The following animal species have been reported as pollinators of this plant species or its genus where their geographic ranges overlap:
Bombus appositus,
Bombus fervidus,
Bombus flavifrons,
Bombus sylvicola,
Bombus pensylvanicus, and
Bombus kirbiellus (Colla and Dumesh 2010, Pyke et al. 2012, Williams et al. 2014, Ogilvie and Thomson 2015).
Stewardship Responsibility
References
- Literature Cited AboveLegend:
 View Online Publication
View Online Publication Colla, S.R. and S. Dumesh. 2010. The bumble bees of southern Ontario: notes on natural history and distribution. Journal of the Entomological Society of Ontario 141:39-68.
Colla, S.R. and S. Dumesh. 2010. The bumble bees of southern Ontario: notes on natural history and distribution. Journal of the Entomological Society of Ontario 141:39-68. Ogilvie, J.E. and J.D. Thomson. 2015. Male bumble bees are important pollinators of a late-blooming plant. Arthropod-Plant Interactions 9:205-213.
Ogilvie, J.E. and J.D. Thomson. 2015. Male bumble bees are important pollinators of a late-blooming plant. Arthropod-Plant Interactions 9:205-213. Pyke, G.H., D.W. Inouye, and J.D. Thomson. 2012. Local geographic distributions of bumble bees near Crested Butte, Colorado: competition and community structure revisited. Environmental Entomology 41(6): 1332-1349.
Pyke, G.H., D.W. Inouye, and J.D. Thomson. 2012. Local geographic distributions of bumble bees near Crested Butte, Colorado: competition and community structure revisited. Environmental Entomology 41(6): 1332-1349. Williams, P., R. Thorp, L. Richardson, and S. Colla. 2014. Bumble Bees of North America. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press. 208 p.
Williams, P., R. Thorp, L. Richardson, and S. Colla. 2014. Bumble Bees of North America. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press. 208 p.
- Additional ReferencesLegend:
 View Online Publication
View Online Publication
Do you know of a citation we're missing? Iltis, H.H. 1965. The genus Gentianopsis (Gentianaceae): transfers and phytogeographic comments. Sida 2:129-153.
Iltis, H.H. 1965. The genus Gentianopsis (Gentianaceae): transfers and phytogeographic comments. Sida 2:129-153. Lesica, P., M.T. Lavin, and P.F. Stickney. 2012. Manual of Montana Vascular Plants. Fort Worth, TX: BRIT Press. viii + 771 p.
Lesica, P., M.T. Lavin, and P.F. Stickney. 2012. Manual of Montana Vascular Plants. Fort Worth, TX: BRIT Press. viii + 771 p. Lesica, P., M.T. Lavin, and P.F. Stickney. 2022. Manual of Montana Vascular Plants, Second Edition. Fort Worth, TX: BRIT Press. viii + 779 p.
Lesica, P., M.T. Lavin, and P.F. Stickney. 2022. Manual of Montana Vascular Plants, Second Edition. Fort Worth, TX: BRIT Press. viii + 779 p.
- Web Search Engines for Articles on "Glaucous Gentian"





