View in other NatureServe Network Field Guides
NatureServe
Montana
Utah
Wyoming
Idaho
Wisconsin
British Columbia
South Carolina
Yukon
California
New York
Gold-moss - Sedum acre
Other Names:
Goldmoss Stonecrop, Mossy Stonecrop
General Description
Stems erect, simple or branched, 2–10 cm. Leaves ovoid, sessile, 3–5 mm long. Flowers 5-merous; petals yellow, lanceolate, 4–5 mm long. Follicles spreading, 5–6 mm long; styles straight, ca. 1 mm long (
Lesica et al. 2012. Manual of Montana Vascular Plants. BRIT Press. Fort Worth, TX).
Species Range
Montana Range
Range Descriptions
 Non-native
Non-native
Range Comments
Introduced to much of northern U.S. and adjacent Canada; native to Europe (Lesica et al. 2012. Manual of Montana Vascular Plants. BRIT Press. Fort Worth, TX).
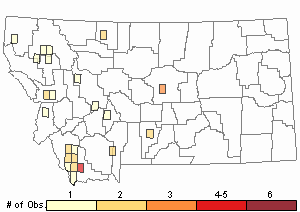
Observations in Montana Natural Heritage Program Database
Number of Observations: 37
(Click on the following maps and charts to see full sized version)
Map Help and Descriptions
Relative Density
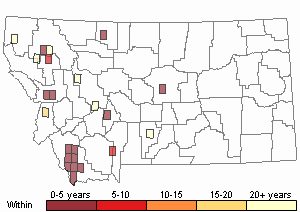
Recency
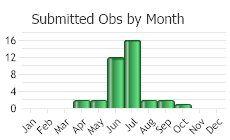
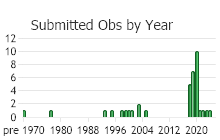
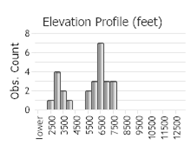 (Observations spanning multiple months or years are excluded from time charts)
(Observations spanning multiple months or years are excluded from time charts)
Habitat
Ecology
POLLINATORS The following animal species have been reported as pollinators of this plant species or its genus where their geographic ranges overlap:
Bombus bifarius,
Bombus flavifrons,
Bombus frigidus,
Bombus huntii,
Bombus melanopygus,
Bombus sylvicola,
Bombus occidentalis,
Bombus griseocollis,
Bombus insularis, and
Bombus kirbiellus (Macior 1974, Thorp et al. 1983, Shaw and Taylor 1986, Wilson et al. 2010, Miller-Struttmann and Galen 2014).
Management
Stewardship Responsibility
References
- Literature Cited AboveLegend:
 View Online Publication
View Online Publication Lesica, P., M.T. Lavin, and P.F. Stickney. 2012. Manual of Montana Vascular Plants. Fort Worth, TX: BRIT Press. viii + 771 p.
Lesica, P., M.T. Lavin, and P.F. Stickney. 2012. Manual of Montana Vascular Plants. Fort Worth, TX: BRIT Press. viii + 771 p. Macior, L.M. 1974. Pollination ecology of the Front Range of the Colorado Rocky Mountains. Melanderia 15: 1-59.
Macior, L.M. 1974. Pollination ecology of the Front Range of the Colorado Rocky Mountains. Melanderia 15: 1-59. Miller-Struttmann, N.E. and C. Galen. 2014. High-altitude multi-taskers: bumble bee food plant use broadens along an altitudinal productivity gradient. Oecologia 176:1033-1045.
Miller-Struttmann, N.E. and C. Galen. 2014. High-altitude multi-taskers: bumble bee food plant use broadens along an altitudinal productivity gradient. Oecologia 176:1033-1045. Shaw, D.C. and R.J. Taylor.1986. Pollination ecology of an alpine fell-field community in the North Cascades. Northwest Science 60:21-31.
Shaw, D.C. and R.J. Taylor.1986. Pollination ecology of an alpine fell-field community in the North Cascades. Northwest Science 60:21-31. Thorp, R.W., D.S. Horning, and L.L. Dunning. 1983. Bumble bees and cuckoo bumble bees of California (Hymenoptera: Apidae). Bulletin of the California Insect Survey 23:1-79.
Thorp, R.W., D.S. Horning, and L.L. Dunning. 1983. Bumble bees and cuckoo bumble bees of California (Hymenoptera: Apidae). Bulletin of the California Insect Survey 23:1-79. Wilson, J.S., L.E. Wilson, L.D. Loftis, and T. Griswold. 2010. The montane bee fauna of north central Washington, USA, with floral associations. Western North American Naturalist 70(2): 198-207.
Wilson, J.S., L.E. Wilson, L.D. Loftis, and T. Griswold. 2010. The montane bee fauna of north central Washington, USA, with floral associations. Western North American Naturalist 70(2): 198-207.
- Additional ReferencesLegend:
 View Online Publication
View Online Publication
Do you know of a citation we're missing? Lesica, P., M.T. Lavin, and P.F. Stickney. 2022. Manual of Montana Vascular Plants, Second Edition. Fort Worth, TX: BRIT Press. viii + 779 p.
Lesica, P., M.T. Lavin, and P.F. Stickney. 2022. Manual of Montana Vascular Plants, Second Edition. Fort Worth, TX: BRIT Press. viii + 779 p.
- Web Search Engines for Articles on "Gold-moss"





