View in other NatureServe Network Field Guides
NatureServe
Montana
Utah
Wyoming
Idaho
Wisconsin
British Columbia
South Carolina
Yukon
California
New York
Merlin - Falco columbarius
Native Species
Global Rank:
G5
State Rank:
S5
(see State Rank Reason below)
Agency Status
USFWS:
MBTA
USFS:
BLM:
PIF:
State Rank Reason (see State Rank above)
Species is relatively common within suitable habitat and widely distributed across portions of the state.
General Description
Males are blue-gray to dark blue above and pale rufous to buff-colored below, with dark streaking or barring. Females are brown above and cream to rufous below with darker streaking. The tail is barred dark with gray to white and exhibits a dark sub-terminal band. The eye is dark brown, and feet are yellow. Juveniles of both sexes resemble females, but are sometimes darker. Merlins are from 10 to 12 inches in length, and have wingspans of 19 to 24 inches. Females are slightly larger than males. A small falcon with pointed wings, a strongly barred tail, a hooked bill, and heavy streaking below; upperparts are gray-blue in males, dark brown in females; overall, plumage is much darker in the Pacific Northwest than in central Canada and the Midwest; average length 31 cm, wingspan 64 cm.
For a comprehensive review of the conservation status, habitat use, and ecology of this and other Montana bird species, please see
Marks et al. 2016, Birds of Montana.Diagnostic Characteristics
Merlins are significantly smaller than Gyrfalcons, Prairie Falcons, and Peregrine Falcons. Differs from American Kestrel, Prairie Falcon, and Peregrine Falcon in lacking a strong facial pattern. Both sexes are more uniform in color, lacking russet back and tail, than the brightly colored American Kestrel. Only about half as big as a Gyrfalcon (average length 31 cm vs. 51 to 64 cm). Immature Merlins resemble immature Sharp-shinned Hawks, but have pointed wings and dark eyes, instead of the short, rounded wings and yellow eyes of the Sharp-shinned Hawk.
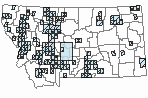
Species Range
Montana Range
Range Descriptions
 Year-round
Year-round
Western Hemisphere Range

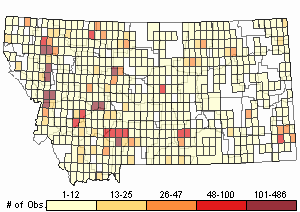
Observations in Montana Natural Heritage Program Database
Number of Observations: 7821
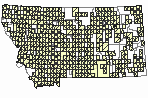
(Click on the following maps and charts to see full sized version)
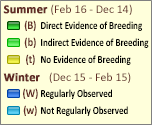
Map Help and Descriptions
Relative Density
Recency
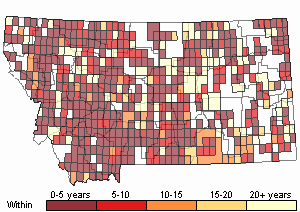
SUMMER (Feb 16 - Dec 14)
Direct Evidence of Breeding
Indirect Evidence of Breeding
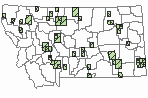
No Evidence of Breeding
WINTER (Dec 15 - Feb 15)
Regularly Observed
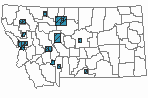
Not Regularly Observed
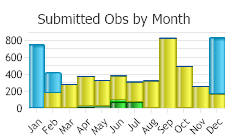
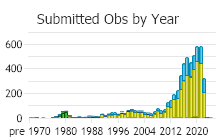
 (Observations spanning multiple months or years are excluded from time charts)
(Observations spanning multiple months or years are excluded from time charts)
Migration
Subspecies bendirei and richardsonii probably migrate thru MT. In Bozeman, birds appear October 1 to November 15, disappear March 1 to 15 (Skaar 1969).
Habitat
Breeding pairs in eastern Montana usually use sparse conifer stands adjacent to prairie habitats, but sometimes use shelterbelts and river bottom forests. In western Montana, they use open stands of conifers and river bottom forests. Merlins sometimes nest in urban areas. In the Bozeman area, found in the Gallatin Valley, not far from wooded areas (Skaar 1969).
National Vegetation Classification System Groups Associated with this Species
Forest and Woodland
Deciduous Forest and Woodland
Low Elevation - Xeric Forest and Woodland
Montane - Subalpine Forest and Woodland
Shrubland
Arid - Saline Shrubland
Foothills - Montane Shrubland
Sagebrush Shrubland
Grassland
Lowland - Prairie Grassland
Montane - Subalpine Grassland
Sparse and Barren
Sparse and Barren
Wetland and Riparian
Alkaline - Saline Wetlands
Riparian and Wetland Forest
Riparian Shrubland
Recently Disturbed or Modified
Introduced Vegetation
Human Land Use
Agriculture
Developed
Food Habits
Merlins primarily eat small birds. In eastern Montana, common prey includes grassland birds such as Horned Larks, Vesper Sparrows, and Lark Buntings. In western Montana, prey includes various sparrows, finches and waxwings. Young Merlins often take larger insects such as grasshoppers and moths.
Ecology
The 1944 raptor survey of MT showed this species to be the least abundant raptor in the state (Davis 1961). Said to be formerly uncommon, now rare in the Fortine area.
Reproductive Characteristics
Male Merlins arrive at nesting areas in late March and early April, and females arrive slightly later. They use nests previously constructed by Black-billed Magpies or American Crows; Merlins, like other falcons, do not build their own nests. Used old corvid nests in MT. Clutches of three to five eggs are laid from mid April to early June, and are incubated for about 30 days. The young fly when about 40 days old, but they remain near their nests. Live to be about eight years old. Nesting dates probably similar to those of Alberta and Saskatchewan, where egg records are from May 7 to June 6 (Johnsgard 1986).
Stewardship Responsibility
References
- Literature Cited AboveLegend:
 View Online Publication
View Online Publication Davis, C.V. 1961. A distributional study of the birds of Montana. Ph.D. Dissertation. Corvallis, OR: Oregon State University. 462 p.
Davis, C.V. 1961. A distributional study of the birds of Montana. Ph.D. Dissertation. Corvallis, OR: Oregon State University. 462 p. Johnsgard, P.A. 1986. Birds of the Rocky Mountains: with particular reference to national parks in the northern Rocky Mountain region. Colorado Associated University Press, Boulder, CO.
Johnsgard, P.A. 1986. Birds of the Rocky Mountains: with particular reference to national parks in the northern Rocky Mountain region. Colorado Associated University Press, Boulder, CO. Marks, J.S., P. Hendricks, and D. Casey. 2016. Birds of Montana. Arrington, VA. Buteo Books. 659 pages.
Marks, J.S., P. Hendricks, and D. Casey. 2016. Birds of Montana. Arrington, VA. Buteo Books. 659 pages. Skaar, P.D. 1969. Birds of the Bozeman latilong: a compilation of data concerning the birds which occur between 45 and 46 N. latitude and 111 and 112 W. longitude, with current lists for Idaho, Montana, Wyoming, impinging Montana counties and Yellowstone National Park. Bozeman, MT. 132 p.
Skaar, P.D. 1969. Birds of the Bozeman latilong: a compilation of data concerning the birds which occur between 45 and 46 N. latitude and 111 and 112 W. longitude, with current lists for Idaho, Montana, Wyoming, impinging Montana counties and Yellowstone National Park. Bozeman, MT. 132 p.
- Additional ReferencesLegend:
 View Online Publication
View Online Publication
Do you know of a citation we're missing? [PRESI] Powder River Eagle Studies Incorporated. 1998b. Spring Creek Mine 1997 wildlife monitoring studies. Powder River Eagle Studies Incorporated. Gillete, WY.
[PRESI] Powder River Eagle Studies Incorporated. 1998b. Spring Creek Mine 1997 wildlife monitoring studies. Powder River Eagle Studies Incorporated. Gillete, WY. Allen, G. T. 1979. An assessment of potential conflicts between nesting raptors and human activities in the Long Pines area of southeastern Montana with special emphasis on uranium development. M.S. thesis, Washington State University, Pullman. 109 pp.
Allen, G. T. 1979. An assessment of potential conflicts between nesting raptors and human activities in the Long Pines area of southeastern Montana with special emphasis on uranium development. M.S. thesis, Washington State University, Pullman. 109 pp. American Ornithologists’ Union [AOU]. 1998. Check-list of North American birds, 7th edition. American Ornithologists’ Union, Washington, D.C. 829 p.
American Ornithologists’ Union [AOU]. 1998. Check-list of North American birds, 7th edition. American Ornithologists’ Union, Washington, D.C. 829 p. Becker and Sieg. 1985. Raptor Res. 19:52-55.
Becker and Sieg. 1985. Raptor Res. 19:52-55. Becker, D. M. 1985. Food habits of Richardson’s Merlins in southeastern Montana. Wilson Bulletin 97:226-230.
Becker, D. M. 1985. Food habits of Richardson’s Merlins in southeastern Montana. Wilson Bulletin 97:226-230. Becker, D.M. 1977. A survey of breeding raptors on and adjacent to Custer National Forest lands in Carter County, Montana. Unpublished report including 1978 progress report. 107 p.
Becker, D.M. 1977. A survey of breeding raptors on and adjacent to Custer National Forest lands in Carter County, Montana. Unpublished report including 1978 progress report. 107 p. Becker, D.M. 1984. Reproductive ecology and habitat utilization of Richardson's Merlins in southeastern Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Missoula, MT: University of Montana. 62 p.
Becker, D.M. 1984. Reproductive ecology and habitat utilization of Richardson's Merlins in southeastern Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Missoula, MT: University of Montana. 62 p. Becker, D.M., and C.H. Sieg. 1987. Eggshell quality and organochlorine residues in eggs of Merlins, Falco columbarius, in southeastern Montana. Canadian Field-Naturalist 101(3):369-372.
Becker, D.M., and C.H. Sieg. 1987. Eggshell quality and organochlorine residues in eggs of Merlins, Falco columbarius, in southeastern Montana. Canadian Field-Naturalist 101(3):369-372. Becker, D.M., and C.H. Sieg. 1987. Home range and habitat utilization of breeding male Merlins, Falco columbarius, in southeastern Montana. The Canadian Field-Naturalist 101(3):398-403.
Becker, D.M., and C.H. Sieg. 1987. Home range and habitat utilization of breeding male Merlins, Falco columbarius, in southeastern Montana. The Canadian Field-Naturalist 101(3):398-403. Becker, Dale M., 1980, A Survey of raptors on national forest land in Carter County, Montana. Final Progress Report: 1977-1979.
Becker, Dale M., 1980, A Survey of raptors on national forest land in Carter County, Montana. Final Progress Report: 1977-1979. Bramblett, R.G., and A.V. Zale. 2002. Montana Prairie Riparian Native Species Report. Montana Cooperative Fishery Research Unit, Montana State University - Bozeman.
Bramblett, R.G., and A.V. Zale. 2002. Montana Prairie Riparian Native Species Report. Montana Cooperative Fishery Research Unit, Montana State University - Bozeman. Cameron, E. S. 1907. The birds of Custer and Dawson counties, Montana. Auk 24(3): 241-270.
Cameron, E. S. 1907. The birds of Custer and Dawson counties, Montana. Auk 24(3): 241-270. Clark, T.W., H.A. Harvey, R.D. Dorn, D.L. Genter, and C. Groves (eds). 1989. Rare, sensitive, and threatened species of the greater Yellowstone ecosystem. Northern Rockies Conservation Cooperative, Montana Natural Heritage Program, The Nature Conservancy, and Mountain West Environmental Services. 153 p.
Clark, T.W., H.A. Harvey, R.D. Dorn, D.L. Genter, and C. Groves (eds). 1989. Rare, sensitive, and threatened species of the greater Yellowstone ecosystem. Northern Rockies Conservation Cooperative, Montana Natural Heritage Program, The Nature Conservancy, and Mountain West Environmental Services. 153 p. Decker Coal Co., 1981, Wildlife survey. July 7, 1981. In North Decker 5-Year Permit Application. Vol. III. Rule 26.4.304(12-14).
Decker Coal Co., 1981, Wildlife survey. July 7, 1981. In North Decker 5-Year Permit Application. Vol. III. Rule 26.4.304(12-14). Dickson, D.C. 1991. Systematic wildlife observations on the Blackfoot-Clearwater Wildlife Management Area. Montana Department of Fish, Wildlife and Parks. Missoula, MT. 14 pp. plus appendices and photographs.
Dickson, D.C. 1991. Systematic wildlife observations on the Blackfoot-Clearwater Wildlife Management Area. Montana Department of Fish, Wildlife and Parks. Missoula, MT. 14 pp. plus appendices and photographs. Dobkin, D. S. 1992. Neotropical migrant landbirds in the Northern Rockies and Great Plains. U.S.D.A. For. Serv. N. Region Publ. R1-93-34. Missoula, Mont.
Dobkin, D. S. 1992. Neotropical migrant landbirds in the Northern Rockies and Great Plains. U.S.D.A. For. Serv. N. Region Publ. R1-93-34. Missoula, Mont. Dood, A.R. 1980. Terry Badlands nongame survey and inventory final report. Montana Department of Fish, Wildlife, and Parks and Bureau of Land Management, Helena, MT. 70 pp.
Dood, A.R. 1980. Terry Badlands nongame survey and inventory final report. Montana Department of Fish, Wildlife, and Parks and Bureau of Land Management, Helena, MT. 70 pp. DuBois, K. and D. Becker. 1987. Identification of Montana's birds of prey. Montana Outdoors Nov/Dec. 20 p.
DuBois, K. and D. Becker. 1987. Identification of Montana's birds of prey. Montana Outdoors Nov/Dec. 20 p. DuBois, K.L. 1979. An inventory of the avifauna in the Long Pines of Southeastern Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 113 p.
DuBois, K.L. 1979. An inventory of the avifauna in the Long Pines of Southeastern Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 113 p. Econ, Inc. (Ecological Consulting Service), Helena, MT., 1977, 1977 wildlife and wildlife habitat monitoring study, Peabody Coal Company Big Sky Mine. Proj. 161-85-A. November 30, 1977.
Econ, Inc. (Ecological Consulting Service), Helena, MT., 1977, 1977 wildlife and wildlife habitat monitoring study, Peabody Coal Company Big Sky Mine. Proj. 161-85-A. November 30, 1977. ECON, Inc. (Ecological Consulting Service), Helena, MT., 1977, Colstrip 10 x 20 Area wildlife and wildlife habitat annual monitoring report, 1977. Proj. 164-85-A. December 31, 1977.
ECON, Inc. (Ecological Consulting Service), Helena, MT., 1977, Colstrip 10 x 20 Area wildlife and wildlife habitat annual monitoring report, 1977. Proj. 164-85-A. December 31, 1977. ECON, Inc. (Ecological Consulting Service), Helena, MT., 1979, Annual wildllife report of the Colstrip Area for 1978. Proj. 195-85-A. April 6, 1979.
ECON, Inc. (Ecological Consulting Service), Helena, MT., 1979, Annual wildllife report of the Colstrip Area for 1978. Proj. 195-85-A. April 6, 1979. Ehrlich, P., D. Dobkin, and D. Wheye. 1988. The birder’s handbook: a field guide to the natural history of North American birds. Simon and Schuster Inc. New York. 785 pp.
Ehrlich, P., D. Dobkin, and D. Wheye. 1988. The birder’s handbook: a field guide to the natural history of North American birds. Simon and Schuster Inc. New York. 785 pp. Ellis, D.H. 1976. First breeding records of merlins in Montana. Condor 78:112-114.
Ellis, D.H. 1976. First breeding records of merlins in Montana. Condor 78:112-114. Farmer, Patrick J., and Thomas W. Butts, Western Technology & Eng., Inc., Helena, MT., 1994, McDonald Project Terrestrial Wildlife Study, November 1989 - November 1993. April 1994. In McDonald Gold Project: Wildlife & Fisheries. [#18]. Seven-up Pete Joint Venture, Lincoln, MT. Unpub. No date.
Farmer, Patrick J., and Thomas W. Butts, Western Technology & Eng., Inc., Helena, MT., 1994, McDonald Project Terrestrial Wildlife Study, November 1989 - November 1993. April 1994. In McDonald Gold Project: Wildlife & Fisheries. [#18]. Seven-up Pete Joint Venture, Lincoln, MT. Unpub. No date. Fjell, Alan K., and Brian R. Mahan, compilers., 1984, Peabody Coal Company Big Sky Mine, Rosebud County, MT. Wildlife monitoring report: 1983 field season. February 1984.
Fjell, Alan K., and Brian R. Mahan, compilers., 1984, Peabody Coal Company Big Sky Mine, Rosebud County, MT. Wildlife monitoring report: 1983 field season. February 1984. Fjell, Alan K., and Brian R. Mahan., 1983, Peabody Coal Company Big Sky Mine, Rosebud County, MT. Wildlife monitoring report: 1982 field season. May 1983.
Fjell, Alan K., and Brian R. Mahan., 1983, Peabody Coal Company Big Sky Mine, Rosebud County, MT. Wildlife monitoring report: 1982 field season. May 1983. Fjell, Alan K., and Brian R. Mahan., 1987, Big Sky Mine, Rosebud County, MT. Wildlife monitoring report: 1986 field season. April 1987.
Fjell, Alan K., and Brian R. Mahan., 1987, Big Sky Mine, Rosebud County, MT. Wildlife monitoring report: 1986 field season. April 1987. Gniadek, S. 1983. Southwest Glendive Wildlife Baseline Inventory. Miles City, Mont: Bureau of Land Management, Miles City District Office. 56 pp with appendices.
Gniadek, S. 1983. Southwest Glendive Wildlife Baseline Inventory. Miles City, Mont: Bureau of Land Management, Miles City District Office. 56 pp with appendices. Gorman, J. D., 1984, Interagency Rocky Mountain Front Wildlife Monitoring/Evaluation Program.
Gorman, J. D., 1984, Interagency Rocky Mountain Front Wildlife Monitoring/Evaluation Program. Hays, R., R.L. Eng, and C.V. Davis (preparers). 1984. A list of Montana birds. Helena, MT: MT Dept. of Fish, Wildlife & Parks.
Hays, R., R.L. Eng, and C.V. Davis (preparers). 1984. A list of Montana birds. Helena, MT: MT Dept. of Fish, Wildlife & Parks. Hejl, S.J., R.L. Hutto, C.R. Preston, and D.M. Finch. 1995. The effects of silvicultural treatments on forest birds in the Rocky Mountains. pp. 220-244 In: T.E. Martin and D.M. Finch (eds). Ecology and Management of Neotropical Migratory Birds. New York, NY: Oxford Univ. Press. 489 p.
Hejl, S.J., R.L. Hutto, C.R. Preston, and D.M. Finch. 1995. The effects of silvicultural treatments on forest birds in the Rocky Mountains. pp. 220-244 In: T.E. Martin and D.M. Finch (eds). Ecology and Management of Neotropical Migratory Birds. New York, NY: Oxford Univ. Press. 489 p. Hendricks, P., and K.H. Dueholm. 1995. Cliff-nesting raptor survey of the Sioux District, Custer National Forest: 1994. Unpubl. report to U.S.D.A. For. Serv., Custer N.F., Billings. 20 pp.
Hendricks, P., and K.H. Dueholm. 1995. Cliff-nesting raptor survey of the Sioux District, Custer National Forest: 1994. Unpubl. report to U.S.D.A. For. Serv., Custer N.F., Billings. 20 pp. Hoffmann, R.S. 1960. Summer birds of the Little Belt Mountains, Montana. Missoula, MT: Occasional Papers of Montana State University No. 1. 18 p.
Hoffmann, R.S. 1960. Summer birds of the Little Belt Mountains, Montana. Missoula, MT: Occasional Papers of Montana State University No. 1. 18 p. Jellison, W.L. 1939. Sylvatic plague: studies of predatory and scavenger birds in relation to its epidemiology. Public Health Report 54: 792-798.
Jellison, W.L. 1939. Sylvatic plague: studies of predatory and scavenger birds in relation to its epidemiology. Public Health Report 54: 792-798. Johnsgard, P.A. 1990. Hawks, eagles, and falcons of North America. Smithsonian Institution Press, Washington, D.C. 403 pp.
Johnsgard, P.A. 1990. Hawks, eagles, and falcons of North America. Smithsonian Institution Press, Washington, D.C. 403 pp. Johnsgard, P.A. 1992. Birds of the Rocky Mountains with particular reference to national parks in the northern Rocky Mountain region. Lincoln: University of Nebraska Press. xi + 504 pp.
Johnsgard, P.A. 1992. Birds of the Rocky Mountains with particular reference to national parks in the northern Rocky Mountain region. Lincoln: University of Nebraska Press. xi + 504 pp. Joslin, Gayle, and Heidi B. Youmans. 1999. Effects of recreation on Rocky Mountain wildlife: a review for Montana. [Montana]: Montana Chapter of the Wildlife Society.
Joslin, Gayle, and Heidi B. Youmans. 1999. Effects of recreation on Rocky Mountain wildlife: a review for Montana. [Montana]: Montana Chapter of the Wildlife Society. Land & Water Consulting, Inc., Missoula, MT., 2002, Montana Dept. of Transportation Wetland Mitigation Monitoring Report, Year 2002: Musgrave Lake, Zurich, Montana. Proj. No. 130091.019. May 2003. In 2002 Wetland Mitigation Monitoring Reports, Vol. II.
Land & Water Consulting, Inc., Missoula, MT., 2002, Montana Dept. of Transportation Wetland Mitigation Monitoring Report, Year 2002: Musgrave Lake, Zurich, Montana. Proj. No. 130091.019. May 2003. In 2002 Wetland Mitigation Monitoring Reports, Vol. II. Lenard, S. and P. Hendricks. 2005. Birds of selected grassland and riparian plots along the Rocky Mountain Front. Montana Natural Heritage Program for US Fish and Wildlife Service and The Nature Conservancy. 17pp + maps.
Lenard, S. and P. Hendricks. 2005. Birds of selected grassland and riparian plots along the Rocky Mountain Front. Montana Natural Heritage Program for US Fish and Wildlife Service and The Nature Conservancy. 17pp + maps. Lenard, S., J. Carlson, J. Ellis, C. Jones, and C. Tilly. 2003. P. D. Skaar's Montana bird distribution, 6th edition. Montana Audubon, Helena, MT. 144 pp.
Lenard, S., J. Carlson, J. Ellis, C. Jones, and C. Tilly. 2003. P. D. Skaar's Montana bird distribution, 6th edition. Montana Audubon, Helena, MT. 144 pp. Lockhart, J. Michael, 1976, Effects of coal extraction and related development on wildlife populations. Annual progress report; Calendar year 1976. In Decker Coal Company West Pit Permit. Vol. 3. 26.4.304(10-11), 305, 306, and 307. Updated Rules Rewrite, July 1, 1991. Appendix F.
Lockhart, J. Michael, 1976, Effects of coal extraction and related development on wildlife populations. Annual progress report; Calendar year 1976. In Decker Coal Company West Pit Permit. Vol. 3. 26.4.304(10-11), 305, 306, and 307. Updated Rules Rewrite, July 1, 1991. Appendix F. Marks, J. and M. Edwards. 1996. Survey of nesting raptors in Harding County, South Dakota, Sioux Ranger District, Custer National Forest, 22 May-3 July 1996. Montana Cooperative Wildlife Research Unit, Univ. of Montana, Missoula, and the Montana Natural Heritage Program, Helena.
Marks, J. and M. Edwards. 1996. Survey of nesting raptors in Harding County, South Dakota, Sioux Ranger District, Custer National Forest, 22 May-3 July 1996. Montana Cooperative Wildlife Research Unit, Univ. of Montana, Missoula, and the Montana Natural Heritage Program, Helena. Matthews, W.L. 1981. Broadus-Pumpkin Creek baseline inventory - wildlife. Bureau of Land Management, Miles City, MT. 83 p.
Matthews, W.L. 1981. Broadus-Pumpkin Creek baseline inventory - wildlife. Bureau of Land Management, Miles City, MT. 83 p. Maxell, B.A. 2016. Northern Goshawk surveys on the Beartooth, Ashland, and Sioux Districts of the Custer-Gallatin National Forest: 2012-2014. Montana Natural Heritage Program. Helena, MT. 114pp.
Maxell, B.A. 2016. Northern Goshawk surveys on the Beartooth, Ashland, and Sioux Districts of the Custer-Gallatin National Forest: 2012-2014. Montana Natural Heritage Program. Helena, MT. 114pp. Montana Bird Distribution Committee. 2012. P.D. Skaar's Montana bird distribution. 7th Edition. Montana Audubon, Helena, Montana. 208 pp. + foldout map.
Montana Bird Distribution Committee. 2012. P.D. Skaar's Montana bird distribution. 7th Edition. Montana Audubon, Helena, Montana. 208 pp. + foldout map. Montana Dept. of State Lands. U.S. Office of Surface Mining Reclamation and Enforcement., 1988, Draft Environmental Impact Statement. Peabody Coal Company's Big Sky Area B Mine, Rosebud County, Montana; July 1988.
Montana Dept. of State Lands. U.S. Office of Surface Mining Reclamation and Enforcement., 1988, Draft Environmental Impact Statement. Peabody Coal Company's Big Sky Area B Mine, Rosebud County, Montana; July 1988. MT Fish, Wildlife & Parks. No date. Blackfoot-Clearwater Wildlife Management Area checklist.
MT Fish, Wildlife & Parks. No date. Blackfoot-Clearwater Wildlife Management Area checklist. Oechsli, L.M. 2000. Ex-urban development in the Rocky Mountain West: consequences for native vegetation, wildlife diversity, and land-use planning in Big Sky, Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Montana State University, Bozeman. 73 p.
Oechsli, L.M. 2000. Ex-urban development in the Rocky Mountain West: consequences for native vegetation, wildlife diversity, and land-use planning in Big Sky, Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Montana State University, Bozeman. 73 p. Omland, K.S. and E.G. Meyer. 1992. Fall 1991 raptor migration study in the Bozeman, Montana vicinity. Prepared for the Gallatin National Forest, by HawkWatch International, Inc. 31 p.
Omland, K.S. and E.G. Meyer. 1992. Fall 1991 raptor migration study in the Bozeman, Montana vicinity. Prepared for the Gallatin National Forest, by HawkWatch International, Inc. 31 p. Phillips, R.L., A.H. Wheeler, N.C. Forrester, J.M. Lockhart, and T.P. McEneaney. 1990. Nesting ecology of golden eagles and other raptors in southeastern Montana and northern Wyoming. U.S. Fish Wildl. Serv. Tech. Rep. 26:1-13.
Phillips, R.L., A.H. Wheeler, N.C. Forrester, J.M. Lockhart, and T.P. McEneaney. 1990. Nesting ecology of golden eagles and other raptors in southeastern Montana and northern Wyoming. U.S. Fish Wildl. Serv. Tech. Rep. 26:1-13. Ralph, J.C., J.R. Sauer, and S. Droege. 1995. Monitoring bird populations by point counts. Gen. Tech. Rep. PSW-GTR-149. Albany, CA: USDA Pacific Southwest Research Station. 181 p.
Ralph, J.C., J.R. Sauer, and S. Droege. 1995. Monitoring bird populations by point counts. Gen. Tech. Rep. PSW-GTR-149. Albany, CA: USDA Pacific Southwest Research Station. 181 p. Richmond, C.W. and F.H. Knowlton. 1894. Birds of south-central Montana. Auk 11:298-308.
Richmond, C.W. and F.H. Knowlton. 1894. Birds of south-central Montana. Auk 11:298-308. Rogers, R., et al. 1994. A survey for: peregrine falcons and other raptors nesting along the Upper Missouri River: Ft. Benton, MT to James Kipp State Park. Prepared for the Bureau of Land Management, Lewistown District Office, Contract # 1422E950P40197. 22 p.
Rogers, R., et al. 1994. A survey for: peregrine falcons and other raptors nesting along the Upper Missouri River: Ft. Benton, MT to James Kipp State Park. Prepared for the Bureau of Land Management, Lewistown District Office, Contract # 1422E950P40197. 22 p. Rogers, R.R and A. Rogers. 1995. A survey of nesting ferruginous hawks (Buteo regalis) on public lands in Petroleum and Fergus counties, Montana. Prepared for the USDI Bureau of Land Management, Judith Resource Area. 17 p.
Rogers, R.R and A. Rogers. 1995. A survey of nesting ferruginous hawks (Buteo regalis) on public lands in Petroleum and Fergus counties, Montana. Prepared for the USDI Bureau of Land Management, Judith Resource Area. 17 p. Rundquist, V.M. 1973. Avian ecology on stock ponds in two vegetational types in north-central Montana. Ph.D. Dissertation. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 112 p.
Rundquist, V.M. 1973. Avian ecology on stock ponds in two vegetational types in north-central Montana. Ph.D. Dissertation. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 112 p. Sater, S. 2022. The insects of Sevenmile Creek, a pictorial guide to their diversity and ecology. Undergraduate Thesis. Helena, MT: Carroll College. 242 p.
Sater, S. 2022. The insects of Sevenmile Creek, a pictorial guide to their diversity and ecology. Undergraduate Thesis. Helena, MT: Carroll College. 242 p. Sibley, D. 2014. The Sibley guide to birds. Alfred A. Knopf, New York, NY. 598 pp.
Sibley, D. 2014. The Sibley guide to birds. Alfred A. Knopf, New York, NY. 598 pp. Sieg, C.H., and D.M. Becker. 1990. Nest-site habitat selected by merlins in southeastern Montana. Condor 92:688-694.
Sieg, C.H., and D.M. Becker. 1990. Nest-site habitat selected by merlins in southeastern Montana. Condor 92:688-694. Skaar, P. D., D. L. Flath, and L. S. Thompson. 1985. Montana bird distribution. Montana Academy of Sciences Monograph 3(44): ii-69.
Skaar, P. D., D. L. Flath, and L. S. Thompson. 1985. Montana bird distribution. Montana Academy of Sciences Monograph 3(44): ii-69. Smith, J. 2000. Recap of the fall 2000 migration season, Bridger Mountains. Raptor Watch 15(1):6-10.
Smith, J. 2000. Recap of the fall 2000 migration season, Bridger Mountains. Raptor Watch 15(1):6-10. Sodhi, N. S., L. W. Oliphant, P. C. James, and I. G. Warkentin. 1993. Merlin (Falco columbarius). In The Birds of North America, No. 44 (A. Poole and F. Gill, Eds.). Philadelphia: The Academy of Natural Sciences; Washington, D.C.: The American Ornithologists' Union.
Sodhi, N. S., L. W. Oliphant, P. C. James, and I. G. Warkentin. 1993. Merlin (Falco columbarius). In The Birds of North America, No. 44 (A. Poole and F. Gill, Eds.). Philadelphia: The Academy of Natural Sciences; Washington, D.C.: The American Ornithologists' Union. Swan River National Wildlife Refuge. 1982. Birds of the Swan River NWR. Kalispell, MT: NW MT Fish and Wildlife Center pamphlet.
Swan River National Wildlife Refuge. 1982. Birds of the Swan River NWR. Kalispell, MT: NW MT Fish and Wildlife Center pamphlet. Temple, S.A. 1972. Systematics and evolution of the North American merlins. Auk 89(2):325-338.
Temple, S.A. 1972. Systematics and evolution of the North American merlins. Auk 89(2):325-338. Thompson, L.S. 1978. Species abundance and habitat relations of an insular montane avifauna. Condor 80(1):1-14.
Thompson, L.S. 1978. Species abundance and habitat relations of an insular montane avifauna. Condor 80(1):1-14. Thompson, L.S. 1981. Circle West wildlife monitoring study: Third annual report. Technical report No. 8. Montana Department of Natural Resources and Conservation. Helena, Montana.
Thompson, L.S. 1981. Circle West wildlife monitoring study: Third annual report. Technical report No. 8. Montana Department of Natural Resources and Conservation. Helena, Montana. Thompson, Richard W., Western Resource Dev. Corp., Boulder, CO., 1996, Wildlife baseline report for the Montana [Montanore] Project, Lincoln and Sanders counties, Montana. In Application for a Hard Rock Operating Permit and Proposed Plan of Operation, Montanore Project, Lincoln and Sanders Counties, Montana. Vol. 5. Stroiazzo, John. Noranda Minerals Corp., Libby, MT. Revised September 1996.
Thompson, Richard W., Western Resource Dev. Corp., Boulder, CO., 1996, Wildlife baseline report for the Montana [Montanore] Project, Lincoln and Sanders counties, Montana. In Application for a Hard Rock Operating Permit and Proposed Plan of Operation, Montanore Project, Lincoln and Sanders Counties, Montana. Vol. 5. Stroiazzo, John. Noranda Minerals Corp., Libby, MT. Revised September 1996. Trimble, S.A. 1974. Habitat management series for unique or endangered species, Report No. 15, Merlin, Falco columbarius. Bureau of Land Management, U.S. Department of Interior, Technical Note, T-N-271, Denver. 41 pp.
Trimble, S.A. 1974. Habitat management series for unique or endangered species, Report No. 15, Merlin, Falco columbarius. Bureau of Land Management, U.S. Department of Interior, Technical Note, T-N-271, Denver. 41 pp. TVX Mineral Hill Mine, Amerikanuak, Inc., Gardiner, MT., 2002, Yearly summary of wildlife observation reports. 1990-2002 Letter reports.
TVX Mineral Hill Mine, Amerikanuak, Inc., Gardiner, MT., 2002, Yearly summary of wildlife observation reports. 1990-2002 Letter reports. U.S. Forest Service. 1991. Forest and rangeland birds of the United States: Natural history and habitat use. U.S. Department of Agriculture, Forest Service Agricultural Handbook 688. 625 pages.
U.S. Forest Service. 1991. Forest and rangeland birds of the United States: Natural history and habitat use. U.S. Department of Agriculture, Forest Service Agricultural Handbook 688. 625 pages. Waage, B.C. 1984. Western Energy Company Rosebud Mine, Rosebud County, Montana: Annual Wildlife Monitoring Report, 1983 Field Season. June 1984.
Waage, B.C. 1984. Western Energy Company Rosebud Mine, Rosebud County, Montana: Annual Wildlife Monitoring Report, 1983 Field Season. June 1984. Waage, B.C. 1986. Western Energy Company Rosebud Mine, Rosebud County, Montana: Annual Wildlife Monitoring Report, 1985 Field Season. December 1985.
Waage, B.C. 1986. Western Energy Company Rosebud Mine, Rosebud County, Montana: Annual Wildlife Monitoring Report, 1985 Field Season. December 1985. Waage, Bruce C., 1995, Western Energy Company Rosebud Mine, Colstrip, Montana:1994 Annual Wildlife Monitoring Report; December 1, 1993 - November 30, 1994. February 27, 1995.
Waage, Bruce C., 1995, Western Energy Company Rosebud Mine, Colstrip, Montana:1994 Annual Wildlife Monitoring Report; December 1, 1993 - November 30, 1994. February 27, 1995. Waage, Bruce C., 1996, Western Energy Company Rosebud Mine, Colstrip, Montana: 1995 Annual Wildlife Monitoring Report; December 1, 1994 - November 30, 1995. February 28, 1996.
Waage, Bruce C., 1996, Western Energy Company Rosebud Mine, Colstrip, Montana: 1995 Annual Wildlife Monitoring Report; December 1, 1994 - November 30, 1995. February 28, 1996. Waage, Bruce C., 1999, Western Energy Company Rosebud Mine, Colstrip, Montana: 1998 Annual Wildlife Monitoring Report; December 1, 1997 - November 30, 1998 Survey Period. February 24, 1999.
Waage, Bruce C., 1999, Western Energy Company Rosebud Mine, Colstrip, Montana: 1998 Annual Wildlife Monitoring Report; December 1, 1997 - November 30, 1998 Survey Period. February 24, 1999. Waage, Bruce C., compiler., 1985, Western Energy Company Rosebud Mine, Rosebud County, Montana: Annual Wildlife Monitoring Report, 1984 Field Season. October 1985.
Waage, Bruce C., compiler., 1985, Western Energy Company Rosebud Mine, Rosebud County, Montana: Annual Wildlife Monitoring Report, 1984 Field Season. October 1985. Walcheck, K.C. 1970. Nesting bird ecology of four plant communities in the Missouri River Breaks, Montana. Wilson Bulletin 82(4):370-382.
Walcheck, K.C. 1970. Nesting bird ecology of four plant communities in the Missouri River Breaks, Montana. Wilson Bulletin 82(4):370-382. Waldt, R. 1995. The Pine Butte Swamp Preserve bird list. Choteau, MT: The Nature Conservancy. Updated August 1995.
Waldt, R. 1995. The Pine Butte Swamp Preserve bird list. Choteau, MT: The Nature Conservancy. Updated August 1995. Warkentin, I.G., N.S. Sodhi, R.H. M. Espie, A.F. Poole, L.W. Oliphant and P.C. James. 2005. Merlin (Falco columbarius). Species Account Number 044. The Birds of North America Online (A. Poole, Ed.). Ithaca, NY: Cornell Laboratory of Ornithology; Retrieved 3/25/2008 from The Birds of North America Online database
Warkentin, I.G., N.S. Sodhi, R.H. M. Espie, A.F. Poole, L.W. Oliphant and P.C. James. 2005. Merlin (Falco columbarius). Species Account Number 044. The Birds of North America Online (A. Poole, Ed.). Ithaca, NY: Cornell Laboratory of Ornithology; Retrieved 3/25/2008 from The Birds of North America Online database Watts, C.R. and L.C. Eichhorn. 1981. Changes in the birds of central Montana. Proceedings of the Montana Academy of Sciences 40:31-40.
Watts, C.R. and L.C. Eichhorn. 1981. Changes in the birds of central Montana. Proceedings of the Montana Academy of Sciences 40:31-40. Western Energy Co., Colstrip, MT. Unpub., 1983, Western Energy Company's Application for Amendment to Surface Mining Permit NO. 8003, Area B: sections 7, 8, 17,18 T1N R41E, sections 12, 13 T1N R40E, Mining Expansion. March 1983.
Western Energy Co., Colstrip, MT. Unpub., 1983, Western Energy Company's Application for Amendment to Surface Mining Permit NO. 8003, Area B: sections 7, 8, 17,18 T1N R41E, sections 12, 13 T1N R40E, Mining Expansion. March 1983. Western Energy Co., Colstrip, MT., 1982, Western Energy Company Rosebud Mine, Colstrip, Montana: Annual Wildlife Report, 1982.
Western Energy Co., Colstrip, MT., 1982, Western Energy Company Rosebud Mine, Colstrip, Montana: Annual Wildlife Report, 1982. Western Technology and Eng., Inc., 1991, Wildlife resources of the Little Rocky Mountains Environmental Study Area. March 1991. In Application for Amendment to Operating Permit No. 00096, Zortman Mining, Inc., Phillips County, Montana. Vol. 3. Jan. 3, 1995.
Western Technology and Eng., Inc., 1991, Wildlife resources of the Little Rocky Mountains Environmental Study Area. March 1991. In Application for Amendment to Operating Permit No. 00096, Zortman Mining, Inc., Phillips County, Montana. Vol. 3. Jan. 3, 1995. Western Technology and Engineering, Inc. (WESTECH). 1994. Wildlife Monitoring Absaloka Mine Area Annual Report, 1993. Montana SMP 85005. OSMP Montana 0007c. Mar. 12, 1994.
Western Technology and Engineering, Inc. (WESTECH). 1994. Wildlife Monitoring Absaloka Mine Area Annual Report, 1993. Montana SMP 85005. OSMP Montana 0007c. Mar. 12, 1994. Western Technology and Engineering, Inc. (WESTECH)., 1999, Wildlife Monitoring Absaloka Mine Area Annual Report, 1998. SMP 85005. OSMP Montana 0007E. April 1999.
Western Technology and Engineering, Inc. (WESTECH)., 1999, Wildlife Monitoring Absaloka Mine Area Annual Report, 1998. SMP 85005. OSMP Montana 0007E. April 1999. Westmoreland Resources, Inc., Hardin, MT., 1981, 1981 Wildlife Report. April 1982.
Westmoreland Resources, Inc., Hardin, MT., 1981, 1981 Wildlife Report. April 1982. Westmoreland Resources, Inc., Hardin, MT., 1983, 1980 Wildlife Monitoring Report. 12/21/79-12/20-80.
Westmoreland Resources, Inc., Hardin, MT., 1983, 1980 Wildlife Monitoring Report. 12/21/79-12/20-80. Westmoreland Resources, Inc., Hardin, MT., 1983, 1983 Wildlife Monitoring.
Westmoreland Resources, Inc., Hardin, MT., 1983, 1983 Wildlife Monitoring. Wittenhagen, K.W. 1991. Progress report on the ferruginous hawk in southeastern Montana. Miles City, MT: unpublished report for USDI BLM, Powder River and Big Dry Resource Areas. 24 p.
Wittenhagen, K.W. 1991. Progress report on the ferruginous hawk in southeastern Montana. Miles City, MT: unpublished report for USDI BLM, Powder River and Big Dry Resource Areas. 24 p.
- Web Search Engines for Articles on "Merlin"
- Additional Sources of Information Related to "Birds"





