View in other NatureServe Network Field Guides
NatureServe
Montana
Utah
Wyoming
Idaho
Wisconsin
British Columbia
South Carolina
Yukon
California
New York
Lesser Scaup - Aythya affinis
Native Species
Global Rank:
G5
State Rank:
S5B
(see State Rank Reason below)
Agency Status
USFWS:
MBTA
USFS:
BLM:
PIF:
State Rank Reason (see State Rank above)
Species is common, widely distributed, and stable.
General Description
A medium-sized (41.9 to 43 cm, 730 to 850 g) black and white diving duck, one of the most abundant and widespread of North American ducks. Adults sexually dimorphic most of year. Male in Definitive Alternate plumage characterized by slaty blue bill; black head with purplish gloss; black neck, breast, and upper mantle; white flanks and belly; gray-flecked lower mantle; and black vent and undertail region. Female is fuscous to chocolate brown with white patch of varying size at base of bill (sometime broken into patches of white); upperparts darker; wing-coverts flecked with gray; bill dark gray. Iris color in males is brilliant yellow, but in females varies with age from olive brown to olive or brownish yellow (Austin et al. 1998).
For a comprehensive review of the conservation status, habitat use, and ecology of this and other Montana bird species, please see
Marks et al. 2016, Birds of Montana.Species Range
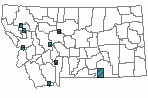
Montana Range
Range Descriptions
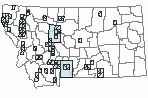
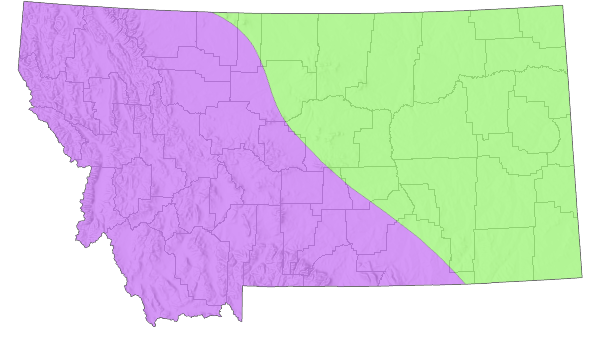 Western Hemisphere Range
Western Hemisphere Range

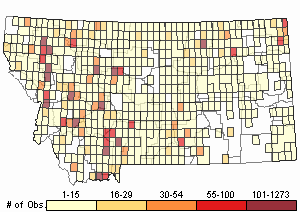
Observations in Montana Natural Heritage Program Database
Number of Observations: 9906
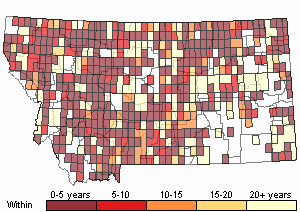
(Click on the following maps and charts to see full sized version)
Map Help and Descriptions
Relative Density
Recency
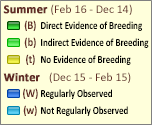
SUMMER (Feb 16 - Dec 14)
Direct Evidence of Breeding
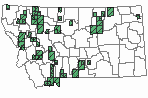
Indirect Evidence of Breeding
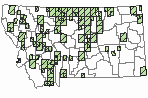
No Evidence of Breeding
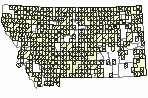
WINTER (Dec 15 - Feb 15)
Regularly Observed
Not Regularly Observed
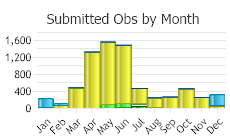
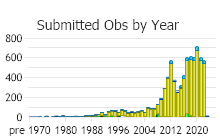
 (Observations spanning multiple months or years are excluded from time charts)
(Observations spanning multiple months or years are excluded from time charts)
Migration
Normal migration periods in the Bozeman area are April 10 to May 25 and October 1 to November 20, with peak numbers on April 25 and October 25 (Skaar 1969).
Habitat
In the Bozeman area, habitat is generally restricted to lakes and ponds (Skaar 1969). Throughout fall and winter this species forms large flocks on rivers, lakes, and large wetlands. Pairs and broods typically associated with fresh to moderately brackish, seasonal and semipermanent wetlands and lakes with emergent vegetation such as bulrush, cattail and river bulrush (Austin et al. 1998).
National Vegetation Classification System Groups Associated with this Species
Forest and Woodland
Deciduous Forest and Woodland
Shrubland
Sagebrush Shrubland
Grassland
Lowland - Prairie Grassland
Wetland and Riparian
Alkaline - Saline Wetlands
Alpine Riparian and Wetland
Peatland
Riparian and Wetland Forest
Riparian Shrubland
Wet Meadow and Marsh
Recently Disturbed or Modified
Introduced Vegetation
Human Land Use
Agriculture
Food Habits
Mainly aquatic invertebrates such as insects, crustaceans, and mollusks. Seeds and vegetative parts of aquatic plants are important in certain areas (Austin et al. 1998).
Ecology
At Bowdoin National Wildlife Refige, 25,000 were seen in November 1949. The major cause of unsuccessful nests at Freezeout Lake was skunk predation.
Reproductive Characteristics
Individuals form new pair bonds during spring migration each year. Female builds nest on the ground near or over water, as well as in uplands, unlike other diving ducks. Eggs are elliptical to nearly oval in shape. The color is pale olive or greenish buff to dark olive buff. Most clutches have 8 to 10 eggs (Austin et al. 1998). Actual nest records are scattered from mid-May to August 10. Hatching dates at Freezeout Lake were from June 1 to August 20. Birds nesting on islands were more successful (60%) than those in other habitat types (average of all was 23.5%). Average clutch size was 9.5.
Stewardship Responsibility
References
- Literature Cited AboveLegend:
 View Online Publication
View Online Publication Austin, Jane E., Christine M. Custer, and Alan D. Afton. 1998. Lesser Scaup (Aythya affinis). Species Account Number 338. The Birds of North America Online (A. Poole, Ed.). Ithaca, NY: Cornell Laboratory of Ornithology; Retrieved 3/25/2008 from The Birds of North America Online database
Austin, Jane E., Christine M. Custer, and Alan D. Afton. 1998. Lesser Scaup (Aythya affinis). Species Account Number 338. The Birds of North America Online (A. Poole, Ed.). Ithaca, NY: Cornell Laboratory of Ornithology; Retrieved 3/25/2008 from The Birds of North America Online database Marks, J.S., P. Hendricks, and D. Casey. 2016. Birds of Montana. Arrington, VA. Buteo Books. 659 pages.
Marks, J.S., P. Hendricks, and D. Casey. 2016. Birds of Montana. Arrington, VA. Buteo Books. 659 pages. Skaar, P.D. 1969. Birds of the Bozeman latilong: a compilation of data concerning the birds which occur between 45 and 46 N. latitude and 111 and 112 W. longitude, with current lists for Idaho, Montana, Wyoming, impinging Montana counties and Yellowstone National Park. Bozeman, MT. 132 p.
Skaar, P.D. 1969. Birds of the Bozeman latilong: a compilation of data concerning the birds which occur between 45 and 46 N. latitude and 111 and 112 W. longitude, with current lists for Idaho, Montana, Wyoming, impinging Montana counties and Yellowstone National Park. Bozeman, MT. 132 p.
- Additional ReferencesLegend:
 View Online Publication
View Online Publication
Do you know of a citation we're missing? [WWPC] Washington Water Power Company. 1995. 1994 wildlife report Noxon Rapids and Cabinet Gorge Reservoirs. Washington Water Power Company. Spokane, WA.
[WWPC] Washington Water Power Company. 1995. 1994 wildlife report Noxon Rapids and Cabinet Gorge Reservoirs. Washington Water Power Company. Spokane, WA. American Ornithologists’ Union [AOU]. 1998. Check-list of North American birds, 7th edition. American Ornithologists’ Union, Washington, D.C. 829 p.
American Ornithologists’ Union [AOU]. 1998. Check-list of North American birds, 7th edition. American Ornithologists’ Union, Washington, D.C. 829 p. Bayless, S.R. 1992. Duck population responses to water development in north central Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 69 p.
Bayless, S.R. 1992. Duck population responses to water development in north central Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 69 p. Bramblett, R.G., and A.V. Zale. 2002. Montana Prairie Riparian Native Species Report. Montana Cooperative Fishery Research Unit, Montana State University - Bozeman.
Bramblett, R.G., and A.V. Zale. 2002. Montana Prairie Riparian Native Species Report. Montana Cooperative Fishery Research Unit, Montana State University - Bozeman. Butler, M.A. 1996. The validity of using artificial nests to assess nest-predation rates in prairie nesting ducks. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 82 p.
Butler, M.A. 1996. The validity of using artificial nests to assess nest-predation rates in prairie nesting ducks. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 82 p. Cameron, E. S. 1907. The birds of Custer and Dawson counties, Montana. Auk 24(3): 241-270.
Cameron, E. S. 1907. The birds of Custer and Dawson counties, Montana. Auk 24(3): 241-270. Cornely, J.E. 1982. Waterfowl production at Malheur National Wildlife Refuge, 1942-1980. Transactions of the 47th North American Wildlife and Natural Resources Conference. pp 559-571.
Cornely, J.E. 1982. Waterfowl production at Malheur National Wildlife Refuge, 1942-1980. Transactions of the 47th North American Wildlife and Natural Resources Conference. pp 559-571. Cutting, K.A. 2010. Nutrient allocation to egg formation of Lesser Scaup. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, Montana: Montana State University. 74 p.
Cutting, K.A. 2010. Nutrient allocation to egg formation of Lesser Scaup. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, Montana: Montana State University. 74 p. Deane, C.E. 2017. Harvest, nasal-markers, and Lesser Scaup vital rates. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 102 p.
Deane, C.E. 2017. Harvest, nasal-markers, and Lesser Scaup vital rates. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 102 p. Dickson, D.C. 1991. Systematic wildlife observations on the Blackfoot-Clearwater Wildlife Management Area. Montana Department of Fish, Wildlife and Parks. Missoula, MT. 14 pp. plus appendices and photographs.
Dickson, D.C. 1991. Systematic wildlife observations on the Blackfoot-Clearwater Wildlife Management Area. Montana Department of Fish, Wildlife and Parks. Missoula, MT. 14 pp. plus appendices and photographs. ECON, Inc. (Ecological Consulting Service), Helena, MT., 1977, Colstrip 10 x 20 Area wildlife and wildlife habitat annual monitoring report, 1977. Proj. 164-85-A. December 31, 1977.
ECON, Inc. (Ecological Consulting Service), Helena, MT., 1977, Colstrip 10 x 20 Area wildlife and wildlife habitat annual monitoring report, 1977. Proj. 164-85-A. December 31, 1977. ECON, Inc. (Ecological Consulting Service), Helena, MT., 1979, Annual wildllife report of the Colstrip Area for 1978. Proj. 195-85-A. April 6, 1979.
ECON, Inc. (Ecological Consulting Service), Helena, MT., 1979, Annual wildllife report of the Colstrip Area for 1978. Proj. 195-85-A. April 6, 1979. ECON, Inc. (Ecological Consulting Service), Helena, MT., 1979, Annual wildllife report of the Colstrip Area for 1979, including a special raptor research study. Proj. 216-85-A. March 1, 1980.
ECON, Inc. (Ecological Consulting Service), Helena, MT., 1979, Annual wildllife report of the Colstrip Area for 1979, including a special raptor research study. Proj. 216-85-A. March 1, 1980. ECON, Inc. (Ecological Consulting Service), Helena, MT., 1979, Area B four-section wildlife report. August 3, 1979.
ECON, Inc. (Ecological Consulting Service), Helena, MT., 1979, Area B four-section wildlife report. August 3, 1979. Ehrlich, P., D. Dobkin, and D. Wheye. 1988. The birder’s handbook: a field guide to the natural history of North American birds. Simon and Schuster Inc. New York. 785 pp.
Ehrlich, P., D. Dobkin, and D. Wheye. 1988. The birder’s handbook: a field guide to the natural history of North American birds. Simon and Schuster Inc. New York. 785 pp. Ellig, L.J. 1953. Waterfowl relationships to Greenfields Lake, Teton County, Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 49 p.
Ellig, L.J. 1953. Waterfowl relationships to Greenfields Lake, Teton County, Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 49 p. Forman, Kurt J., 1993. Influence of skunk removal on nest success and breeding populations of upland nesting ducks. M.S. Thesis. University of Montana. Missoula, MT.
Forman, Kurt J., 1993. Influence of skunk removal on nest success and breeding populations of upland nesting ducks. M.S. Thesis. University of Montana. Missoula, MT. Gjersing, F.M. 1971. A study of waterfowl production on two rest rotation grazing units in northcentral Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 42 p.
Gjersing, F.M. 1971. A study of waterfowl production on two rest rotation grazing units in northcentral Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 42 p. Gjersing, F.M. 1975. Waterfowl production in relation to rest-rotation grazing. Journal of Range Management 28:37-42.
Gjersing, F.M. 1975. Waterfowl production in relation to rest-rotation grazing. Journal of Range Management 28:37-42. Gniadek, S. 1983. Southwest Glendive Wildlife Baseline Inventory. Miles City, Mont: Bureau of Land Management, Miles City District Office. 56 pp with appendices.
Gniadek, S. 1983. Southwest Glendive Wildlife Baseline Inventory. Miles City, Mont: Bureau of Land Management, Miles City District Office. 56 pp with appendices. Golden Sunlight Mines, Inc. 2000. Golden Sunlight Mines, Inc., Whitehall, MT. Annual Permit Reports.
Golden Sunlight Mines, Inc. 2000. Golden Sunlight Mines, Inc., Whitehall, MT. Annual Permit Reports. Goodell, J. 2012. Morse Land Company Breeding Bird Inventory And Analysis. High Desert Museum. Bend, OR. 42 pp + Appendices.
Goodell, J. 2012. Morse Land Company Breeding Bird Inventory And Analysis. High Desert Museum. Bend, OR. 42 pp + Appendices. Hall, Nathan E. 1995. Effects of Striped Skunk removal on duck nest success in the Mission Valley, Montana. M.S. Thesis. University of Montana. Missoula, MT.
Hall, Nathan E. 1995. Effects of Striped Skunk removal on duck nest success in the Mission Valley, Montana. M.S. Thesis. University of Montana. Missoula, MT. Hays, R., R.L. Eng, and C.V. Davis (preparers). 1984. A list of Montana birds. Helena, MT: MT Dept. of Fish, Wildlife & Parks.
Hays, R., R.L. Eng, and C.V. Davis (preparers). 1984. A list of Montana birds. Helena, MT: MT Dept. of Fish, Wildlife & Parks. Hendricks, P, S. Lenard, and C. Currier. 2012. Grassland Bird Surveys in North Valley County and Northwest Phillips County, Montana: 2011 Summary. Report to the USDI Bureau of Land Management. Montana Natural Heritage Program. Helena, MT. 7pp.
Hendricks, P, S. Lenard, and C. Currier. 2012. Grassland Bird Surveys in North Valley County and Northwest Phillips County, Montana: 2011 Summary. Report to the USDI Bureau of Land Management. Montana Natural Heritage Program. Helena, MT. 7pp. Hendricks, P. and C.J. Norment. 1986. Additions to the alpine avifauna of the Beartooth Mountains. The Murrelet 67:90-92.
Hendricks, P. and C.J. Norment. 1986. Additions to the alpine avifauna of the Beartooth Mountains. The Murrelet 67:90-92. Hendricks, P., S. Lenard, C. Currier, B. A. Maxell, and J. Carlson. 2008. Surveys for grassland birds of the Malta Field Office-BLM, including a seven-year study in north Valley County. Montana Natural Heritage Program, Helena.
Hendricks, P., S. Lenard, C. Currier, B. A. Maxell, and J. Carlson. 2008. Surveys for grassland birds of the Malta Field Office-BLM, including a seven-year study in north Valley County. Montana Natural Heritage Program, Helena. Hildebrand, B. D. 1979. Habitat requirements of molting Canada Geese at Lima Reservoir, Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 79 p.
Hildebrand, B. D. 1979. Habitat requirements of molting Canada Geese at Lima Reservoir, Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 79 p. Holm, J.W. 1984. Nest success and cover relationships of upland-nesting ducks in northcentral Montana. M.S. thesis. University of Montana. Missoula. 35 pp.
Holm, J.W. 1984. Nest success and cover relationships of upland-nesting ducks in northcentral Montana. M.S. thesis. University of Montana. Missoula. 35 pp. Hudson, M.S. 1980. Waterfowl production on three age-classes of stock ponds in north central Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 45 p.
Hudson, M.S. 1980. Waterfowl production on three age-classes of stock ponds in north central Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 45 p. Johnsgard, P.A. 1975. Waterfowl of North America. Bloomington, IN: Indiana University Press. 575 p.
Johnsgard, P.A. 1975. Waterfowl of North America. Bloomington, IN: Indiana University Press. 575 p. Johnsgard, P.A. 1979. Birds of the Great Plains: breeding species and their distribution. University of Nebraska Press, Lincoln. 539 pp.
Johnsgard, P.A. 1979. Birds of the Great Plains: breeding species and their distribution. University of Nebraska Press, Lincoln. 539 pp. Johnsgard, P.A. 1992. Birds of the Rocky Mountains with particular reference to national parks in the northern Rocky Mountain region. Lincoln: University of Nebraska Press. xi + 504 pp.
Johnsgard, P.A. 1992. Birds of the Rocky Mountains with particular reference to national parks in the northern Rocky Mountain region. Lincoln: University of Nebraska Press. xi + 504 pp. Johnson, K.M. 1990. Aquatic vegetation, salinity, aquatic invertebrates, and duck brood use at Bowdoin National Wildlife Refuge, Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 77 p.
Johnson, K.M. 1990. Aquatic vegetation, salinity, aquatic invertebrates, and duck brood use at Bowdoin National Wildlife Refuge, Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 77 p. Joslin, Gayle, and Heidi B. Youmans. 1999. Effects of recreation on Rocky Mountain wildlife: a review for Montana. [Montana]: Montana Chapter of the Wildlife Society.
Joslin, Gayle, and Heidi B. Youmans. 1999. Effects of recreation on Rocky Mountain wildlife: a review for Montana. [Montana]: Montana Chapter of the Wildlife Society. Knight, R.R. 1960. Vegetative characteristics of two water areas in Teton County, Montana, in relation to waterfowl usage. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 38 p.
Knight, R.R. 1960. Vegetative characteristics of two water areas in Teton County, Montana, in relation to waterfowl usage. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 38 p. Knight, R.R. 1965. Vegetative characteristics and waterfowl usage of a Montana water area. J. Wildl. Manage. 29(4):782-788.
Knight, R.R. 1965. Vegetative characteristics and waterfowl usage of a Montana water area. J. Wildl. Manage. 29(4):782-788. Korschgen, C.E., and R.B. Dahlgren. 1992. Human disturbances of waterfowl: causes, effects, and management. Ch. 13.2.15 In: Waterfowl Management Handbook. Fish and Wildlife Service Leaflet. 8 p.
Korschgen, C.E., and R.B. Dahlgren. 1992. Human disturbances of waterfowl: causes, effects, and management. Ch. 13.2.15 In: Waterfowl Management Handbook. Fish and Wildlife Service Leaflet. 8 p. Lambing, J. H., D. A. Nimick, J. R. Knapton, and D. U. Palawski. 1994. Physical, chemical, and biological data for detailed study of the Sun River Irrigation Project, Freezout Lake Wildlife Management Area, and Benton Lake National Wildlife Refuge, west-central Montana, 1990-92, with selected data for 1987-89. Open-File Report 94-120, U.S. Geological Survey, Helena, Montana.
Lambing, J. H., D. A. Nimick, J. R. Knapton, and D. U. Palawski. 1994. Physical, chemical, and biological data for detailed study of the Sun River Irrigation Project, Freezout Lake Wildlife Management Area, and Benton Lake National Wildlife Refuge, west-central Montana, 1990-92, with selected data for 1987-89. Open-File Report 94-120, U.S. Geological Survey, Helena, Montana. Lenard, S. 2006. Birds of Blaine County, Riparian Point Count Surveys 2005. Report to the Bureau of LandManagement, Havre Field Station, Havre, Montana. Montana Natural Heritage Program, Helena, MT. 16pp.plus appendices.
Lenard, S. 2006. Birds of Blaine County, Riparian Point Count Surveys 2005. Report to the Bureau of LandManagement, Havre Field Station, Havre, Montana. Montana Natural Heritage Program, Helena, MT. 16pp.plus appendices. Lenard, S., J. Carlson, J. Ellis, C. Jones, and C. Tilly. 2003. P. D. Skaar's Montana bird distribution, 6th edition. Montana Audubon, Helena, MT. 144 pp.
Lenard, S., J. Carlson, J. Ellis, C. Jones, and C. Tilly. 2003. P. D. Skaar's Montana bird distribution, 6th edition. Montana Audubon, Helena, MT. 144 pp. Lokemoen, J.T. 1966. Breeding ecology of the redhead duck in western Montana. Journal of Wildlife Management 30(4):668-681.
Lokemoen, J.T. 1966. Breeding ecology of the redhead duck in western Montana. Journal of Wildlife Management 30(4):668-681. Lokemoen, J.T. 1993. Increasing waterfowl nesting success on islands and peninsulas. Ch. 13.2.11 In: Waterfowl Management Handbook. Fish and Wildlife Service Leaflet. 7 p.
Lokemoen, J.T. 1993. Increasing waterfowl nesting success on islands and peninsulas. Ch. 13.2.11 In: Waterfowl Management Handbook. Fish and Wildlife Service Leaflet. 7 p. Lokemoen, J.T., and R.O. Woodward. 1992. Nesting waterfowl and water birds on natural islands in the Dakotas and Montana. Wildlife Society Bulletin 20:163-171.
Lokemoen, J.T., and R.O. Woodward. 1992. Nesting waterfowl and water birds on natural islands in the Dakotas and Montana. Wildlife Society Bulletin 20:163-171. Lorang, K.D. 1979. Waterfowl and hunter use of Freezeout Lake Game Management Area. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, Montana: Montana State University. 79 p.
Lorang, K.D. 1979. Waterfowl and hunter use of Freezeout Lake Game Management Area. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, Montana: Montana State University. 79 p. Matthews, W.L. 1981. Broadus-Pumpkin Creek baseline inventory - wildlife. Bureau of Land Management, Miles City, MT. 83 p.
Matthews, W.L. 1981. Broadus-Pumpkin Creek baseline inventory - wildlife. Bureau of Land Management, Miles City, MT. 83 p. McCarthy, J.J. 1973. Response of nesting Canada geese (Branta canadensis) to islands in stockdams in northcentral Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 36 p.
McCarthy, J.J. 1973. Response of nesting Canada geese (Branta canadensis) to islands in stockdams in northcentral Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 36 p. Miller, M.G. 1980. The influence of habitat features on waterfowl productivity on stock reservoirs in south Valley County, Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 43 p.
Miller, M.G. 1980. The influence of habitat features on waterfowl productivity on stock reservoirs in south Valley County, Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 43 p. Montana Bird Distribution Committee. 2012. P.D. Skaar's Montana bird distribution. 7th Edition. Montana Audubon, Helena, Montana. 208 pp. + foldout map.
Montana Bird Distribution Committee. 2012. P.D. Skaar's Montana bird distribution. 7th Edition. Montana Audubon, Helena, Montana. 208 pp. + foldout map. MT Fish, Wildlife & Parks. No date. Blackfoot-Clearwater Wildlife Management Area checklist.
MT Fish, Wildlife & Parks. No date. Blackfoot-Clearwater Wildlife Management Area checklist. Mundinger, J.G. 1975. The influence of rest-rotation grazing management on waterfowl production on stock-water reservoirs in Phillips County, Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 100 p.
Mundinger, J.G. 1975. The influence of rest-rotation grazing management on waterfowl production on stock-water reservoirs in Phillips County, Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 100 p. Oechsli, L.M. 2000. Ex-urban development in the Rocky Mountain West: consequences for native vegetation, wildlife diversity, and land-use planning in Big Sky, Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Montana State University, Bozeman. 73 p.
Oechsli, L.M. 2000. Ex-urban development in the Rocky Mountain West: consequences for native vegetation, wildlife diversity, and land-use planning in Big Sky, Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Montana State University, Bozeman. 73 p. Palawski, D.U., et al., 1991, Contaminant biomonitoring at the Benton Lake National Wildlife Refuge in 1988.
Palawski, D.U., et al., 1991, Contaminant biomonitoring at the Benton Lake National Wildlife Refuge in 1988. Palmer, R.S. 1962. Handbook of North American birds. Volume 1. Loons through flamingos. Yale University Press, New Haven. 567 pp.
Palmer, R.S. 1962. Handbook of North American birds. Volume 1. Loons through flamingos. Yale University Press, New Haven. 567 pp. Perkins, A. E. H. 2003. Habitat use, reproductive biology, and nest-site selection of ground-nesting birds at Freezout Lake WMA in central Montana. M.S. thesis, University of Montana, Missoula.
Perkins, A. E. H. 2003. Habitat use, reproductive biology, and nest-site selection of ground-nesting birds at Freezout Lake WMA in central Montana. M.S. thesis, University of Montana, Missoula. Powder River Eagle Studies, Inc., Gillette, WY., 1995, Spring Creek Mine 1994 Wildlife Monitoring Studies. 4/94 to 4/95. Spring Creek Coal Company 1995 Mining Annual Report. Appendix I. May 1995.
Powder River Eagle Studies, Inc., Gillette, WY., 1995, Spring Creek Mine 1994 Wildlife Monitoring Studies. 4/94 to 4/95. Spring Creek Coal Company 1995 Mining Annual Report. Appendix I. May 1995. Powder River Eagle Studies, Inc., Gillette, WY., 2000, Spring Creek Mine 1999 Wildlife Monitoring. March 2000.
Powder River Eagle Studies, Inc., Gillette, WY., 2000, Spring Creek Mine 1999 Wildlife Monitoring. March 2000. Powder River Eagle Studies, Inc., Gillette, WY., 2000, Spring Creek Mine 2000 Wildlife Monitoring. March 2000.
Powder River Eagle Studies, Inc., Gillette, WY., 2000, Spring Creek Mine 2000 Wildlife Monitoring. March 2000. Rhodes, O.E., Jr., L.M. Smith and M.H. Smith. 1991. Conservation and genetic resources in waterfowl. Trans. N. Amer. Wildl. & Nat. Res. Conf. 56:462-472.
Rhodes, O.E., Jr., L.M. Smith and M.H. Smith. 1991. Conservation and genetic resources in waterfowl. Trans. N. Amer. Wildl. & Nat. Res. Conf. 56:462-472. Rogers, R.R and A. Rogers. 1995. A survey of nesting ferruginous hawks (Buteo regalis) on public lands in Petroleum and Fergus counties, Montana. Prepared for the USDI Bureau of Land Management, Judith Resource Area. 17 p.
Rogers, R.R and A. Rogers. 1995. A survey of nesting ferruginous hawks (Buteo regalis) on public lands in Petroleum and Fergus counties, Montana. Prepared for the USDI Bureau of Land Management, Judith Resource Area. 17 p. Rundquist, V.M. 1973. Avian ecology on stock ponds in two vegetational types in north-central Montana. Ph.D. Dissertation. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 112 p.
Rundquist, V.M. 1973. Avian ecology on stock ponds in two vegetational types in north-central Montana. Ph.D. Dissertation. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 112 p. Saunders, A.A. 1914. The birds of Teton and northern Lewis & Clark counties, Montana. Condor 16:124-144.
Saunders, A.A. 1914. The birds of Teton and northern Lewis & Clark counties, Montana. Condor 16:124-144. Sibley, D. 2014. The Sibley guide to birds. Alfred A. Knopf, New York, NY. 598 pp.
Sibley, D. 2014. The Sibley guide to birds. Alfred A. Knopf, New York, NY. 598 pp. Skaar, P. D., D. L. Flath, and L. S. Thompson. 1985. Montana bird distribution. Montana Academy of Sciences Monograph 3(44): ii-69.
Skaar, P. D., D. L. Flath, and L. S. Thompson. 1985. Montana bird distribution. Montana Academy of Sciences Monograph 3(44): ii-69. Smith, R.H. 1952. A study of waterfowl production on artificial reservoirs in eastern Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, Montana: Montana State University. 43 p.
Smith, R.H. 1952. A study of waterfowl production on artificial reservoirs in eastern Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, Montana: Montana State University. 43 p. Stewart, R. E., and H. A. Kantrud. 1973. Ecological distribution of breeding waterfowl populations in North Dakota. Journal of Wildlife Management 37(1):39-50.
Stewart, R. E., and H. A. Kantrud. 1973. Ecological distribution of breeding waterfowl populations in North Dakota. Journal of Wildlife Management 37(1):39-50. Stewart, R.E. and H.A. Kantrud. 1972. Population estimates of breeding birds in North Dakota. The Auk 89(4):766-788.
Stewart, R.E. and H.A. Kantrud. 1972. Population estimates of breeding birds in North Dakota. The Auk 89(4):766-788. Swan River National Wildlife Refuge. 1982. Birds of the Swan River NWR. Kalispell, MT: NW MT Fish and Wildlife Center pamphlet.
Swan River National Wildlife Refuge. 1982. Birds of the Swan River NWR. Kalispell, MT: NW MT Fish and Wildlife Center pamphlet. The Anaconda Co., 1976, Wildlife survey: The Anaconda Company Berkeley Complex 1976 Proposed Permit Area. May 6, 1976.
The Anaconda Co., 1976, Wildlife survey: The Anaconda Company Berkeley Complex 1976 Proposed Permit Area. May 6, 1976. Thompson, L.S. 1981. Circle West wildlife monitoring study: Third annual report. Technical report No. 8. Montana Department of Natural Resources and Conservation. Helena, Montana.
Thompson, L.S. 1981. Circle West wildlife monitoring study: Third annual report. Technical report No. 8. Montana Department of Natural Resources and Conservation. Helena, Montana. Thompson, Richard W., Western Resource Dev. Corp., Boulder, CO., 1996, Wildlife baseline report for the Montana [Montanore] Project, Lincoln and Sanders counties, Montana. In Application for a Hard Rock Operating Permit and Proposed Plan of Operation, Montanore Project, Lincoln and Sanders Counties, Montana. Vol. 5. Stroiazzo, John. Noranda Minerals Corp., Libby, MT. Revised September 1996.
Thompson, Richard W., Western Resource Dev. Corp., Boulder, CO., 1996, Wildlife baseline report for the Montana [Montanore] Project, Lincoln and Sanders counties, Montana. In Application for a Hard Rock Operating Permit and Proposed Plan of Operation, Montanore Project, Lincoln and Sanders Counties, Montana. Vol. 5. Stroiazzo, John. Noranda Minerals Corp., Libby, MT. Revised September 1996. Thunderbird Wildlife Consulting, Inc., Gillette, WY., 2003, Spring Creek Mine 2002 Wildlife Monitoring. March 2003.
Thunderbird Wildlife Consulting, Inc., Gillette, WY., 2003, Spring Creek Mine 2002 Wildlife Monitoring. March 2003. U.S. Forest Service. 1991. Forest and rangeland birds of the United States: Natural history and habitat use. U.S. Department of Agriculture, Forest Service Agricultural Handbook 688. 625 pages.
U.S. Forest Service. 1991. Forest and rangeland birds of the United States: Natural history and habitat use. U.S. Department of Agriculture, Forest Service Agricultural Handbook 688. 625 pages. Waage, Bruce C., 1995, Western Energy Company Rosebud Mine, Colstrip, Montana:1994 Annual Wildlife Monitoring Report; December 1, 1993 - November 30, 1994. February 27, 1995.
Waage, Bruce C., 1995, Western Energy Company Rosebud Mine, Colstrip, Montana:1994 Annual Wildlife Monitoring Report; December 1, 1993 - November 30, 1994. February 27, 1995. Waage, Bruce C., 1996, Western Energy Company Rosebud Mine, Colstrip, Montana: 1995 Annual Wildlife Monitoring Report; December 1, 1994 - November 30, 1995. February 28, 1996.
Waage, Bruce C., 1996, Western Energy Company Rosebud Mine, Colstrip, Montana: 1995 Annual Wildlife Monitoring Report; December 1, 1994 - November 30, 1995. February 28, 1996. Waage, Bruce C., 1999, Western Energy Company Rosebud Mine, Colstrip, Montana: 1998 Annual Wildlife Monitoring Report; December 1, 1997 - November 30, 1998 Survey Period. February 24, 1999.
Waage, Bruce C., 1999, Western Energy Company Rosebud Mine, Colstrip, Montana: 1998 Annual Wildlife Monitoring Report; December 1, 1997 - November 30, 1998 Survey Period. February 24, 1999. Waage, Bruce C., 2001, Western Energy Company Rosebud Mine, Colstrip, Montana: 2000 Annual Wildlife Monitoring Report; December 1, 1999 - November 30, 2000. March 30, 2001.
Waage, Bruce C., 2001, Western Energy Company Rosebud Mine, Colstrip, Montana: 2000 Annual Wildlife Monitoring Report; December 1, 1999 - November 30, 2000. March 30, 2001. Waage, Bruce C., 2002, Western Energy Company Rosebud Mine, Colstrip, Montana. 2001 Annual Wildlife Monitoring Report; December 1, 2000 - November 30, 2001. Febr. 26, 2002.
Waage, Bruce C., 2002, Western Energy Company Rosebud Mine, Colstrip, Montana. 2001 Annual Wildlife Monitoring Report; December 1, 2000 - November 30, 2001. Febr. 26, 2002. Waldt, R. 1995. The Pine Butte Swamp Preserve bird list. Choteau, MT: The Nature Conservancy. Updated August 1995.
Waldt, R. 1995. The Pine Butte Swamp Preserve bird list. Choteau, MT: The Nature Conservancy. Updated August 1995. Watts, C.R. and L.C. Eichhorn. 1981. Changes in the birds of central Montana. Proceedings of the Montana Academy of Sciences 40:31-40.
Watts, C.R. and L.C. Eichhorn. 1981. Changes in the birds of central Montana. Proceedings of the Montana Academy of Sciences 40:31-40. Western Energy Co., Colstrip, MT., 1980, Western Energy Company Rosebud Mine, Colstrip, Montana: Annual Wildlife Report, 1980.
Western Energy Co., Colstrip, MT., 1980, Western Energy Company Rosebud Mine, Colstrip, Montana: Annual Wildlife Report, 1980. Western Energy Co., Colstrip, MT., 1981, Western Energy Company Rosebud Mine, Colstrip, Montana: Annual Wildlife Report, 1981.
Western Energy Co., Colstrip, MT., 1981, Western Energy Company Rosebud Mine, Colstrip, Montana: Annual Wildlife Report, 1981. Western Technology and Engineering, Inc. (WESTECH)., 1989, Wildlife Monitoring: Absaloka Mine Area Annual Report, 1989. 12/21/88-12/20/89. Montana SMP 85005 R1. OSMP Montana 0007B. Febr. 15, 1990.
Western Technology and Engineering, Inc. (WESTECH)., 1989, Wildlife Monitoring: Absaloka Mine Area Annual Report, 1989. 12/21/88-12/20/89. Montana SMP 85005 R1. OSMP Montana 0007B. Febr. 15, 1990.
- Web Search Engines for Articles on "Lesser Scaup"
- Additional Sources of Information Related to "Birds"





