View in other NatureServe Network Field Guides
NatureServe
Montana
Utah
Wyoming
Idaho
Wisconsin
British Columbia
South Carolina
Yukon
California
New York
Big-leaf Sedge - Carex amplifolia
State Rank Reason (see State Rank above)
Carex amplifolia occurs in temperate western North America where it is usually uncommon or rare from coastal lowlands to middle elevations in the mountains (FNA 2002). The previous SH rank in Montana was based on a 1978 herbarium specimen. In recent years it has been collected from several wetlands in Sanders and Flathead Counties. Additional wetland surveys are needed to accurately document its distribution and population size in Montana.
- Details on Status Ranking and Review
Range Extent
ScoreE - 5,000-20,000 sq km (~2,000-8,000 sq mi)
Area of Occupancy
ScoreD - 6-25 4-km2 grid cells
Number of Populations
ScoreB - 6 - 20
Number of Occurrences or Percent Area with Good Viability / Ecological Integrity
ScoreB - Very few (1-3) occurrences with excellent or good viability or ecological integrity
Environmental Specificity
ScoreC - Moderate. Generalist or community with some key requirements scarce
Threats
ScoreD - Low
CommentThreat categories include: Invasive non-native/alien species/diseases
General Description
PLANTS: Cespitose (tufted) with stout rhizomes (FNA 2002). Culms erect, 50–100 cm, and reddish at the base (Lesica et al. 2012).
LEAVES: Basal and cauline; Sheaths hispidulous; blades 1–2 cm wide (FNA 2002; Lesica et al. 2012). Light or glaucous green (FNA 2002).
INFLORESCENCE: 4 to 8 overlapping, pedunculate spikes (Lesica et al. 2012). The lowest bract is taller than the inflorescence. Spikes ascending, 3–10 cm long, linear.
Phenology
Fruiting late May through September (FNA 2002).
Diagnostic Characteristics
Carex amplifolia is characterized by a combination of stout, winged, and wide (10 mm or more) leaves and narrow spikes that contain numerous, small, dull, and green-brown perigynia (Hurd et al. 1998). Carex amplifolia could be confused with C. utriculata, but the perigynia of the latter are 4-7 mm long. Carex amplifolia superficially resembles Carex scopulorum var. prionophylla but their perigynia differ (with hand-lens ready consult Lesica et al. 2012).
Species Range
Montana Range
Range Descriptions
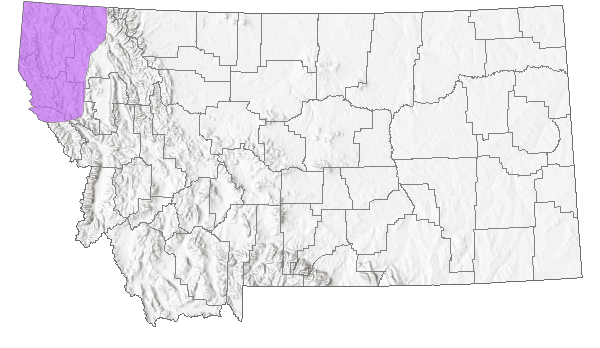
 Native
Native
Range Comments
British Columbia, Canada. California, Idaho, Montana, New Mexico, Oregon, and Washington, U.S. (FNA 2002).
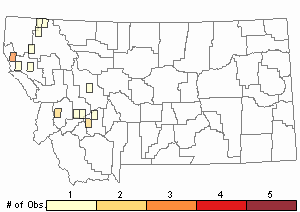
Observations in Montana Natural Heritage Program Database
Number of Observations: 17
(Click on the following maps and charts to see full sized version)
Map Help and Descriptions
Relative Density
Recency
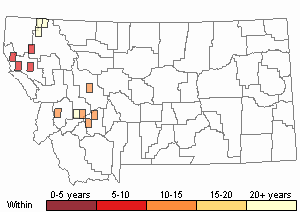
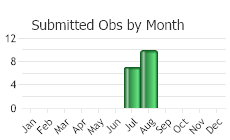
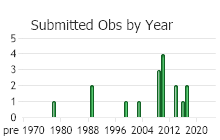
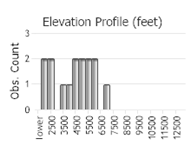 (Observations spanning multiple months or years are excluded from time charts)
(Observations spanning multiple months or years are excluded from time charts)
Habitat
Swamps, bogs, wet meadows, ditches, wetlands in cedar forests, and along streams in coniferous forests (western hemlock, Douglas-fir, and Engelmann spruce zones, and less often in ponderosa pine stands) (FNA 2002).
Ecological Systems Associated with this Species
Reproductive Characteristics
The uppermost spike is male, the remaining lower spikes are female (Lesica et al. 2012).
Within a spike, the perigynia are ascending, green to brown, ovoid, glabrous, 3–4 mm long (includes the 1–2 mm long beak), and 2-ribbed. Female scales are acute to mucronate, reddish brown with a hyaline tip and a light midstripe, longer or shorter than the perigynia. Achene is 3-sided, filling the perigynium.
Stewardship Responsibility
Threats or Limiting Factors
STATE THREAT SCORE REASON
Reported threats to Montana's populations of Big-leaf Sedge include minor impacts of livestock trampling, and potential concerns related to a road (MTNHP Threat Assessment 2021). An abandoned roadbed intersecting one population poses a potential threat of use for fire line installation. A proposal to bulldoze fire line through a part of the population was mitigated in 2017.
References
- Literature Cited AboveLegend:
 View Online Publication
View Online Publication Cronquist, A., A. H. Holmgren, N. H. Holmgren, J. L. Reveal, and P. K. Holmgren. 1977. Intermountain flora: Vascular Plants of the Intermountain West, U.S.A. Volume 6: The Monocotyledons. New York, NY: Columbia University Press. 584 pp.
Cronquist, A., A. H. Holmgren, N. H. Holmgren, J. L. Reveal, and P. K. Holmgren. 1977. Intermountain flora: Vascular Plants of the Intermountain West, U.S.A. Volume 6: The Monocotyledons. New York, NY: Columbia University Press. 584 pp. Flora of North America Editorial Committee(FNA). 2002. Flora of North America north of Mexico. Vol. 23. Magnoliophyta: Commelinidae (in part): Cyperaceae. Oxford Univ. Press, New York. xxiv + 608 pp.
Flora of North America Editorial Committee(FNA). 2002. Flora of North America north of Mexico. Vol. 23. Magnoliophyta: Commelinidae (in part): Cyperaceae. Oxford Univ. Press, New York. xxiv + 608 pp. Hurd, E.G., N.L. Shaw, J. Mastrogiuseppe, L.C. Smithman, and S. Goodrich. 1998. Field Guide to Intermountain Sedges. General Technical Report RMS-GTR-10. Ogden, UT: U.S. Department of Agriculture, Forest Service, Rocky Mountain Research Station. 282 pp.
Hurd, E.G., N.L. Shaw, J. Mastrogiuseppe, L.C. Smithman, and S. Goodrich. 1998. Field Guide to Intermountain Sedges. General Technical Report RMS-GTR-10. Ogden, UT: U.S. Department of Agriculture, Forest Service, Rocky Mountain Research Station. 282 pp. Lesica, P., M.T. Lavin, and P.F. Stickney. 2012. Manual of Montana Vascular Plants. Fort Worth, TX: BRIT Press. viii + 771 p.
Lesica, P., M.T. Lavin, and P.F. Stickney. 2012. Manual of Montana Vascular Plants. Fort Worth, TX: BRIT Press. viii + 771 p. MTNHP Threat Assessment. 2021. State Threat Score Assignment and Assessment of Reported Threats from 2006 to 2021 for State-listed Vascular Plants. Botany Program, Montana Natural Heritage Program, Helena, Montana.
MTNHP Threat Assessment. 2021. State Threat Score Assignment and Assessment of Reported Threats from 2006 to 2021 for State-listed Vascular Plants. Botany Program, Montana Natural Heritage Program, Helena, Montana.
- Additional ReferencesLegend:
 View Online Publication
View Online Publication
Do you know of a citation we're missing? Hermann, F. J. 1970. Manual of the Carices of the Rocky Mountains and Colorado Basin. Agricultural Handbook No. 374. USDA Forest Service. 397 pp.
Hermann, F. J. 1970. Manual of the Carices of the Rocky Mountains and Colorado Basin. Agricultural Handbook No. 374. USDA Forest Service. 397 pp. Lesica, P., M.T. Lavin, and P.F. Stickney. 2022. Manual of Montana Vascular Plants, Second Edition. Fort Worth, TX: BRIT Press. viii + 779 p.
Lesica, P., M.T. Lavin, and P.F. Stickney. 2022. Manual of Montana Vascular Plants, Second Edition. Fort Worth, TX: BRIT Press. viii + 779 p.
- Web Search Engines for Articles on "Big-leaf Sedge"





