View in other NatureServe Network Field Guides
NatureServe
Montana
Utah
Wyoming
Idaho
Wisconsin
British Columbia
South Carolina
Yukon
California
New York
Colorado Alpine - Erebia callias
General Description
[From Ferris and Brown 1981, Scott 1986, Glassberg 2001) Forewing 1.7-2.0 cm. A small alpine; lead-gray in flight with visible reddish flush on dorsal and ventral forewings, two eyespots in reddish forewing patch; ventral surface of hindwing mottled soft-gray
Phenology
One flight; mid-July to late August (Nabokov 1953, Ferris and Brown 1981, Scott 1986).
Diagnostic Characteristics
Soft gray hindwing and reddish-orange forewing disk are distinctive.
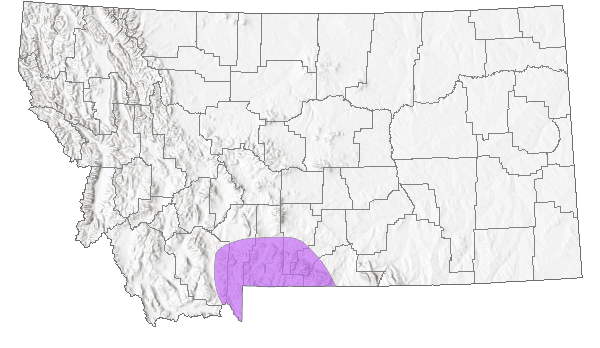
Species Range
Montana Range
Range Descriptions
 Native
Native
Range Comments
Disjunct populations in southern Montana (Carbon and Stillwater counties, Beartooth Mountains), northwestern Wyoming, northeastern Utah (Uinta Mountains), and Colorado. Above 3350 m in Colorado and Utah, 2900 m in Wyoming and Montana (Nabokov 1953, Ferris 1974, Ferris and Brown 1981, Kohler 1980, Scott 1986, Stanford and Opler 1993). Locally uncommon (Glassberg 2001).
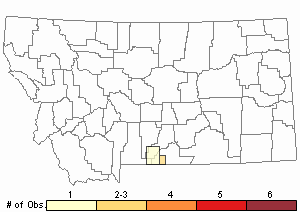
Observations in Montana Natural Heritage Program Database
Number of Observations: 4
(Click on the following maps and charts to see full sized version)
Map Help and Descriptions
Relative Density
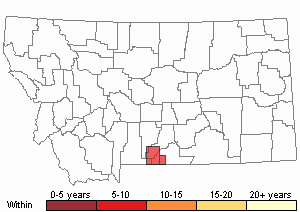
Recency
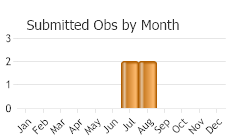
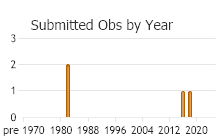
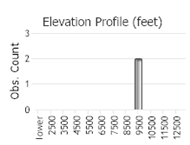 (Observations spanning multiple months or years are excluded from time charts)
(Observations spanning multiple months or years are excluded from time charts)
Migration
Apparently non-migratory.
Habitat
At and above treeline in alpine grassland and meadows, rocky outcroppings (fellfield, but not rock slides), gravel patches (Nabokov 1953, Ferris 1974, Ferris and Brown 1981, Scott 1986).
National Vegetation Classification System Groups Associated with this Species
Alpine
Alpine - Vegetated
Grassland
Montane - Subalpine Grassland
Wetland and Riparian
Alpine Riparian and Wetland
Peatland
Wet Meadow and Marsh
Food Habits
Little information. Larval food plant unknown; possibly alpine grasses (Poa) and/or sedges (Carex, Kobresia). Adults feed on flower nectar (Achillea, Agoseris, Arnica, Erigeron, Heterotheca, Hymenoxys, Potentilla, Sedum, and Senecio); also at mud puddles and dung (Scott 1986, 2014).
Reproductive Characteristics
Little information. Females lay eggs singly on dead blades near alpine grasses (Poa) and sedges (Carex, Kobresia) but larval food plants unknown. Males patrol throughout the day, usually over alpine cushion-plant communities and rounded ridges, but also slopes (Scott 1975b, 1986).
Management
Demonstrably secure globally, though it may be quite rare in parts of its range, especially at the periphery.
Stewardship Responsibility
Threats or Limiting Factors
None reported
References
- Literature Cited AboveLegend:
 View Online Publication
View Online Publication Ferris, C.D. 1974. Variation of Erebia callias (Satyridae) in the United States. Journal of the Lepidopterists' Society 28(3): 230-236.
Ferris, C.D. 1974. Variation of Erebia callias (Satyridae) in the United States. Journal of the Lepidopterists' Society 28(3): 230-236. Ferris, C.D. and F.M. Brown (eds). 1981. Butterflies of the Rocky Mountains. Univ. of Oklahoma Press. Norman. 442 pp.
Ferris, C.D. and F.M. Brown (eds). 1981. Butterflies of the Rocky Mountains. Univ. of Oklahoma Press. Norman. 442 pp. Glassberg, J. 2001. Butterflies through Binoculars: A Field Guide to the Butterflies of Western North America. Oxford University Press.
Glassberg, J. 2001. Butterflies through Binoculars: A Field Guide to the Butterflies of Western North America. Oxford University Press. Kohler, S. 1980. Checklist of Montana Butterflies (Rhopalocera). Journal of the Lepidopterists' Society 34(1): 1-19.
Kohler, S. 1980. Checklist of Montana Butterflies (Rhopalocera). Journal of the Lepidopterists' Society 34(1): 1-19. Nabokov, V. 1953. Butterfly collecting in Wyoming, 1952. The Lepidopterists' News 7(2): 49-52.
Nabokov, V. 1953. Butterfly collecting in Wyoming, 1952. The Lepidopterists' News 7(2): 49-52. Scott, J.A. 1975b. Mate-locating behavior of western North American butterflies. Journal of Research on the Lepidoptera 14:1-40.
Scott, J.A. 1975b. Mate-locating behavior of western North American butterflies. Journal of Research on the Lepidoptera 14:1-40. Scott, J.A. 1986. The butterflies of North America: a natural history and field guide. Stanford University Press, Stanford, California.
Scott, J.A. 1986. The butterflies of North America: a natural history and field guide. Stanford University Press, Stanford, California. Scott, J.A. 2014. Lepidoptera of North America 13. Flower visitation by Colorado butterflies (40,615 records) with a review of the literature on pollination of Colorado plants and butterfly attraction (Lepidoptera: Hersperioidea and Papilionoidea). Contributions of the C.P. Gillette Museum of Arthopod Diversity. Fort Collins, CO: Colorado State University. 190 p.
Scott, J.A. 2014. Lepidoptera of North America 13. Flower visitation by Colorado butterflies (40,615 records) with a review of the literature on pollination of Colorado plants and butterfly attraction (Lepidoptera: Hersperioidea and Papilionoidea). Contributions of the C.P. Gillette Museum of Arthopod Diversity. Fort Collins, CO: Colorado State University. 190 p. Stanford, R.E. and P.A. Opler. 1993. Atlas of western USA butterflies: including adjacent parts of Canada and Mexico. Unpubl. Report. Denver and Fort Collins, Colorado 275 pp.
Stanford, R.E. and P.A. Opler. 1993. Atlas of western USA butterflies: including adjacent parts of Canada and Mexico. Unpubl. Report. Denver and Fort Collins, Colorado 275 pp.
- Additional ReferencesLegend:
 View Online Publication
View Online Publication
Do you know of a citation we're missing? Allen, T.J., J.P. Brock, and J. Glassberg. 2005. Caterpillars in the field and garden: a field guide to the butterfly caterpillars of North America. Oxford University Press.
Allen, T.J., J.P. Brock, and J. Glassberg. 2005. Caterpillars in the field and garden: a field guide to the butterfly caterpillars of North America. Oxford University Press. Brock, J.P. and K. Kaufman. 2003. Kaufman Field Guide to Butterflies of North America. Houghton Mifflin Company, New York, NY 284 pp.
Brock, J.P. and K. Kaufman. 2003. Kaufman Field Guide to Butterflies of North America. Houghton Mifflin Company, New York, NY 284 pp. Forister, M.L., C.A. Halsch, C.C. Nice, J.A. Fordyce, T.E. Dilts, J.C. Oliver, K.L. Prudic, A.M. Shapiro, J.K. Wilson, J. Glassberg. 2021. Fewer butterflies seen by community scientists across the warming and drying landscapes of the American West. Science 371:1042-1045.
Forister, M.L., C.A. Halsch, C.C. Nice, J.A. Fordyce, T.E. Dilts, J.C. Oliver, K.L. Prudic, A.M. Shapiro, J.K. Wilson, J. Glassberg. 2021. Fewer butterflies seen by community scientists across the warming and drying landscapes of the American West. Science 371:1042-1045. Forister, M.L., E.M. Grames, C.A. Halsch, K.J. Burls, C.F. Carroll, K.L. Bell, J.P. Jahner, et al. 2023. Assessing risk for butterflies in the context of climate change, demographic uncertainty, and heterogeneous data sources. Ecological Monographs 93(3):e1584. https://doi.org/10.1002/ecm.1584
Forister, M.L., E.M. Grames, C.A. Halsch, K.J. Burls, C.F. Carroll, K.L. Bell, J.P. Jahner, et al. 2023. Assessing risk for butterflies in the context of climate change, demographic uncertainty, and heterogeneous data sources. Ecological Monographs 93(3):e1584. https://doi.org/10.1002/ecm.1584
- Web Search Engines for Articles on "Colorado Alpine"
- Additional Sources of Information Related to "Insects"





