View in other NatureServe Network Field Guides
NatureServe
Montana
Utah
Wyoming
Idaho
Wisconsin
British Columbia
South Carolina
Yukon
California
New York
Rhesus Skipper - Polites rhesus
General Description
[From Ferris and Brown 1981; Scott 1986; Layberry et al. 1998; Opler and Wright 1999; Glassberg 2001] Forewing 1.2-1.3 cm. Small, wing fringes white. Uppersurface dark gray-brown with a few white forewing spots (larger, more prominent in female), white shoulders, male stigma slender and not obvious. Undersurface of hindwing with scattered patches of chocolate brown and yellow-green, white postbasal mark and postmedian band (chevron), the band extending outward along veins.
Phenology
One flight; mostly May, late May to mid-June at high elevation (Scott 1986). Mainly May to mid-June, as late as mid-July at some localities (Glassberg 2001). May and June in Canada (Layberry et al. 1998). Early May to mid-June in the Rocky Mountain states (Ferris and Brown 1981). Late April to late June in Colorado (Scott and Scott 1978), mid-May to mid-June in western Nebraska (Johnson and Nixon 1967), mid-May to early July in North Dakota (McCabe and Post 1976).
Diagnostic Characteristics
Best determined by a combination of small size, white wing fringes, white shoulders, dark uppersurfae with a few white forewing spots; undersurface of hindwing with scattered patches of chocolate-brown and yellow-green, white postbasal mark and postmedian band (chevron) with white outward extensions along veins.
Species Range
Montana Range
Range Descriptions
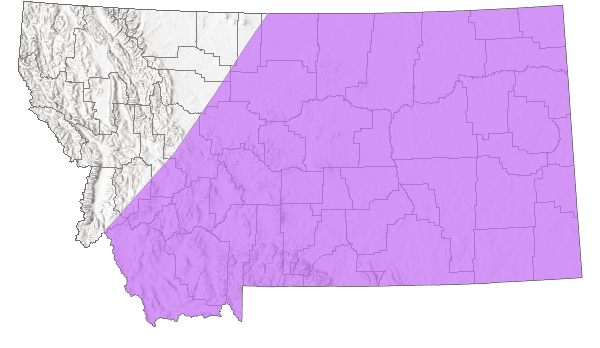
 Native
Native
Range Comments
Southern Alberta and southern Saskatchewan, south in high plains and foothills through Rocky Mountain region to New Mexico, northern Arizona, northern Mexico to Durango, east to western North Dakota, western South Dakota, western Nebraska, western Kansas, northern Texas (Ferris and Brown 1981; Scott 1986; Layberry et al. 1998; Opler and Wright 1999; Glassberg 2001); 1158 m to 2835 m elevation in the Rocky Mountain states (Ferris and Brown 1981), 1311 m to 2743 m elevation in Colorado (Brown 1957; Scott and Scott 1978), to 3048 m elevation in Mexico (Burns 1994). In Montana, not reported through 1993 (Kohler 1980; Stanford and Opler 1993), since reported from at least 11 counties, mostly in the western 1/2 of the state east of the Continental Divide as far east as Hill County in the north, Gallatin County in the south, but also in Carter County adjacent to Harding County, South Dakota (FLMNH Lepidopterists' Society database; Butterflies and Moths of North America database), to at least 1792 m elevation. Mainly rare, but common in some locations and years (Glassberg 2001).
Migration
Non-migratory.
Habitat
Short-grass and mixed-grass prairie, foothill prairie, badlands, urban areas (Johnson and Nixon 1967; McCabe and Post 1976; Scott 1986; Layberry et al. 1998; Opler and Wright 1999; Glassberg 2001). Habitat in Montana not described but probably similar.
Food Habits
Larval food plants are grasses, in particular Bouteloua gracilis (Scott and Scott 1978; Ferris and Brown 1981; Scott 1986, 1992, 2006). Adults feed on flower nectar, including Allium, Astragalus, Erigeron, Erysimum, Hymenoxys, Musineon, Opuntia, Oxytropis, Penstemon, Phlox, Scutellaria, Senecio, Syringa, Taraxacum, and Vicea (Johnson and Nixon 1967; Scott 2014).
Reproductive Characteristics
Limited information. Females lay eggs singly on host plant leaves, usually low to the ground (3 cm). Larvae probably feed on host plant leaves, live in silk tube nests in the lower leaves and in the ground, pupate after growing to L5 instar, overwinter (diapause) as L5 instar (Scott 1986, 1992). Males perch throughout the day on low mesa tops (2 m rises), flats, awaiting passing females (Scott 1975b, 1986).
References
- Literature Cited AboveLegend:
 View Online Publication
View Online Publication Brown, F.M. 1957. Colorado Butterflies. Proceedings; Numbers Three through Seven. Denver Museum of Natural History, Denver, Co.
Brown, F.M. 1957. Colorado Butterflies. Proceedings; Numbers Three through Seven. Denver Museum of Natural History, Denver, Co. Burns, J. M. 1994. Split skippers: Mexican genus Poanopsis goes in the origenes group - and Yvretta forms the rhesus group - of Polites (Hesperiidae). Journal of the Lepidopterists' Society 48(1): 24-45.
Burns, J. M. 1994. Split skippers: Mexican genus Poanopsis goes in the origenes group - and Yvretta forms the rhesus group - of Polites (Hesperiidae). Journal of the Lepidopterists' Society 48(1): 24-45. Ferris, C.D. and F.M. Brown (eds). 1981. Butterflies of the Rocky Mountains. Univ. of Oklahoma Press. Norman. 442 pp.
Ferris, C.D. and F.M. Brown (eds). 1981. Butterflies of the Rocky Mountains. Univ. of Oklahoma Press. Norman. 442 pp. Glassberg, J. 2001. Butterflies through Binoculars: A Field Guide to the Butterflies of Western North America. Oxford University Press.
Glassberg, J. 2001. Butterflies through Binoculars: A Field Guide to the Butterflies of Western North America. Oxford University Press. Johnson, K. and E. S. Nixon. 1967. The Rhopalocera of northwestern Nebraska. American Midland Naturalist 78:508-528.
Johnson, K. and E. S. Nixon. 1967. The Rhopalocera of northwestern Nebraska. American Midland Naturalist 78:508-528. Kohler, S. 1980. Checklist of Montana Butterflies (Rhopalocera). Journal of the Lepidopterists' Society 34(1): 1-19.
Kohler, S. 1980. Checklist of Montana Butterflies (Rhopalocera). Journal of the Lepidopterists' Society 34(1): 1-19. Layberry, R.A., P.W. Hall, and J.D. LaFontaine. 1998. The Butterflies of Canada. University of Toronto Press. 280 pp. + color plates.
Layberry, R.A., P.W. Hall, and J.D. LaFontaine. 1998. The Butterflies of Canada. University of Toronto Press. 280 pp. + color plates. McCabe, T.L. and R.L. Post. 1976. North Dakota butterfly calendar (including possible strays). Journal of Research on the Lepidoptera 15:93-99.
McCabe, T.L. and R.L. Post. 1976. North Dakota butterfly calendar (including possible strays). Journal of Research on the Lepidoptera 15:93-99. Opler, P.A. and A.B. Wright. 1999. A field guide to western butterflies. Second edition. Peterson Field Guides. Houghton Mifflin Company, Boston, Massachusetts. 540 pp.
Opler, P.A. and A.B. Wright. 1999. A field guide to western butterflies. Second edition. Peterson Field Guides. Houghton Mifflin Company, Boston, Massachusetts. 540 pp. Scott, J.A. 1975b. Mate-locating behavior of western North American butterflies. Journal of Research on the Lepidoptera 14:1-40.
Scott, J.A. 1975b. Mate-locating behavior of western North American butterflies. Journal of Research on the Lepidoptera 14:1-40. Scott, J.A. 1986. The butterflies of North America: a natural history and field guide. Stanford University Press, Stanford, California.
Scott, J.A. 1986. The butterflies of North America: a natural history and field guide. Stanford University Press, Stanford, California. Scott, J.A. 1992. Hostplant records for butterflies and skippers (mostly from Colorado) 1959-1992, with new life histories and notes on oviposition, immatures, and ecology. Papilio new series #6. 185 p.
Scott, J.A. 1992. Hostplant records for butterflies and skippers (mostly from Colorado) 1959-1992, with new life histories and notes on oviposition, immatures, and ecology. Papilio new series #6. 185 p. Scott, J.A. 2006. Butterfly hostplant records, 1992-2005, with a treatise on the evolution of Erynnis, and a note on new terminology for mate-locating behavior. Papilio new series #14. 74 p.
Scott, J.A. 2006. Butterfly hostplant records, 1992-2005, with a treatise on the evolution of Erynnis, and a note on new terminology for mate-locating behavior. Papilio new series #14. 74 p. Scott, J.A. 2014. Lepidoptera of North America 13. Flower visitation by Colorado butterflies (40,615 records) with a review of the literature on pollination of Colorado plants and butterfly attraction (Lepidoptera: Hersperioidea and Papilionoidea). Contributions of the C.P. Gillette Museum of Arthopod Diversity. Fort Collins, CO: Colorado State University. 190 p.
Scott, J.A. 2014. Lepidoptera of North America 13. Flower visitation by Colorado butterflies (40,615 records) with a review of the literature on pollination of Colorado plants and butterfly attraction (Lepidoptera: Hersperioidea and Papilionoidea). Contributions of the C.P. Gillette Museum of Arthopod Diversity. Fort Collins, CO: Colorado State University. 190 p. Scott, J.A. and G.R. Scott. 1978. Ecology and distribution of the butterflies of southern central Colorado. Journal of Research on the Lepidoptera 17(2): 73-128.
Scott, J.A. and G.R. Scott. 1978. Ecology and distribution of the butterflies of southern central Colorado. Journal of Research on the Lepidoptera 17(2): 73-128. Scudder, S.H., W.M. Davis, C.W. Woodworth, L.O. Howard, C.V. Riley, S.W. Williston. 1889. The Butterflies of the Eastern United States and Canada. Privately Published. Cambridge, MA.
Scudder, S.H., W.M. Davis, C.W. Woodworth, L.O. Howard, C.V. Riley, S.W. Williston. 1889. The Butterflies of the Eastern United States and Canada. Privately Published. Cambridge, MA. Stanford, R.E. 1981. Hesperiodea. In: Ferris, C.D. and F.M. Brown. Butterflies of the Rocky Mountain States. University of Oklahoma Press, Norman. pp. 67-140.
Stanford, R.E. 1981. Hesperiodea. In: Ferris, C.D. and F.M. Brown. Butterflies of the Rocky Mountain States. University of Oklahoma Press, Norman. pp. 67-140. Stanford, R.E. and P.A. Opler. 1993. Atlas of western USA butterflies: including adjacent parts of Canada and Mexico. Unpubl. Report. Denver and Fort Collins, Colorado 275 pp.
Stanford, R.E. and P.A. Opler. 1993. Atlas of western USA butterflies: including adjacent parts of Canada and Mexico. Unpubl. Report. Denver and Fort Collins, Colorado 275 pp. Tilden, J.W. and A.C. Smith. 1986. A Field Guide to the Western Butterflies. The Peterson Field Guide Series. Houghton Mifflin Co. Boston, Mass.
Tilden, J.W. and A.C. Smith. 1986. A Field Guide to the Western Butterflies. The Peterson Field Guide Series. Houghton Mifflin Co. Boston, Mass.
- Additional ReferencesLegend:
 View Online Publication
View Online Publication
Do you know of a citation we're missing? Allen, T.J., J.P. Brock, and J. Glassberg. 2005. Caterpillars in the field and garden: a field guide to the butterfly caterpillars of North America. Oxford University Press.
Allen, T.J., J.P. Brock, and J. Glassberg. 2005. Caterpillars in the field and garden: a field guide to the butterfly caterpillars of North America. Oxford University Press. Brock, J.P. and K. Kaufman. 2003. Kaufman Field Guide to Butterflies of North America. Houghton Mifflin Company, New York, NY 284 pp.
Brock, J.P. and K. Kaufman. 2003. Kaufman Field Guide to Butterflies of North America. Houghton Mifflin Company, New York, NY 284 pp. Forister, M.L., E.M. Grames, C.A. Halsch, K.J. Burls, C.F. Carroll, K.L. Bell, J.P. Jahner, et al. 2023. Assessing risk for butterflies in the context of climate change, demographic uncertainty, and heterogeneous data sources. Ecological Monographs 93(3):e1584. https://doi.org/10.1002/ecm.1584
Forister, M.L., E.M. Grames, C.A. Halsch, K.J. Burls, C.F. Carroll, K.L. Bell, J.P. Jahner, et al. 2023. Assessing risk for butterflies in the context of climate change, demographic uncertainty, and heterogeneous data sources. Ecological Monographs 93(3):e1584. https://doi.org/10.1002/ecm.1584
- Web Search Engines for Articles on "Rhesus Skipper"
- Additional Sources of Information Related to "Insects"





