View in other NatureServe Network Field Guides
NatureServe
Montana
Utah
Wyoming
Idaho
Wisconsin
British Columbia
South Carolina
Yukon
California
New York
American Ermine - Mustela richardsonii
Other Names:
Short-tailed Weasel,
Mustela erminea
Native Species
Global Rank:
G5
State Rank:
S5
(see State Rank Reason below)
Agency Status
USFWS:
USFS:
BLM:
State Rank Reason (see State Rank above)
Species is relatively common across much of western Montana and in the Greater Yellowstone Area. Is may be experiencing declines but faces no know threats.
General Description
Of the three North American weasels (Genus Mustela), the Short-tailed Weasel is intermediate in size. Males are distinctly larger than females of the same age. During summer the fur is dark brown with white (not buff) under-parts, white feet, and white along the inside of the hind legs. The tip of the tail is black. Molts to entirely white during winter, except for the black on the tip of the tail. Total length: seven to 13 inches. Weight: one to six ounces.
Diagnostic Characteristics
Long-tailed Weasel is larger and tail its is longer. Least Weasel is smaller, has a short tail, and lacks a black tip on the tail. American Mink are larger with a uniform color.
Species Range
Montana Range
Range Descriptions
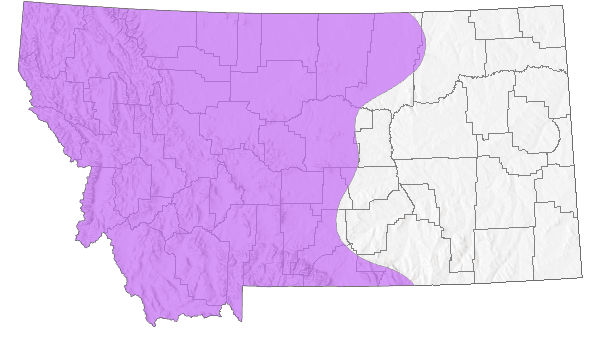
 Native
Native
Global Range

Estimated global breeding range area is: 16,764,117 km
2 (Approximately 1% in Montana)
See information about
 iNaturalist Geomodels
iNaturalist Geomodels
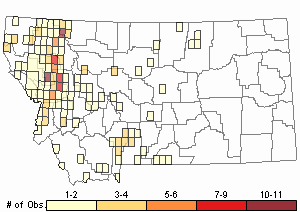
Observations in Montana Natural Heritage Program Database
Number of Observations: 304
(Click on the following maps and charts to see full sized version)
Map Help and Descriptions
Relative Density
Recency
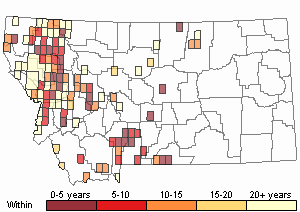
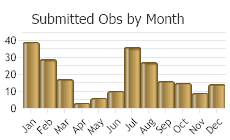
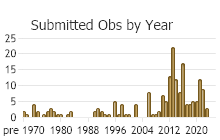
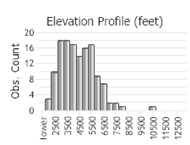 (Observations spanning multiple months or years are excluded from time charts)
(Observations spanning multiple months or years are excluded from time charts)
Migration
Non-migratory.
Habitat
Inhabits brushy or wooded areas, usually not far from water. Tends to avoid dense forests. Prefers areas with high densities of small mammals. Most abundant in ecotones. Mostly nocturnal but will hunt during the day. Active throughout the year. Dens in ground burrows, under stumps, rock piles, or old buildings. In Montana, apparently prone to montane forest associations. Elsewhere occupies a diverse range of habitats. Nests in hollow trees, rock piles or burrows.
National Vegetation Classification System Groups Associated with this Species
Alpine
Alpine - Vegetated
Forest and Woodland
Deciduous Forest and Woodland
Low Elevation - Xeric Forest and Woodland
Montane - Subalpine Forest and Woodland
Shrubland
Foothills - Montane Shrubland
Sagebrush Shrubland
Grassland
Lowland - Prairie Grassland
Montane - Subalpine Grassland
Wetland and Riparian
Alpine Riparian and Wetland
Peatland
Riparian and Wetland Forest
Riparian Shrubland
Wet Meadow and Marsh
Recently Disturbed or Modified
Harvested Forest
Insect-Killed Forest
Recently Burned
Human Land Use
Agriculture
Developed
Food Habits
Short-tailed Weasels prey on a variety of small mammals and birds, they specialize in hunting voles. Mostly small warm-blooded vertebrates, primarily cricetidae. Hunts under snow in winter. Females generally eat smaller prey. May use invertebrates. Short-tailed Weasels will kill larger prey such rabbits.
Ecology
As in many mustelids, two degrees sexual dimorphism is pronounced. Males 30% larger than females. Local distribution and densities probably tied to prey availability. Well adapted to snowy environments.
Reproductive Characteristics
Breeds during summer (June to July); 8.5- to 10-month gestation; delayed implantation; young born April or May; one litter per year of four to 13 young. Induced ovulation. 8.5 to 9 months delay of implantation. Females first breed at 2.5 months. Males at 14 months.
Stewardship Responsibility
References
- Additional ReferencesLegend:
 View Online Publication
View Online Publication
Do you know of a citation we're missing? Adelman, E.B. 1979. A survey of the nongame mammals in the Upper Rattlesnake Creek drainage of western Montana. M.S. thesis. University of Montana, Missoula. 129 pp.
Adelman, E.B. 1979. A survey of the nongame mammals in the Upper Rattlesnake Creek drainage of western Montana. M.S. thesis. University of Montana, Missoula. 129 pp. Butts, T.W., Western Technology and R.L. Eng. 1993. Continental Lime Indian Creek Mine, Townsend, MT. Life of Mine Wildlife Reconnaissance. In Life-of-Mine Amendment. Continental Lime, Inc., Indian Creek Mine & Plant. Vol. 2. October 13, 1992.
Butts, T.W., Western Technology and R.L. Eng. 1993. Continental Lime Indian Creek Mine, Townsend, MT. Life of Mine Wildlife Reconnaissance. In Life-of-Mine Amendment. Continental Lime, Inc., Indian Creek Mine & Plant. Vol. 2. October 13, 1992. Chapman, J.A., and G.A. Feldhamer. 1982. Wild mammals of North America: biology, management, and economics. Johns Hopkins University Press, Baltimore, Maryland.
Chapman, J.A., and G.A. Feldhamer. 1982. Wild mammals of North America: biology, management, and economics. Johns Hopkins University Press, Baltimore, Maryland. Connolly-Newman, Hayley R. 2013. Effect of cover on small mammal abundance and movement through wildlife underpasses. M.S. Thesis. University of Montana. Missoula, MT.
Connolly-Newman, Hayley R. 2013. Effect of cover on small mammal abundance and movement through wildlife underpasses. M.S. Thesis. University of Montana. Missoula, MT. Cramer, P.C. 1992. Small mammal diversity and abundance in Douglas Fir old growth forests. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 64 p.
Cramer, P.C. 1992. Small mammal diversity and abundance in Douglas Fir old growth forests. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 64 p. Deems, E.F., Jr. and D. Pursley (eds). 1978. North American furbearers: their management, research and harvest status in 1976. Int. Assoc. Fish and Wildlife Agencies and University of Maryland. 171 p.
Deems, E.F., Jr. and D. Pursley (eds). 1978. North American furbearers: their management, research and harvest status in 1976. Int. Assoc. Fish and Wildlife Agencies and University of Maryland. 171 p. Fitzgerald, B. M. 1977. Weasel predation on a cyclic population of the montane vole (Microtus montanus) in California. J. Anim. Ecol. 46: 367-397.
Fitzgerald, B. M. 1977. Weasel predation on a cyclic population of the montane vole (Microtus montanus) in California. J. Anim. Ecol. 46: 367-397. Foresman, K. and C. Henderson. 1992. Summary report: small mammal populations in harvested and mature douglas-fir stands: Rivulet Site 1991. [report submitted to Intermtn. Res. Station, For. Sci. Lab.]. Missoula, MT. 14 pp.
Foresman, K. and C. Henderson. 1992. Summary report: small mammal populations in harvested and mature douglas-fir stands: Rivulet Site 1991. [report submitted to Intermtn. Res. Station, For. Sci. Lab.]. Missoula, MT. 14 pp. Foresman, K.R. 2001. The wild mammals of Montana. American Society of Mammalogists, Special Publication Number 12. Lawrence, KS. 278 pp.
Foresman, K.R. 2001. The wild mammals of Montana. American Society of Mammalogists, Special Publication Number 12. Lawrence, KS. 278 pp. Foresman, K.R. 2012. Mammals of Montana. Second edition. Mountain Press Publishing, Missoula, Montana. 429 pp.
Foresman, K.R. 2012. Mammals of Montana. Second edition. Mountain Press Publishing, Missoula, Montana. 429 pp. Geppert, T. J. 1984. Small mammals of the Shield Trap, East Pryor Mountain, Montana. M.S. thesis. University of Iowa, Iowa City. 45 pp.
Geppert, T. J. 1984. Small mammals of the Shield Trap, East Pryor Mountain, Montana. M.S. thesis. University of Iowa, Iowa City. 45 pp. Gillingham, B. J. 1978. A Quantitative Analysis of Prey Killing and Its Ontogeny in the Ermine Mustela Erminea. M.A. Thesis. University of Montana, Missoula.
Gillingham, B. J. 1978. A Quantitative Analysis of Prey Killing and Its Ontogeny in the Ermine Mustela Erminea. M.A. Thesis. University of Montana, Missoula. Halvorson, C.H., R.M. Engleman. 1983. Survival Analysis for a Red Squirrel Population. Journal of Mammalogy. 64(2): 332-336.
Halvorson, C.H., R.M. Engleman. 1983. Survival Analysis for a Red Squirrel Population. Journal of Mammalogy. 64(2): 332-336. Hanauska-Brown, L., B.A. Maxell, A. Petersen, and S. Story. 2014. Diversity Monitoring in Montana 2008-2010 Final Report. Montana Fish, Wildlife & Parks. Helena, MT. 78 pp.
Hanauska-Brown, L., B.A. Maxell, A. Petersen, and S. Story. 2014. Diversity Monitoring in Montana 2008-2010 Final Report. Montana Fish, Wildlife & Parks. Helena, MT. 78 pp. Hatier, K.G. 1995. Effects of helping behaviors on Coyote packs in Yellowstone National Park, Wyoming. M Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 78 p.
Hatier, K.G. 1995. Effects of helping behaviors on Coyote packs in Yellowstone National Park, Wyoming. M Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 78 p. Heath, M.L. 1973. Small mammal populations in clearcuts of various ages in south central Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, Montana: Montana State University. 33 p.
Heath, M.L. 1973. Small mammal populations in clearcuts of various ages in south central Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, Montana: Montana State University. 33 p. Hoffmann, R.S. and D.L. Pattie. 1968. A guide to Montana mammals: identification, habitat, distribution, and abundance. Missoula, MT: University of Montana. 133 p.
Hoffmann, R.S. and D.L. Pattie. 1968. A guide to Montana mammals: identification, habitat, distribution, and abundance. Missoula, MT: University of Montana. 133 p. Johnson, L.J. 1960. Mammal studies on the Lubrecht Forest, Montana: a preliminary report. Proc. Mont. Acad. Sci. 20: 40-47.
Johnson, L.J. 1960. Mammal studies on the Lubrecht Forest, Montana: a preliminary report. Proc. Mont. Acad. Sci. 20: 40-47. Joslin, Gayle, and Heidi B. Youmans. 1999. Effects of recreation on Rocky Mountain wildlife: a review for Montana. [Montana]: Montana Chapter of the Wildlife Society.
Joslin, Gayle, and Heidi B. Youmans. 1999. Effects of recreation on Rocky Mountain wildlife: a review for Montana. [Montana]: Montana Chapter of the Wildlife Society. Keith, L. B. and J. R. Cary 1991. Mustelid, squirrel and porcupine population trends during a snowshoe hare cycle. J. Mammal. 72(2):373-378.
Keith, L. B. and J. R. Cary 1991. Mustelid, squirrel and porcupine population trends during a snowshoe hare cycle. J. Mammal. 72(2):373-378. Key, C.H. 1979. Mammalian utilization of floodplain habitats along the North Fork of the Flathead River in Glacier National Park, Montana. M.S. thesis. University of Montana, Missoula.
Key, C.H. 1979. Mammalian utilization of floodplain habitats along the North Fork of the Flathead River in Glacier National Park, Montana. M.S. thesis. University of Montana, Missoula. King, C. M. 1989. The natural history of weasels and stoats. Comstock Pub. Assoc. Ithaca, NY. 253 pp.
King, C. M. 1989. The natural history of weasels and stoats. Comstock Pub. Assoc. Ithaca, NY. 253 pp. King, C.M. 1983. Mustela erminea. Mammalian. Species No. 195. 8 pp.
King, C.M. 1983. Mustela erminea. Mammalian. Species No. 195. 8 pp. Mead, E.M. and J.I. Mead. 1989. Snake Creek burial cave and a review of the Quaternary mustelids of the Great Basin. Great Basin Naturalist 49(2):143-154.
Mead, E.M. and J.I. Mead. 1989. Snake Creek burial cave and a review of the Quaternary mustelids of the Great Basin. Great Basin Naturalist 49(2):143-154. Oechsli, L.M. 2000. Ex-urban development in the Rocky Mountain West: consequences for native vegetation, wildlife diversity, and land-use planning in Big Sky, Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Montana State University, Bozeman. 73 p.
Oechsli, L.M. 2000. Ex-urban development in the Rocky Mountain West: consequences for native vegetation, wildlife diversity, and land-use planning in Big Sky, Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Montana State University, Bozeman. 73 p. Pattie, D.L. and N.A. M. Verbeek. 1967. Alpine mammals of the Beartooth Plateau. Northwest Science 41(3): 110-117.
Pattie, D.L. and N.A. M. Verbeek. 1967. Alpine mammals of the Beartooth Plateau. Northwest Science 41(3): 110-117. Quick, H.F. 1951. Notes on the ecology of weasels in Gunnison County, Colorado. J. Mammal. 32: 281-290.
Quick, H.F. 1951. Notes on the ecology of weasels in Gunnison County, Colorado. J. Mammal. 32: 281-290. Reid, F. 2006. Peterson Field Guide to Mammals of North America, 4th Edition. Houghton Mifflin Company: Boston and New York, 608 pp.
Reid, F. 2006. Peterson Field Guide to Mammals of North America, 4th Edition. Houghton Mifflin Company: Boston and New York, 608 pp. Rust, H. J. 1946. Mammals of northern Idaho. J. Mammal. 27(4): 308-327.
Rust, H. J. 1946. Mammals of northern Idaho. J. Mammal. 27(4): 308-327. Simms, D.A. 1979. Studies of an ermine population in southern Ontario. Can. J. Zool. 57:504-520.
Simms, D.A. 1979. Studies of an ermine population in southern Ontario. Can. J. Zool. 57:504-520. Stearns-Roger Inc., 1975, Environmental baseline information of the Mount Vernon Region, Montana. January 31, 1975.
Stearns-Roger Inc., 1975, Environmental baseline information of the Mount Vernon Region, Montana. January 31, 1975. Thompson, I. D., I. J. Davidson, S. O'Donnell and F. Brazeau. 1989. Use of track transects to measure the relative occurrence of some boreal mammals in uncut forest and regeneration stands. Can. J. Zool. 67:1816-1823.
Thompson, I. D., I. J. Davidson, S. O'Donnell and F. Brazeau. 1989. Use of track transects to measure the relative occurrence of some boreal mammals in uncut forest and regeneration stands. Can. J. Zool. 67:1816-1823. Thompson, L.S. 1982. Distribution of Montana amphibians, reptiles, and mammals. Bozeman: Montana Audubon Council. 24 pp.
Thompson, L.S. 1982. Distribution of Montana amphibians, reptiles, and mammals. Bozeman: Montana Audubon Council. 24 pp. Thompson, Richard W., Western Resource Dev. Corp., Boulder, CO., 1996, Wildlife baseline report for the Montana [Montanore] Project, Lincoln and Sanders counties, Montana. In Application for a Hard Rock Operating Permit and Proposed Plan of Operation, Montanore Project, Lincoln and Sanders Counties, Montana. Vol. 5. Stroiazzo, John. Noranda Minerals Corp., Libby, MT. Revised September 1996.
Thompson, Richard W., Western Resource Dev. Corp., Boulder, CO., 1996, Wildlife baseline report for the Montana [Montanore] Project, Lincoln and Sanders counties, Montana. In Application for a Hard Rock Operating Permit and Proposed Plan of Operation, Montanore Project, Lincoln and Sanders Counties, Montana. Vol. 5. Stroiazzo, John. Noranda Minerals Corp., Libby, MT. Revised September 1996. Weckwerth, R.P. 1957. The relationship between the marten population and the abundance of small mammals in Glacier National Park. M.S. thesis. University of Montana, Missoula. 76 pp.
Weckwerth, R.P. 1957. The relationship between the marten population and the abundance of small mammals in Glacier National Park. M.S. thesis. University of Montana, Missoula. 76 pp. Western Technology and Engineering, Inc. (WESTECH)., 1997, Wildlife Monitoring Absaloka Mine Area Annual Report, 1996. Montana SMP 85005. OSMP Montana 0007D. Mar. 1997.
Western Technology and Engineering, Inc. (WESTECH)., 1997, Wildlife Monitoring Absaloka Mine Area Annual Report, 1996. Montana SMP 85005. OSMP Montana 0007D. Mar. 1997.
- Web Search Engines for Articles on "American Ermine"
- Additional Sources of Information Related to "Mammals"





