View in other NatureServe Network Field Guides
NatureServe
Montana
Utah
Wyoming
Idaho
Wisconsin
British Columbia
South Carolina
Yukon
California
New York
Channel Catfish - Ictalurus punctatus
Native Species
Global Rank:
G5
State Rank:
S5
(see State Rank Reason below)
Agency Status
USFWS:
USFS:
BLM:
State Rank Reason (see State Rank above)
Widespread, common, and secure
General Description
The largest and most important catfish to sport fishermen in Montana is the native channel catfish of the Yellowstone and Missouri River drainages. These fish prefer warm, muddy rivers and lakes where they forage on just about any animal and some plants, living or dead. They are excellent eaters and millions of pounds of channel catfish are raised commercially in southern states for that purpose. Like all catfish, channel cats spawn in the spring or early summer. The female lays her jelly-like mass of eggs in a nesting site in a dark, protected cavity such as a muskrat burrow, under a stump, etc. and the male guards the nest until the eggs hatch. Biologists have captured channel catfish over 30 pounds in Montana but 2 to 4 pound fish are more common and better eating. The deeply-forked tail separates the channel catfish from the bullheads.
Diagnostic Characteristics
Other Montana catfishes do not have a deeply forked tail.
Species Range
Montana Range
Range Descriptions
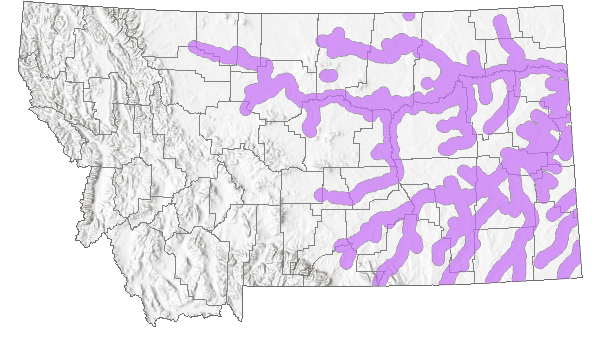
 Native
Native
Western Hemisphere Range

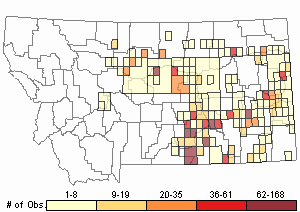
Observations in Montana Natural Heritage Program Database
Number of Observations: 2168
(Click on the following maps and charts to see full sized version)
Map Help and Descriptions
Relative Density
Recency
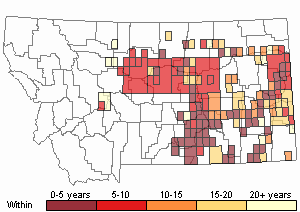
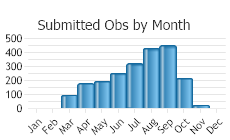
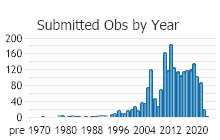
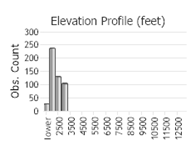 (Observations spanning multiple months or years are excluded from time charts)
(Observations spanning multiple months or years are excluded from time charts)
Migration
May migrate considerable distances to spawn in tributary streams.
Habitat
Prefers large rivers and lowland lakes. Thrives at water temperatures above 70 degrees. Tolerates turbid water.
Food Habits
Omnivorous feeder. Uses almost any living or dead organisms available.
Ecology
Small tributary streams may be vital for reproduction in the lower Yellowstone system.
Reproductive Characteristics
Sexually mature in 3 years. Spawns May-July after water temperature exceeds 75 degrees F. Incubation: 6-10 days. Spawned late May-mid.Aug. in middle Missouri River study with peak in July. Spawns 66 degrees F. Marias River.
Management
The management of this and other native and non-native fish species and their habitats is outlined in Montana Fish, Wildlife and Parks'
2023-2026 Statewide Fisheries Management PlanStewardship Responsibility
References
- Literature Cited AboveLegend:
 View Online Publication
View Online Publication Lee, D.S., C.R. Gilbert, C.H. Hocutt, R.E. Jenkins, D. E. McAllister, J. R. Stauffer, Jr. 1980. Atlas of North American freshwater fishes. North Carolina State Musuem of Natural History. 867 p.
Lee, D.S., C.R. Gilbert, C.H. Hocutt, R.E. Jenkins, D. E. McAllister, J. R. Stauffer, Jr. 1980. Atlas of North American freshwater fishes. North Carolina State Musuem of Natural History. 867 p. Scott, W.B. and E.J. Crossman. 1973. Rainbow trout, Kamloops trout, Steelhead trout Salmo gairdneri Richardson. pp. 184-191. In: Freshwater fishes of Canada. Ottawa, Canada: Fisheries Research Board of Canada, Bulletin 184. 966 p.
Scott, W.B. and E.J. Crossman. 1973. Rainbow trout, Kamloops trout, Steelhead trout Salmo gairdneri Richardson. pp. 184-191. In: Freshwater fishes of Canada. Ottawa, Canada: Fisheries Research Board of Canada, Bulletin 184. 966 p.
- Additional ReferencesLegend:
 View Online Publication
View Online Publication
Do you know of a citation we're missing? Craig, V.E. 1952. A story of fish production as it applies to Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 92 p.
Craig, V.E. 1952. A story of fish production as it applies to Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 92 p. Dieterman, D.J., M.P. Ruggles, M.L. Wildhaber, and D.L. Galat (eds). 1996. Population structure and habitat use of benthic fishes along the Missouri and Lower Yellowstone Rivers. 1996 Annual report of Missouri River Benthic Fish Study PD-95-5832 to U.S. Army Corps of Engineers and U.S. Bureau of Reclamation. 238 p.
Dieterman, D.J., M.P. Ruggles, M.L. Wildhaber, and D.L. Galat (eds). 1996. Population structure and habitat use of benthic fishes along the Missouri and Lower Yellowstone Rivers. 1996 Annual report of Missouri River Benthic Fish Study PD-95-5832 to U.S. Army Corps of Engineers and U.S. Bureau of Reclamation. 238 p. Duncan, M.B. 2019. Distributions, abundances, and movements of small, nongame fishes in a large Great Plains river network. Ph.D. Dissertation. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 255 p.
Duncan, M.B. 2019. Distributions, abundances, and movements of small, nongame fishes in a large Great Plains river network. Ph.D. Dissertation. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 255 p. Holton, G.D. 1981. Identification of Montana's most common game and sport fishes. Montana Outdoors May/June reprint. 8 p.
Holton, G.D. 1981. Identification of Montana's most common game and sport fishes. Montana Outdoors May/June reprint. 8 p. Joslin, Gayle, and Heidi B. Youmans. 1999. Effects of recreation on Rocky Mountain wildlife: a review for Montana. [Montana]: Montana Chapter of the Wildlife Society.
Joslin, Gayle, and Heidi B. Youmans. 1999. Effects of recreation on Rocky Mountain wildlife: a review for Montana. [Montana]: Montana Chapter of the Wildlife Society. Layher, W.G. and O.E. Maughan. 1985. Relations between habitat variables and channel catfish populations in prairie streams. Transactions of the American Fisheries Society 114(6):771-781.
Layher, W.G. and O.E. Maughan. 1985. Relations between habitat variables and channel catfish populations in prairie streams. Transactions of the American Fisheries Society 114(6):771-781. Megargle, D.J. 1997. Temporal variation in food selection of shovelnose sturgeon in the Missouri River above Fort Peck Reservoir, MT. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 127 p.
Megargle, D.J. 1997. Temporal variation in food selection of shovelnose sturgeon in the Missouri River above Fort Peck Reservoir, MT. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 127 p. Montana Department of Fish, Wildlife and Parks. 1989. Northeast Montana Warmwater Ecosystem Investigations: project period 7/1/88 through 6/30/89. Proj.# F-46-R-2; Job# V-e. 21p.
Montana Department of Fish, Wildlife and Parks. 1989. Northeast Montana Warmwater Ecosystem Investigations: project period 7/1/88 through 6/30/89. Proj.# F-46-R-2; Job# V-e. 21p. Mullen, J.A. 2007. Spatiotemporal variation of fish assemblages in Montana prairie streams. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 102 p.
Mullen, J.A. 2007. Spatiotemporal variation of fish assemblages in Montana prairie streams. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 102 p. Mullins, M.S. 1991. Biology and predator use of cisco (Coregonus artedi) in Fort Peck Reservoir, Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 68 p.
Mullins, M.S. 1991. Biology and predator use of cisco (Coregonus artedi) in Fort Peck Reservoir, Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 68 p. Penkal, R.F. 1977. Black bass populations of the Tongue River Reservoir, Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 111 p.
Penkal, R.F. 1977. Black bass populations of the Tongue River Reservoir, Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 111 p. Penkal, R.F. 1981. Life history and flow requirements of paddlefish, shovelnose sturgeon, channel catfish, and other fish in the lower Yellowstone River system. Montana Department of Fish, Wildlife, and Parks. 53 p.
Penkal, R.F. 1981. Life history and flow requirements of paddlefish, shovelnose sturgeon, channel catfish, and other fish in the lower Yellowstone River system. Montana Department of Fish, Wildlife, and Parks. 53 p. Rosenthal, L.R. 2007. Evaluation of distribution and fish passage in relation to road culverts in two eastern Montana prairie streams. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 78 p.
Rosenthal, L.R. 2007. Evaluation of distribution and fish passage in relation to road culverts in two eastern Montana prairie streams. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 78 p. Stash, S.W. 2001. Distribution, relative abundance, and habitat associations of Milk River fishes related to irrigation diversion dams. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 82 p.
Stash, S.W. 2001. Distribution, relative abundance, and habitat associations of Milk River fishes related to irrigation diversion dams. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 82 p. Stringer, A.L. 2018. Status of Northern Pearl Dace and chrosomid dace in prairie streams of Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 150 p.
Stringer, A.L. 2018. Status of Northern Pearl Dace and chrosomid dace in prairie streams of Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 150 p. Trenka, R.J. 2000. Community structure and habitat associations of fishes of the lower Tongue and Powder Rivers. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 85 p.
Trenka, R.J. 2000. Community structure and habitat associations of fishes of the lower Tongue and Powder Rivers. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 85 p. USDI Bureau of Land Management. No date. Fishes of the Miles city, Montana BLM District. Miles City, MT: Miles City BLM District pamphlet. 12 p.
USDI Bureau of Land Management. No date. Fishes of the Miles city, Montana BLM District. Miles City, MT: Miles City BLM District pamphlet. 12 p. Wuellner, M.R. 2007. Influence of reach and watershed characteristics on fish distributions in small streams of eastern Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 80 p.
Wuellner, M.R. 2007. Influence of reach and watershed characteristics on fish distributions in small streams of eastern Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 80 p. Young, B.A., T.L. Welker, M.L. Wildhaber, C.R. Berry, and D. Scarnecchia (eds). 1997. Population structure and habitat use of benthic fishes along the Missouri and Lower Yellowstone Rivers. 1997 Annual report of Missouri River Benthic Fish Study PD-95-5832 to U.S. Army Corps of Engineers and U.S. Bureau of Reclamation. 207 p.
Young, B.A., T.L. Welker, M.L. Wildhaber, C.R. Berry, and D. Scarnecchia (eds). 1997. Population structure and habitat use of benthic fishes along the Missouri and Lower Yellowstone Rivers. 1997 Annual report of Missouri River Benthic Fish Study PD-95-5832 to U.S. Army Corps of Engineers and U.S. Bureau of Reclamation. 207 p.
- Web Search Engines for Articles on "Channel Catfish"
- Additional Sources of Information Related to "Fish"





