View in other NatureServe Network Field Guides
NatureServe
Montana
Utah
Wyoming
Idaho
Wisconsin
British Columbia
South Carolina
Yukon
California
New York
Eyed Brown - Lethe eurydice
Other Names:
Satyrodes eurydice
General Description
[From Ferris and Brown 1981; Scott 1986; Glassberg 2001] Forewing 2.2-2.9 cm. Upper surface ground color a warm dark brown; under surface ground color paler with dark brown lines within and just outside the cells of both wings, postmedian line on hindwing zigzags, strong submarginal eyespots (4-5 on forewing, 6-7 on hindwing) individually surrounded by pale yellow rings, eyespots pupilled with white.
Shropshire and Tallamy (2025) provide a list, with synonymies, of 13,055 described native, exotic, and occasional straying Lepidoptera species of North America, north of Mexico; known but undescribed taxa, taxa with unresolved taxonomy, and excluded species are also included. The
main manuscript includes links to supplementary materials, including a reference list for Lepidoptera of North America north of Mexico, and a filterable spreadsheet with information on taxonomy, synonymy, size ranges of species, distribution by state, province, and country with references, and host-plant Family and Genus associations with references.
Phenology
One flight; late June to July (Scott 1986; Glassberg 2001), adult emergence scattered from mid-June to late August (Ferris and Brown 1981).
Diagnostic Characteristics
Determined by underwing pattern and structure of eyespots combined with zigzag of hindwing postmedian line.
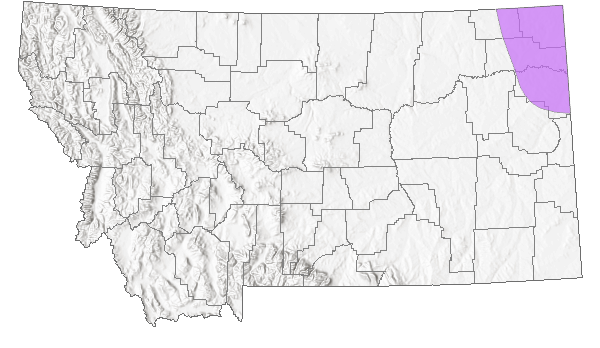
Species Range
Montana Range
Range Descriptions
 Native
Native
Range Comments
Northern half of the eastern US and adjacent southern Canada, from the Atlantic coast west to extreme northeastern Montana and south in the west to northeastern Colorado; also extending northwest into boreal regions of central Saskatchewan and northern Alberta (Scott 1986; Glassberg 2001). Considered a Pleistocene relic of a eastern deciduous forest extension into the Pine Ridge region of northwestern Nebraska (Johnson 1975). In Montana, reported from three extreme northeastern counties: Richland, Roosevelt, Sheridan (FLMNH Lepidopterists' Society database; MNHP), perhaps adjacent Daniels County (Standford and Opler 1993). Rare in the west (Glassberg 2001).
Shropshire and Tallamy (2025) provide link to a supplemental filterable spreadsheet with information on distribution by state, province, and country with references for all Lepidoptera species of North America, north of Mexico.
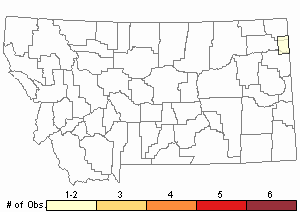
Observations in Montana Natural Heritage Program Database
Number of Observations: 2
(Click on the following maps and charts to see full sized version)
Map Help and Descriptions
Relative Density
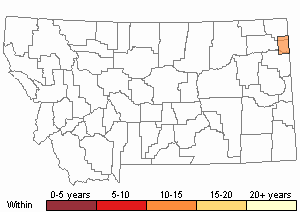
Recency
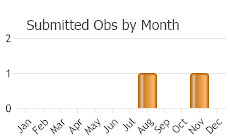
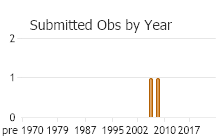
 (Observations spanning multiple months or years are excluded from time charts)
(Observations spanning multiple months or years are excluded from time charts)
Migration
Non-migratory.
Habitat
Open sedge marshes, wet meadows, wooded and open riparian areas including ditches, streams, and sloughs (Shapiro and Carde 1970; Ferris and Brown 1981; Scott 1986, 1992; Glassberg 2001). At least one Montana locality (Medicine Lake National Wildlife Refuge) is a prairie-pothole wetland complex.
Shropshire and Tallamy (2025) provide a link to a supplemental filterable spreadsheet with information on host-plant Family and Genus associations with references for all Lepidoptera species of North America, north of Mexico.
National Vegetation Classification System Groups Associated with this Species
Grassland
Lowland - Prairie Grassland
Wetland and Riparian
Alkaline - Saline Wetlands
Peatland
Riparian and Wetland Forest
Riparian Shrubland
Wet Meadow and Marsh
Food Habits
Larval food plants include sedges (Carex, Scirpus) and grasses (Agrostis, Dactylis, Poa)(Shapiro and Carde 1970; Ferris and Brown 1981; Scott 1986, 1992); grasses preferred over sedges in Colorado. Adults seldom visit flowers, but do feed on flower nectar of Asclepias, Cirsium, Nasturtium, and also sap, dung, and mud (Scott 1986, 2014).
Reproductive Characteristics
Females often lay eggs singly and haphazardly on many plants; in Colorado reported to lay an average of 2 eggs per host plant. Larvae feed on leaves, build no nests. L3 and L4 instars hibernate (Scott 1986). Males in search of females patrol just above the vegetation and perch throughout the day; adults spend 80% of their time resting, typically flying no more than 6 m before landing, although distances of 30 m reported (Scott 1992).
Stewardship Responsibility
References
- Literature Cited AboveLegend:
 View Online Publication
View Online Publication Ferris, C.D. and F.M. Brown (eds). 1981. Butterflies of the Rocky Mountains. Univ. of Oklahoma Press. Norman. 442 pp.
Ferris, C.D. and F.M. Brown (eds). 1981. Butterflies of the Rocky Mountains. Univ. of Oklahoma Press. Norman. 442 pp. Glassberg, J. 2001. Butterflies through Binoculars: A Field Guide to the Butterflies of Western North America. Oxford University Press.
Glassberg, J. 2001. Butterflies through Binoculars: A Field Guide to the Butterflies of Western North America. Oxford University Press. Johnson, K. 1975. Post-Pleistocene environments and montane butterfly relicts on the western Great Plains. Journal of Research on the Lepidoptera 14(4): 216-232.
Johnson, K. 1975. Post-Pleistocene environments and montane butterfly relicts on the western Great Plains. Journal of Research on the Lepidoptera 14(4): 216-232. Scott, J.A. 1986. The butterflies of North America: a natural history and field guide. Stanford University Press, Stanford, California.
Scott, J.A. 1986. The butterflies of North America: a natural history and field guide. Stanford University Press, Stanford, California. Scott, J.A. 1992. Hostplant records for butterflies and skippers (mostly from Colorado) 1959-1992, with new life histories and notes on oviposition, immatures, and ecology. Papilio new series #6. 185 p.
Scott, J.A. 1992. Hostplant records for butterflies and skippers (mostly from Colorado) 1959-1992, with new life histories and notes on oviposition, immatures, and ecology. Papilio new series #6. 185 p. Scott, J.A. 2014. Lepidoptera of North America 13. Flower visitation by Colorado butterflies (40,615 records) with a review of the literature on pollination of Colorado plants and butterfly attraction (Lepidoptera: Hersperioidea and Papilionoidea). Contributions of the C.P. Gillette Museum of Arthopod Diversity. Fort Collins, CO: Colorado State University. 190 p.
Scott, J.A. 2014. Lepidoptera of North America 13. Flower visitation by Colorado butterflies (40,615 records) with a review of the literature on pollination of Colorado plants and butterfly attraction (Lepidoptera: Hersperioidea and Papilionoidea). Contributions of the C.P. Gillette Museum of Arthopod Diversity. Fort Collins, CO: Colorado State University. 190 p. Shapiro, A.M. and R.T. Cardé. 1970. Habitat selection and competition among sibling species of satyrid butterflies. Evolution 24(1): 48-54.
Shapiro, A.M. and R.T. Cardé. 1970. Habitat selection and competition among sibling species of satyrid butterflies. Evolution 24(1): 48-54. Stanford, R.E. and P.A. Opler. 1993. Atlas of western USA butterflies: including adjacent parts of Canada and Mexico. Unpubl. Report. Denver and Fort Collins, Colorado 275 pp.
Stanford, R.E. and P.A. Opler. 1993. Atlas of western USA butterflies: including adjacent parts of Canada and Mexico. Unpubl. Report. Denver and Fort Collins, Colorado 275 pp.
- Additional ReferencesLegend:
 View Online Publication
View Online Publication
Do you know of a citation we're missing? Allen, T.J., J.P. Brock, and J. Glassberg. 2005. Caterpillars in the field and garden: a field guide to the butterfly caterpillars of North America. Oxford University Press.
Allen, T.J., J.P. Brock, and J. Glassberg. 2005. Caterpillars in the field and garden: a field guide to the butterfly caterpillars of North America. Oxford University Press. Brock, J.P. and K. Kaufman. 2003. Kaufman Field Guide to Butterflies of North America. Houghton Mifflin Company, New York, NY 284 pp.
Brock, J.P. and K. Kaufman. 2003. Kaufman Field Guide to Butterflies of North America. Houghton Mifflin Company, New York, NY 284 pp. Shropshire, K.J. and D.W. Tallamy. 2025. Lepidoptera of North America, north of Mexico: an annotated list containing geographic ranges and host-plant records. Zookeys.1261:101-113.
Shropshire, K.J. and D.W. Tallamy. 2025. Lepidoptera of North America, north of Mexico: an annotated list containing geographic ranges and host-plant records. Zookeys.1261:101-113.
- Web Search Engines for Articles on "Eyed Brown"
- Additional Sources of Information Related to "Insects"





