View in other NatureServe Network Field Guides
NatureServe
Montana
Utah
Wyoming
Idaho
Wisconsin
British Columbia
South Carolina
Yukon
California
New York
Bog Fritillary - Boloria eunomia
General Description
[From Ferris and Brown 1981, Scott 1986, Glassberg 2001, Guppy and Shepard 2001] Forewing 1.8-2.0 cm. Variable in ground color; dorsal surface pale yellowish-brown to rich orangish-brown with dark scaling at wing base; dorsal hindwing with black border and inward-pointing chevrons enclosing pale spots; ventral hindwing with row of large marginal spots silver to clear-yellowish, an even row of white-centered postmedian spots outlined in black, and a white median cell spot at inner margin which is outwardly convex.
Shropshire and Tallamy (2025) provide a list, with synonymies, of 13,055 described native, exotic, and occasional straying Lepidoptera species of North America, north of Mexico; known but undescribed taxa, taxa with unresolved taxonomy, and excluded species are also included. The
main manuscript includes links to supplementary materials, including a reference list for Lepidoptera of North America north of Mexico, and a filterable spreadsheet with information on taxonomy, synonymy, size ranges of species, distribution by state, province, and country with references, and host-plant Family and Genus associations with references.
Phenology
One flight: July to early August in the south at higher elevations, mid-June to July in north, mid-July to August in Labrador and central Wyoming (Ferris and Brown 1981, Scott 1986); in British Columbia, mid-June to early August (Guppy and Shepard 2001).
Diagnostic Characteristics
Identified by the ventral hindwing with row of large marginal spots silver to clear-yellowish, an even row of white-centered postmedian spots outlined in black, and a white median cell spot at inner margin which is outwardly convex.
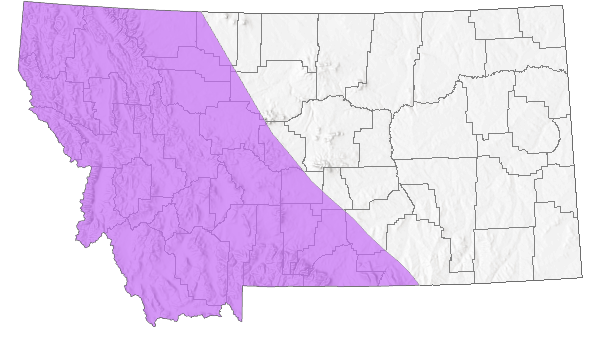
Species Range
Montana Range
Range Descriptions
 Native
Native
Range Comments
Alaska and most of boreal and arctic Canada south to the bordering United States including northern Maine and the northern Great Lakes region; south in the Rocky Mountains of Montana, Wyoming, and Colorado in disjunct populations (Scott 1986, Guppy and Shepard 2001). In Montana, reported from the Beartooth Mountains in Carbon and Stillwater counties, and Glacier National Park in Glacier County (Kohler 1980, Stanford and Opler 1993). Locally rare to locally uncommon (Glassberg 2001).
Shropshire and Tallamy (2025) provide link to a supplemental filterable spreadsheet with information on distribution by state, province, and country with references for all Lepidoptera species of North America, north of Mexico.
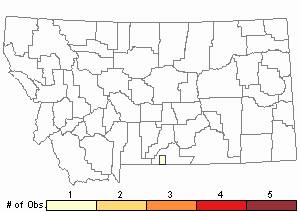
Observations in Montana Natural Heritage Program Database
Number of Observations: 4
(Click on the following maps and charts to see full sized version)
Map Help and Descriptions
Relative Density
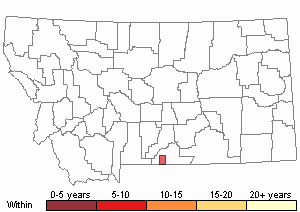
Recency
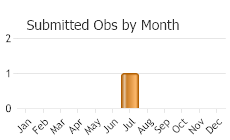
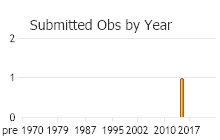
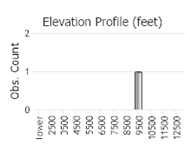 (Observations spanning multiple months or years are excluded from time charts)
(Observations spanning multiple months or years are excluded from time charts)
Migration
Non-migratory; often move a few hundred meters through woods between wet habitat areas (Scott 1986).
Habitat
Spruce forest meadows along streams, sphagnum fens and bog edges, margins of glacial tarns, moist tundra above treeline (Ferris and Brown 1981, Scott 1986, Guppy and Shepard 2001).
Shropshire and Tallamy (2025) provide a link to a supplemental filterable spreadsheet with information on host-plant Family and Genus associations with references for all Lepidoptera species of North America, north of Mexico.
National Vegetation Classification System Groups Associated with this Species
Alpine
Alpine - Vegetated
Grassland
Montane - Subalpine Grassland
Wetland and Riparian
Alkaline - Saline Wetlands
Alpine Riparian and Wetland
Peatland
Wet Meadow and Marsh
Food Habits
Larval food plants include Bistorta, Polygonum, Salix, and Viola, with Salix and Viola readily eaten in captivity (Ferris and Brown 1981, Scott 1986). Adults feed on flower nectar.
Reproductive Characteristics
Little information. Eggs laid in clusters of 2-4 (rarely 20) under leaves of host plants; larvae overwinter as L3-L4 instars. Males patrol throughout the day low over bogs in search of females (Scott 1986).
Stewardship Responsibility
References
- Literature Cited AboveLegend:
 View Online Publication
View Online Publication Ferris, C.D. and F.M. Brown (eds). 1981. Butterflies of the Rocky Mountains. Univ. of Oklahoma Press. Norman. 442 pp.
Ferris, C.D. and F.M. Brown (eds). 1981. Butterflies of the Rocky Mountains. Univ. of Oklahoma Press. Norman. 442 pp. Glassberg, J. 2001. Butterflies through Binoculars: A Field Guide to the Butterflies of Western North America. Oxford University Press.
Glassberg, J. 2001. Butterflies through Binoculars: A Field Guide to the Butterflies of Western North America. Oxford University Press. Guppy, C.S. and J.H. Shepard. 2001. Butterflies of British Columbia: including western Alberta, southern Yukon, the Alaska Panhandle, Washington, northern Oregon, northern Idaho, northwestern Montana. UBC Press (Vancouver, BC) and Royal British Columbia Museum (Victoria, BC). 414 pp.
Guppy, C.S. and J.H. Shepard. 2001. Butterflies of British Columbia: including western Alberta, southern Yukon, the Alaska Panhandle, Washington, northern Oregon, northern Idaho, northwestern Montana. UBC Press (Vancouver, BC) and Royal British Columbia Museum (Victoria, BC). 414 pp. Kohler, S. 1980. Checklist of Montana Butterflies (Rhopalocera). Journal of the Lepidopterists' Society 34(1): 1-19.
Kohler, S. 1980. Checklist of Montana Butterflies (Rhopalocera). Journal of the Lepidopterists' Society 34(1): 1-19. Scott, J.A. 1986. The butterflies of North America: a natural history and field guide. Stanford University Press, Stanford, California.
Scott, J.A. 1986. The butterflies of North America: a natural history and field guide. Stanford University Press, Stanford, California. Stanford, R.E. and P.A. Opler. 1993. Atlas of western USA butterflies: including adjacent parts of Canada and Mexico. Unpubl. Report. Denver and Fort Collins, Colorado 275 pp.
Stanford, R.E. and P.A. Opler. 1993. Atlas of western USA butterflies: including adjacent parts of Canada and Mexico. Unpubl. Report. Denver and Fort Collins, Colorado 275 pp.
- Additional ReferencesLegend:
 View Online Publication
View Online Publication
Do you know of a citation we're missing? Allen, T.J., J.P. Brock, and J. Glassberg. 2005. Caterpillars in the field and garden: a field guide to the butterfly caterpillars of North America. Oxford University Press.
Allen, T.J., J.P. Brock, and J. Glassberg. 2005. Caterpillars in the field and garden: a field guide to the butterfly caterpillars of North America. Oxford University Press. Brock, J.P. and K. Kaufman. 2003. Kaufman Field Guide to Butterflies of North America. Houghton Mifflin Company, New York, NY 284 pp.
Brock, J.P. and K. Kaufman. 2003. Kaufman Field Guide to Butterflies of North America. Houghton Mifflin Company, New York, NY 284 pp. Forister, M.L., E.M. Grames, C.A. Halsch, K.J. Burls, C.F. Carroll, K.L. Bell, J.P. Jahner, et al. 2023. Assessing risk for butterflies in the context of climate change, demographic uncertainty, and heterogeneous data sources. Ecological Monographs 93(3):e1584. https://doi.org/10.1002/ecm.1584
Forister, M.L., E.M. Grames, C.A. Halsch, K.J. Burls, C.F. Carroll, K.L. Bell, J.P. Jahner, et al. 2023. Assessing risk for butterflies in the context of climate change, demographic uncertainty, and heterogeneous data sources. Ecological Monographs 93(3):e1584. https://doi.org/10.1002/ecm.1584 Layberry, R.A., P.W. Hall, and J.D. LaFontaine. 1998. The Butterflies of Canada. University of Toronto Press. 280 pp. + color plates.
Layberry, R.A., P.W. Hall, and J.D. LaFontaine. 1998. The Butterflies of Canada. University of Toronto Press. 280 pp. + color plates. Opler, P.A. and A.B. Wright. 1999. A field guide to western butterflies. Second edition. Peterson Field Guides. Houghton Mifflin Company, Boston, Massachusetts. 540 pp.
Opler, P.A. and A.B. Wright. 1999. A field guide to western butterflies. Second edition. Peterson Field Guides. Houghton Mifflin Company, Boston, Massachusetts. 540 pp. Opler, P.A. and A.D. Warren. 2002. Scientific names list for butterfly species of North America, north of Mexico. C.P Gillette Museum of Arthropod Diversity, Department of Bioagricultural Sciences and Pest Management, Colorado State University, Fort Collins, Colorado. 79 pp.
Opler, P.A. and A.D. Warren. 2002. Scientific names list for butterfly species of North America, north of Mexico. C.P Gillette Museum of Arthropod Diversity, Department of Bioagricultural Sciences and Pest Management, Colorado State University, Fort Collins, Colorado. 79 pp. Opler, P.A., K. Lotts, and T. Naberhaus, coordinators. 2010. Butterflies and moths of North America. Big Sky Institute, Bozeman, MT. Available at: www.butterfliesandmoths.org (Accessed 15 June 2015).
Opler, P.A., K. Lotts, and T. Naberhaus, coordinators. 2010. Butterflies and moths of North America. Big Sky Institute, Bozeman, MT. Available at: www.butterfliesandmoths.org (Accessed 15 June 2015). Shropshire, K.J. and D.W. Tallamy. 2025. Lepidoptera of North America, north of Mexico: an annotated list containing geographic ranges and host-plant records. Zookeys.1261:101-113.
Shropshire, K.J. and D.W. Tallamy. 2025. Lepidoptera of North America, north of Mexico: an annotated list containing geographic ranges and host-plant records. Zookeys.1261:101-113.
- Web Search Engines for Articles on "Bog Fritillary"
- Additional Sources of Information Related to "Insects"





