View in other NatureServe Network Field Guides
NatureServe
Montana
Utah
Wyoming
Idaho
Wisconsin
British Columbia
South Carolina
Yukon
California
New York
North American Water Vole - Microtus richardsoni
State Rank Reason (see State Rank above)
Species is uncommon across much of western and portions of central Montana. It is likely stable but faces threats from drought.
General Description
The North American Water Vole, also known as a water rat or Richardson Vole, is the largest vole in Montana. At over 9 inches and around 4 ounces, the male adult is about twice the length and four times the weight of other voles in the state. Long fur covers water voles, dark brown to reddish brown on top, and gray, mixed with white or silver on their bellies. They have long bicolored tails and enlarged flank glands during breeding season (Zeveloff 1988). Foresman (2001) points to the long hind feet and protruding incisors as other characteristics that distinguish these very large, semiaquatic voles.
Species Range
Montana Range
Range Descriptions
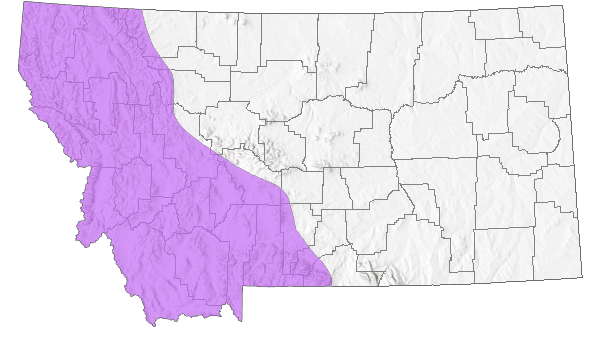
 Native
Native
Western Hemisphere Range

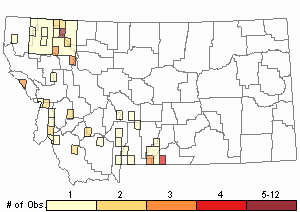
Observations in Montana Natural Heritage Program Database
Number of Observations: 71
(Click on the following maps and charts to see full sized version)
Map Help and Descriptions
Relative Density
Recency
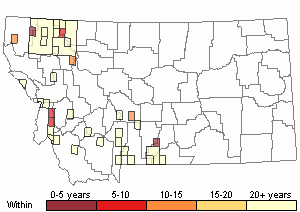
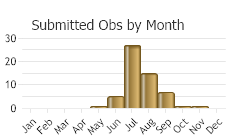
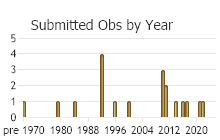
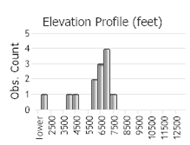 (Observations spanning multiple months or years are excluded from time charts)
(Observations spanning multiple months or years are excluded from time charts)
Migration
Non-migratory.
Habitat
Semi-aquatic. Near streams and lakes in subalpine and alpine zones. Normally above 5000 ft. in western mountains. Moist grass and sedge areas, streamside hummocks overhung with willows (Hoffmann and Pattie 1968, Pattie 1967).
National Vegetation Classification System Groups Associated with this Species
Alpine
Alpine - Sparse and Barren
Alpine - Vegetated
Forest and Woodland
Montane - Subalpine Forest and Woodland
Shrubland
Foothills - Montane Shrubland
Grassland
Montane - Subalpine Grassland
Wetland and Riparian
Alpine Riparian and Wetland
Peatland
Riparian and Wetland Forest
Riparian Shrubland
Wet Meadow and Marsh
Recently Disturbed or Modified
Insect-Killed Forest
Food Habits
Pattie (1967) mentions possible heavy use of graminoids. Composite data from a variety of areas suggest forbs and willows also eaten. Use of Vaccinium, erythronium bulbs, conifer seeds, insects reported.
Ecology
Burrows, runways and cuttings are conspicuous in summer (Hoffmann and Pattie 1968). Density estimated 0.18 to 1.03/acre in Beartooths (Pattie 1967). A very large vole.
Reproductive Characteristics
In Beartooths begins breeding in early June. Adults average 5.9 young/litter. Some female young breed as subadults. During first year some young males become sexually mature in August (Pattie 1967).
Stewardship Responsibility
References
- Literature Cited AboveLegend:
 View Online Publication
View Online Publication Foresman, K.R. 2001. The wild mammals of Montana. American Society of Mammalogists, Special Publication Number 12. Lawrence, KS. 278 pp.
Foresman, K.R. 2001. The wild mammals of Montana. American Society of Mammalogists, Special Publication Number 12. Lawrence, KS. 278 pp. Hoffmann, R.S. and D.L. Pattie. 1968. A guide to Montana mammals: identification, habitat, distribution, and abundance. Missoula, MT: University of Montana. 133 p.
Hoffmann, R.S. and D.L. Pattie. 1968. A guide to Montana mammals: identification, habitat, distribution, and abundance. Missoula, MT: University of Montana. 133 p. Pattie, D.L. and N.A. M. Verbeek. 1967. Alpine mammals of the Beartooth Plateau. Northwest Science 41(3): 110-117.
Pattie, D.L. and N.A. M. Verbeek. 1967. Alpine mammals of the Beartooth Plateau. Northwest Science 41(3): 110-117. Zeveloff, S.I. and F.R. Collett. 1988. Mammals of the Intermountain west. University of Utah Press, Salt Lake City, Utah.
Zeveloff, S.I. and F.R. Collett. 1988. Mammals of the Intermountain west. University of Utah Press, Salt Lake City, Utah.
- Additional ReferencesLegend:
 View Online Publication
View Online Publication
Do you know of a citation we're missing? Anaconda Minerals Company, and Camp, Dresser & McKee. 1981. Anaconda Stillwater Project 6-month environmental baseline report. CDM Project No. 3139. Vol. I Appendix. Jan. 15, 1981.
Anaconda Minerals Company, and Camp, Dresser & McKee. 1981. Anaconda Stillwater Project 6-month environmental baseline report. CDM Project No. 3139. Vol. I Appendix. Jan. 15, 1981. Brown, L.N. 1977. Litter size and notes on reproduction in the giant water vole (Arricola richardsoni). Southwest. Nat. 22:281-282.
Brown, L.N. 1977. Litter size and notes on reproduction in the giant water vole (Arricola richardsoni). Southwest. Nat. 22:281-282. Clark, S.G. and M.R. Stromberg. 1987. Mammals in Wyoming. University of Kansas Museum of Natural History, Public Education Series Number 10. xii + 314 pp.
Clark, S.G. and M.R. Stromberg. 1987. Mammals in Wyoming. University of Kansas Museum of Natural History, Public Education Series Number 10. xii + 314 pp. Confluence Consulting Inc. 2011. Montana Department of Transportation Wetland Mitigation Monitoring Reports (various sites). MDT Helena, MT.
Confluence Consulting Inc. 2011. Montana Department of Transportation Wetland Mitigation Monitoring Reports (various sites). MDT Helena, MT. Craighead, A.C. 2000. Pellet and scat analysis as indicators of present and past habitats. M.Sc. Theses. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 219 p.
Craighead, A.C. 2000. Pellet and scat analysis as indicators of present and past habitats. M.Sc. Theses. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 219 p. Feigley, H.P. 1981. Studies on native small mammals as intermediate hosts of Echinococcus multilocularis. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, Montana: Montana State University. 50 p.
Feigley, H.P. 1981. Studies on native small mammals as intermediate hosts of Echinococcus multilocularis. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, Montana: Montana State University. 50 p. Foresman, K.R. 2012. Mammals of Montana. Second edition. Mountain Press Publishing, Missoula, Montana. 429 pp.
Foresman, K.R. 2012. Mammals of Montana. Second edition. Mountain Press Publishing, Missoula, Montana. 429 pp. Hanauska-Brown, L., B.A. Maxell, A. Petersen, and S. Story. 2014. Diversity Monitoring in Montana 2008-2010 Final Report. Montana Fish, Wildlife & Parks. Helena, MT. 78 pp.
Hanauska-Brown, L., B.A. Maxell, A. Petersen, and S. Story. 2014. Diversity Monitoring in Montana 2008-2010 Final Report. Montana Fish, Wildlife & Parks. Helena, MT. 78 pp. Hoffmann, R.S., P.L. Wright, and F.E. Newby. 1969. The distribution of some mammals in Montana. I. Mammals other than bats. Journal of Mammalogy 50(3): 579-604.
Hoffmann, R.S., P.L. Wright, and F.E. Newby. 1969. The distribution of some mammals in Montana. I. Mammals other than bats. Journal of Mammalogy 50(3): 579-604. Joslin, Gayle, and Heidi B. Youmans. 1999. Effects of recreation on Rocky Mountain wildlife: a review for Montana. [Montana]: Montana Chapter of the Wildlife Society.
Joslin, Gayle, and Heidi B. Youmans. 1999. Effects of recreation on Rocky Mountain wildlife: a review for Montana. [Montana]: Montana Chapter of the Wildlife Society. Klaus, M. 1997. Dispersal of Microtus richardsoni in the Beartooth Mountains of Montana and Wyoming. Ph.D. Dissertation. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 56 p.
Klaus, M. 1997. Dispersal of Microtus richardsoni in the Beartooth Mountains of Montana and Wyoming. Ph.D. Dissertation. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 56 p. Kritzman, E.B. 1977. Little mammals of the Pacific Northwest. Pacific Search Press, Seattle, WA.
Kritzman, E.B. 1977. Little mammals of the Pacific Northwest. Pacific Search Press, Seattle, WA. Ludwig, D. R. 1984. Microtus richardsoni. Mamm. Species 223:1-6.
Ludwig, D. R. 1984. Microtus richardsoni. Mamm. Species 223:1-6. Oechsli, L.M. 2000. Ex-urban development in the Rocky Mountain West: consequences for native vegetation, wildlife diversity, and land-use planning in Big Sky, Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Montana State University, Bozeman. 73 p.
Oechsli, L.M. 2000. Ex-urban development in the Rocky Mountain West: consequences for native vegetation, wildlife diversity, and land-use planning in Big Sky, Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Montana State University, Bozeman. 73 p. Pattie, D.L. 1967. Dynamics of alpine small mammal populations. Ph.D dissertation. University of Montana, Missoula. 102 pp.
Pattie, D.L. 1967. Dynamics of alpine small mammal populations. Ph.D dissertation. University of Montana, Missoula. 102 pp. Reichel, J.D. 1986. Habitat use by alpine mammals in the Pacific Northwest. Arctic and Alpine Research. 18(1): 111-119.
Reichel, J.D. 1986. Habitat use by alpine mammals in the Pacific Northwest. Arctic and Alpine Research. 18(1): 111-119. Reichel, J.D. and S.G. Beckstrom. 1993. Northern bog lemming survey: 1992. Unpublished report. Montana Natural Heritage Program, Helena, MT. 64 p.
Reichel, J.D. and S.G. Beckstrom. 1993. Northern bog lemming survey: 1992. Unpublished report. Montana Natural Heritage Program, Helena, MT. 64 p. Reid, F. 2006. Peterson Field Guide to Mammals of North America, 4th Edition. Houghton Mifflin Company: Boston and New York, 608 pp.
Reid, F. 2006. Peterson Field Guide to Mammals of North America, 4th Edition. Houghton Mifflin Company: Boston and New York, 608 pp. Russell, R. J. and S. Anderson. 1956. Small mammals from Silver Bow County, Montana. Murrelet 37:2-3.
Russell, R. J. and S. Anderson. 1956. Small mammals from Silver Bow County, Montana. Murrelet 37:2-3. Rust, H. J. 1946. Mammals of northern Idaho. J. Mammal. 27(4): 308-327.
Rust, H. J. 1946. Mammals of northern Idaho. J. Mammal. 27(4): 308-327. Soper, J.D. 1973. The mammals of Waterton Lakes National Park, Alberta. Canadian Wildlife Service Report Series, No. 23. 57 pp.
Soper, J.D. 1973. The mammals of Waterton Lakes National Park, Alberta. Canadian Wildlife Service Report Series, No. 23. 57 pp. Thompson, L.S. 1982. Distribution of Montana amphibians, reptiles, and mammals. Bozeman: Montana Audubon Council. 24 pp.
Thompson, L.S. 1982. Distribution of Montana amphibians, reptiles, and mammals. Bozeman: Montana Audubon Council. 24 pp.
- Web Search Engines for Articles on "North American Water Vole"
- Additional Sources of Information Related to "Mammals"





