View in other NatureServe Network Field Guides
NatureServe
Montana
Utah
Wyoming
Idaho
Wisconsin
British Columbia
South Carolina
Yukon
California
New York
General Description
Utah chub were introduced into Montana in the 1930's, probably by bait fishermen. They were released into Hebgen Lake, a headwater reservoir on the Missouri River system, and have since extended their range about 200 miles downstream. In time, they could even move into North Dakota. Utah chubs are omnivorous and can grow to a size of up to 2 pounds. They are considered to be a very undesirable fish. In some reservoirs, they have become very abundant and may compete for food with trout. These chubs can become too large to be preyed upon by trout and are annoying because they readily take fishermen's bait.
Diagnostic Characteristics
Back olive brown to nearly black, occasionally bluish; sides usually brassy but sometimes silvery. Underside whitish or silver. No barbels.
Species Range
Montana Range
Range Descriptions
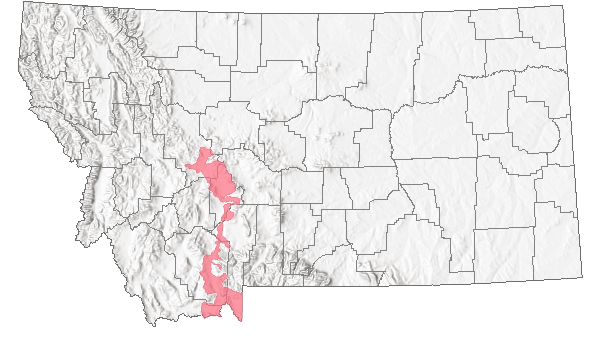
 Non-native
Non-native
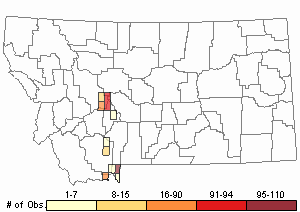
Observations in Montana Natural Heritage Program Database
Number of Observations: 355
(Click on the following maps and charts to see full sized version)
Map Help and Descriptions
Relative Density
Recency
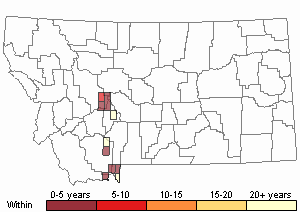
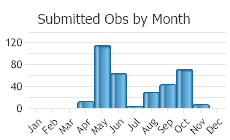
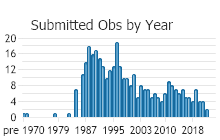
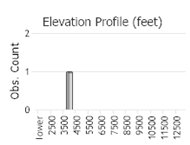 (Observations spanning multiple months or years are excluded from time charts)
(Observations spanning multiple months or years are excluded from time charts)
Migration
Found to move at least short distances up streams and tributaries in Hebgen Lake Study.
Habitat
Very generalized habitat requirements. Found in both stream and lakes with abundant aquatic vegetation. Prefers slow-moving or still water as in sloughs backwaters, and reservoirs. Spawns in littoral waters.
Food Habits
Young feed largely on zooplankton. Adults become omnivorous utilizing aquatic plants, insects, and crustaceans.
Ecology
Rooted aquatic vegetation important for spawning and rearing areas. Adult chubs found in 1978 Montana study were not associated with aquatic vegetation.
Reproductive Characteristics
Sexually mature: males in 3 yrs, and females in 4 years. Spawns in mid-May - mid-Aug. in Hebgen Lake when water temp. exceeds 54 degrees F. with late June - early July peak.
Management
Stewardship Responsibility
References
- Additional ReferencesLegend:
 View Online Publication
View Online Publication
Do you know of a citation we're missing? Gillespie, D.M. 1966. Population studies of four species of mollusks in the Madison River, Yellowstone National Park. Ph.D. Dissertation. Bozeman, Montana: Montana State University. 43 p.
Gillespie, D.M. 1966. Population studies of four species of mollusks in the Madison River, Yellowstone National Park. Ph.D. Dissertation. Bozeman, Montana: Montana State University. 43 p. Graham, R.J. 1955. Biology of the Utah chub in Hebgen Lake, Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 32 p.
Graham, R.J. 1955. Biology of the Utah chub in Hebgen Lake, Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 32 p. Jeanes, E.D. 1996. Behavioral responses to water current of age-0 Arctic Grayling from the Madison River, and their use of stream habitat. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 60p.
Jeanes, E.D. 1996. Behavioral responses to water current of age-0 Arctic Grayling from the Madison River, and their use of stream habitat. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 60p. Joslin, Gayle, and Heidi B. Youmans. 1999. Effects of recreation on Rocky Mountain wildlife: a review for Montana. [Montana]: Montana Chapter of the Wildlife Society.
Joslin, Gayle, and Heidi B. Youmans. 1999. Effects of recreation on Rocky Mountain wildlife: a review for Montana. [Montana]: Montana Chapter of the Wildlife Society. Montana Fish, Wildlife and Parks. 1989. Hauser Reservoir fisheries management plan: September 1989-September 1994. 16 p.
Montana Fish, Wildlife and Parks. 1989. Hauser Reservoir fisheries management plan: September 1989-September 1994. 16 p. Sundeen, D.R. 1968. Abundance and movement of young trout in a portion of the Madison River, Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, Montana: Montana State University. 19 p.
Sundeen, D.R. 1968. Abundance and movement of young trout in a portion of the Madison River, Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, Montana: Montana State University. 19 p. Watschke, D.A. 2006. Assessment of tributary potential for wild rainbow trout recruitment in Hebgen Reservoir, Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 139 p.
Watschke, D.A. 2006. Assessment of tributary potential for wild rainbow trout recruitment in Hebgen Reservoir, Montana. M.Sc. Thesis. Bozeman, MT: Montana State University. 139 p.
- Web Search Engines for Articles on "Utah Chub"
- Additional Sources of Information Related to "Fish"





