View in other NatureServe Network Field Guides
NatureServe
Montana
Utah
Wyoming
Idaho
Wisconsin
British Columbia
South Carolina
Yukon
California
New York
Long-tailed Duck - Clangula hyemalis
General Description
In North America. Long-tailed Ducks breed in the Arctic and sub-Arctic and winter south along the Pacific coast to Oregon, the Atlantic coast to North Carolina, and the Great Lakes. The species is an uncommon migrant to Montana with fewer than 16 observations reported in the typical year (Robertson et al. 2002, MTNHP 2019).
For a comprehensive review of the conservation status, habitat use, and ecology of this and other Montana bird species, please see
Marks et al. 2016, Birds of Montana.Species Range
Montana Range
Range Descriptions
 Migratory
Migratory
Western Hemisphere Range

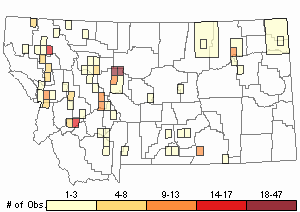
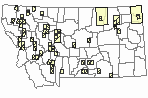
Observations in Montana Natural Heritage Program Database
Number of Observations: 343
(Click on the following maps and charts to see full sized version)
Map Help and Descriptions
Relative Density
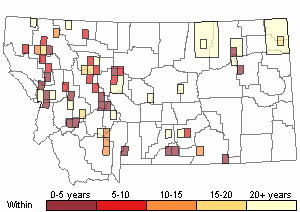
Recency
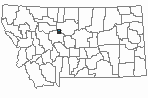
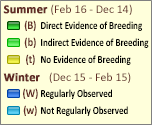
SUMMER (Feb 16 - Dec 14)
Direct Evidence of Breeding
Indirect Evidence of Breeding
No Evidence of Breeding
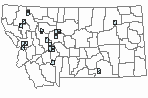
WINTER (Dec 15 - Feb 15)
Regularly Observed
Not Regularly Observed
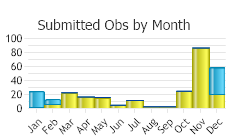
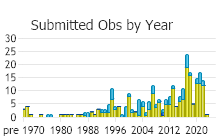
 (Observations spanning multiple months or years are excluded from time charts)
(Observations spanning multiple months or years are excluded from time charts)
Habitat
During migration they are likely to be observed on reservoirs, lakes or large rivers, usually far from shore (Johnsgard 1986).
National Vegetation Classification System Groups Associated with this Species
Wetland and Riparian
Riparian and Wetland Forest
Riparian Shrubland
Stewardship Responsibility
References
- Literature Cited AboveLegend:
 View Online Publication
View Online Publication [MTNHP] Montana Natural Heritage Program. 2019. Point observation database. Helena, MT.
[MTNHP] Montana Natural Heritage Program. 2019. Point observation database. Helena, MT. Johnsgard, P.A. 1986. Birds of the Rocky Mountains: with particular reference to national parks in the northern Rocky Mountain region. Colorado Associated University Press, Boulder, CO.
Johnsgard, P.A. 1986. Birds of the Rocky Mountains: with particular reference to national parks in the northern Rocky Mountain region. Colorado Associated University Press, Boulder, CO. Marks, J.S., P. Hendricks, and D. Casey. 2016. Birds of Montana. Arrington, VA. Buteo Books. 659 pages.
Marks, J.S., P. Hendricks, and D. Casey. 2016. Birds of Montana. Arrington, VA. Buteo Books. 659 pages. Robertson, G.J. and J.L. Savard. 2002. Long-tailed Duck (Clangula hyemalis), version 2.0. In The Birds of North America (A.F. Poole and F.B. Gill, Editors). Cornell Lab of Ornithology, Ithaca, NY, USA. https://doi-org.weblib.lib.umt.edu:2443/10.2173/bna.651
Robertson, G.J. and J.L. Savard. 2002. Long-tailed Duck (Clangula hyemalis), version 2.0. In The Birds of North America (A.F. Poole and F.B. Gill, Editors). Cornell Lab of Ornithology, Ithaca, NY, USA. https://doi-org.weblib.lib.umt.edu:2443/10.2173/bna.651
- Additional ReferencesLegend:
 View Online Publication
View Online Publication
Do you know of a citation we're missing? American Ornithologists’ Union [AOU]. 1998. Check-list of North American birds, 7th edition. American Ornithologists’ Union, Washington, D.C. 829 p.
American Ornithologists’ Union [AOU]. 1998. Check-list of North American birds, 7th edition. American Ornithologists’ Union, Washington, D.C. 829 p. Coudie. R. I. 1984. Comparative ecology of Common eiders, black scoters, oldsquaws and harlequin ducks wintering in southeast Newfoundland. Thesis. Univ. of W. Ontario. London, Ontario. Canada.
Coudie. R. I. 1984. Comparative ecology of Common eiders, black scoters, oldsquaws and harlequin ducks wintering in southeast Newfoundland. Thesis. Univ. of W. Ontario. London, Ontario. Canada. Ehrlich, P., D. Dobkin, and D. Wheye. 1988. The birder’s handbook: a field guide to the natural history of North American birds. Simon and Schuster Inc. New York. 785 pp.
Ehrlich, P., D. Dobkin, and D. Wheye. 1988. The birder’s handbook: a field guide to the natural history of North American birds. Simon and Schuster Inc. New York. 785 pp. Hays, R., R.L. Eng, and C.V. Davis (preparers). 1984. A list of Montana birds. Helena, MT: MT Dept. of Fish, Wildlife & Parks.
Hays, R., R.L. Eng, and C.V. Davis (preparers). 1984. A list of Montana birds. Helena, MT: MT Dept. of Fish, Wildlife & Parks. Hoffmann, R.S., R.L. Hand, and P.L. Wright. 1959. Recent bird records from western Montana. The Condor 61(2):147-151.
Hoffmann, R.S., R.L. Hand, and P.L. Wright. 1959. Recent bird records from western Montana. The Condor 61(2):147-151. Johnsgard, P.A. 1992. Birds of the Rocky Mountains with particular reference to national parks in the northern Rocky Mountain region. Lincoln: University of Nebraska Press. xi + 504 pp.
Johnsgard, P.A. 1992. Birds of the Rocky Mountains with particular reference to national parks in the northern Rocky Mountain region. Lincoln: University of Nebraska Press. xi + 504 pp. Joslin, Gayle, and Heidi B. Youmans. 1999. Effects of recreation on Rocky Mountain wildlife: a review for Montana. [Montana]: Montana Chapter of the Wildlife Society.
Joslin, Gayle, and Heidi B. Youmans. 1999. Effects of recreation on Rocky Mountain wildlife: a review for Montana. [Montana]: Montana Chapter of the Wildlife Society. Lenard, S., J. Carlson, J. Ellis, C. Jones, and C. Tilly. 2003. P. D. Skaar's Montana bird distribution, 6th edition. Montana Audubon, Helena, MT. 144 pp.
Lenard, S., J. Carlson, J. Ellis, C. Jones, and C. Tilly. 2003. P. D. Skaar's Montana bird distribution, 6th edition. Montana Audubon, Helena, MT. 144 pp. Montana Bird Distribution Committee. 2012. P.D. Skaar's Montana bird distribution. 7th Edition. Montana Audubon, Helena, Montana. 208 pp. + foldout map.
Montana Bird Distribution Committee. 2012. P.D. Skaar's Montana bird distribution. 7th Edition. Montana Audubon, Helena, Montana. 208 pp. + foldout map. Rhodes, O.E., Jr., L.M. Smith and M.H. Smith. 1991. Conservation and genetic resources in waterfowl. Trans. N. Amer. Wildl. & Nat. Res. Conf. 56:462-472.
Rhodes, O.E., Jr., L.M. Smith and M.H. Smith. 1991. Conservation and genetic resources in waterfowl. Trans. N. Amer. Wildl. & Nat. Res. Conf. 56:462-472. Robertson, G. J., and J.-P. L. Savard. 2002. Long-tailed Duck (Clangula hyemalis). In The birds of North America, No. 651 (A. Poole and F. Gill, Eds.). Academy of Natural Sciences of Philadelphia and American Ornithologists’ Union.
Robertson, G. J., and J.-P. L. Savard. 2002. Long-tailed Duck (Clangula hyemalis). In The birds of North America, No. 651 (A. Poole and F. Gill, Eds.). Academy of Natural Sciences of Philadelphia and American Ornithologists’ Union. Sea Duck Joint Venture Management Board. 2001. Sea Duck Joint Venture Strategic Plan: 2001-2006. SDJV Continental Technical Team. Unpubl. report c/o USFWS, Anchorage, AK; CWS, Sackville, New Brunswick. 14 p. plus appendices.
Sea Duck Joint Venture Management Board. 2001. Sea Duck Joint Venture Strategic Plan: 2001-2006. SDJV Continental Technical Team. Unpubl. report c/o USFWS, Anchorage, AK; CWS, Sackville, New Brunswick. 14 p. plus appendices. Sibley, D. 2014. The Sibley guide to birds. Alfred A. Knopf, New York, NY. 598 pp.
Sibley, D. 2014. The Sibley guide to birds. Alfred A. Knopf, New York, NY. 598 pp. Skaar, P. D., D. L. Flath, and L. S. Thompson. 1985. Montana bird distribution. Montana Academy of Sciences Monograph 3(44): ii-69.
Skaar, P. D., D. L. Flath, and L. S. Thompson. 1985. Montana bird distribution. Montana Academy of Sciences Monograph 3(44): ii-69. Skaar, P.D. 1969. Birds of the Bozeman latilong: a compilation of data concerning the birds which occur between 45 and 46 N. latitude and 111 and 112 W. longitude, with current lists for Idaho, Montana, Wyoming, impinging Montana counties and Yellowstone National Park. Bozeman, MT. 132 p.
Skaar, P.D. 1969. Birds of the Bozeman latilong: a compilation of data concerning the birds which occur between 45 and 46 N. latitude and 111 and 112 W. longitude, with current lists for Idaho, Montana, Wyoming, impinging Montana counties and Yellowstone National Park. Bozeman, MT. 132 p. Taylor, D.M. and C.H. Trost. 1987. The status of historically rare of unrecorded birds in Idaho. Unpublished manuscript. 68 p.
Taylor, D.M. and C.H. Trost. 1987. The status of historically rare of unrecorded birds in Idaho. Unpublished manuscript. 68 p. Watts, C.R. and L.C. Eichhorn. 1981. Changes in the birds of central Montana. Proceedings of the Montana Academy of Sciences 40:31-40.
Watts, C.R. and L.C. Eichhorn. 1981. Changes in the birds of central Montana. Proceedings of the Montana Academy of Sciences 40:31-40.
- Web Search Engines for Articles on "Long-tailed Duck"
- Additional Sources of Information Related to "Birds"





