View in other NatureServe Network Field Guides
NatureServe
Montana
Utah
Wyoming
Idaho
Wisconsin
British Columbia
South Carolina
Yukon
California
New York
Mead's Wood Nymph - Cercyonis meadii
Native Species
Global Rank:
G4
State Rank:
S5
Agency Status
USFWS:
USFS:
BLM:
External Links
General Description
[From Ferris and Brown 1981; Scott 1986; Opler and Wright 1999; Glassberg 2001] Forewing 2.2-2.4 cm. Uppersurface of forewing with red-orange flush surrounding eyespots, upper submarginal eyespot usually larger than lower; undersurface more extensive red-orange flush on forewing encompassing two prominent eyespots, postmedian eyespots not extensively developed.
Phenology
One flight; late July to early September, rarely October (Scott 1986; Opler and Wright 1999). July to September in the south, late July to August in the north (Glassberg 2001).
Diagnostic Characteristics
Best determined by the extensive red-orange flush on forewing, encompassing two prominent eyespots.
Species Range
Montana Range
Range Descriptions
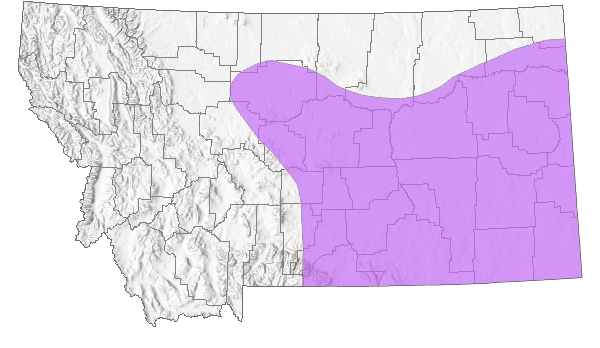
 Native
Native
Range Comments
Discontinuous. Central Montana and eastern Wyoming to western North and South Dakota where it is considered a Pleistocene relic of a more-continuous coniferous area (Johnson 1975); central Colorado; southwestern Colorado and southern Utah to northern Mexico and western Texas (Scott 1986; Opler and Wright 1999; Glassberg 2001); usually below 3050 m elevation in Colorado (Brown 1957; Emmel 1969). Reported in Montana from most counties in the southeastern quarter of the state (Kohler 1980; Stanford and Opler 1993). Uncommon to locally common in the south, rare in the north (Glassberg 2001).
Migration
Non-migratory.
Habitat
Canyons, open pine woodlands, forest margins, dry meadows, sagebrush-steppe (Brown 1957; Emmel 1964; Ferris and Brown 1981; Scott 1986; Opler and Wright 1999; Glassberg 2001). Not described for Montana, but likely in open ponderosa pine woodland and open woodland margins.
Food Habits
Larval food plants include Bouteloua, Carex, and possibly others (Scott 1992, 2006). Adults feed on flower nectar (including Achillea, Aster, Chrysothamnus, Cirsium, Geranium, Grindelia, Heterotheca, Senecio, Solidago) and mud (Scott 1986, 2014).
Reproductive Characteristics
Females lay eggs singly in dead plant litter (Pinus needles, dried Quercus leaves, dead Carex leaves) near larval host plants, usually a shaded location under tree/shrub canopy. L1 instar overwinters, then resumes growth through L5 instar the following spring and pupates; pupae suspended from host plant (Brown 1957; Emmel 1969; Ferris and Brown 1981; Scott 1986, 2006). Males patrol throughout the day in woods and valley bottoms in search of females (Scott 1975b, 1986).
References
- Literature Cited AboveLegend:
 View Online Publication
View Online Publication Brown, F.M. 1957. Colorado Butterflies. Proceedings; Numbers Three through Seven. Denver Museum of Natural History, Denver, Co.
Brown, F.M. 1957. Colorado Butterflies. Proceedings; Numbers Three through Seven. Denver Museum of Natural History, Denver, Co. Emmel, T.C. 1964. The ecology and distribution of butterflies in a montane community near Florissant, Colorado. American Midland Naturalist 72(2): 358-373.
Emmel, T.C. 1964. The ecology and distribution of butterflies in a montane community near Florissant, Colorado. American Midland Naturalist 72(2): 358-373. Emmel, T.C. 1969. Taxonomy, distribution and biology of the genus Cercyonis (Satyridae). I. Characteristics of the genus. Journal of the Lepidopterists' Society 23:165-175.
Emmel, T.C. 1969. Taxonomy, distribution and biology of the genus Cercyonis (Satyridae). I. Characteristics of the genus. Journal of the Lepidopterists' Society 23:165-175. Ferris, C.D. and F.M. Brown (eds). 1981. Butterflies of the Rocky Mountains. Univ. of Oklahoma Press. Norman. 442 pp.
Ferris, C.D. and F.M. Brown (eds). 1981. Butterflies of the Rocky Mountains. Univ. of Oklahoma Press. Norman. 442 pp. Glassberg, J. 2001. Butterflies through Binoculars: A Field Guide to the Butterflies of Western North America. Oxford University Press.
Glassberg, J. 2001. Butterflies through Binoculars: A Field Guide to the Butterflies of Western North America. Oxford University Press. Johnson, K. 1975. Post-Pleistocene environments and montane butterfly relicts on the western Great Plains. Journal of Research on the Lepidoptera 14(4): 216-232.
Johnson, K. 1975. Post-Pleistocene environments and montane butterfly relicts on the western Great Plains. Journal of Research on the Lepidoptera 14(4): 216-232. Kohler, S. 1980. Checklist of Montana Butterflies (Rhopalocera). Journal of the Lepidopterists' Society 34(1): 1-19.
Kohler, S. 1980. Checklist of Montana Butterflies (Rhopalocera). Journal of the Lepidopterists' Society 34(1): 1-19. Opler, P.A. and A.B. Wright. 1999. A field guide to western butterflies. Second edition. Peterson Field Guides. Houghton Mifflin Company, Boston, Massachusetts. 540 pp.
Opler, P.A. and A.B. Wright. 1999. A field guide to western butterflies. Second edition. Peterson Field Guides. Houghton Mifflin Company, Boston, Massachusetts. 540 pp. Scott, J.A. 1975b. Mate-locating behavior of western North American butterflies. Journal of Research on the Lepidoptera 14:1-40.
Scott, J.A. 1975b. Mate-locating behavior of western North American butterflies. Journal of Research on the Lepidoptera 14:1-40. Scott, J.A. 1986. The butterflies of North America: a natural history and field guide. Stanford University Press, Stanford, California.
Scott, J.A. 1986. The butterflies of North America: a natural history and field guide. Stanford University Press, Stanford, California. Scott, J.A. 1992. Hostplant records for butterflies and skippers (mostly from Colorado) 1959-1992, with new life histories and notes on oviposition, immatures, and ecology. Papilio new series #6. 185 p.
Scott, J.A. 1992. Hostplant records for butterflies and skippers (mostly from Colorado) 1959-1992, with new life histories and notes on oviposition, immatures, and ecology. Papilio new series #6. 185 p. Scott, J.A. 2006. Butterfly hostplant records, 1992-2005, with a treatise on the evolution of Erynnis, and a note on new terminology for mate-locating behavior. Papilio new series #14. 74 p.
Scott, J.A. 2006. Butterfly hostplant records, 1992-2005, with a treatise on the evolution of Erynnis, and a note on new terminology for mate-locating behavior. Papilio new series #14. 74 p. Scott, J.A. 2014. Lepidoptera of North America 13. Flower visitation by Colorado butterflies (40,615 records) with a review of the literature on pollination of Colorado plants and butterfly attraction (Lepidoptera: Hersperioidea and Papilionoidea). Contributions of the C.P. Gillette Museum of Arthopod Diversity. Fort Collins, CO: Colorado State University. 190 p.
Scott, J.A. 2014. Lepidoptera of North America 13. Flower visitation by Colorado butterflies (40,615 records) with a review of the literature on pollination of Colorado plants and butterfly attraction (Lepidoptera: Hersperioidea and Papilionoidea). Contributions of the C.P. Gillette Museum of Arthopod Diversity. Fort Collins, CO: Colorado State University. 190 p. Stanford, R.E. and P.A. Opler. 1993. Atlas of western USA butterflies: including adjacent parts of Canada and Mexico. Unpubl. Report. Denver and Fort Collins, Colorado 275 pp.
Stanford, R.E. and P.A. Opler. 1993. Atlas of western USA butterflies: including adjacent parts of Canada and Mexico. Unpubl. Report. Denver and Fort Collins, Colorado 275 pp.
- Additional ReferencesLegend:
 View Online Publication
View Online Publication
Do you know of a citation we're missing? Allen, T.J., J.P. Brock, and J. Glassberg. 2005. Caterpillars in the field and garden: a field guide to the butterfly caterpillars of North America. Oxford University Press.
Allen, T.J., J.P. Brock, and J. Glassberg. 2005. Caterpillars in the field and garden: a field guide to the butterfly caterpillars of North America. Oxford University Press. Brock, J.P. and K. Kaufman. 2003. Kaufman Field Guide to Butterflies of North America. Houghton Mifflin Company, New York, NY 284 pp.
Brock, J.P. and K. Kaufman. 2003. Kaufman Field Guide to Butterflies of North America. Houghton Mifflin Company, New York, NY 284 pp. Forister, M.L., C.A. Halsch, C.C. Nice, J.A. Fordyce, T.E. Dilts, J.C. Oliver, K.L. Prudic, A.M. Shapiro, J.K. Wilson, J. Glassberg. 2021. Fewer butterflies seen by community scientists across the warming and drying landscapes of the American West. Science 371:1042-1045.
Forister, M.L., C.A. Halsch, C.C. Nice, J.A. Fordyce, T.E. Dilts, J.C. Oliver, K.L. Prudic, A.M. Shapiro, J.K. Wilson, J. Glassberg. 2021. Fewer butterflies seen by community scientists across the warming and drying landscapes of the American West. Science 371:1042-1045. Forister, M.L., E.M. Grames, C.A. Halsch, K.J. Burls, C.F. Carroll, K.L. Bell, J.P. Jahner, et al. 2023. Assessing risk for butterflies in the context of climate change, demographic uncertainty, and heterogeneous data sources. Ecological Monographs 93(3):e1584. https://doi.org/10.1002/ecm.1584
Forister, M.L., E.M. Grames, C.A. Halsch, K.J. Burls, C.F. Carroll, K.L. Bell, J.P. Jahner, et al. 2023. Assessing risk for butterflies in the context of climate change, demographic uncertainty, and heterogeneous data sources. Ecological Monographs 93(3):e1584. https://doi.org/10.1002/ecm.1584 Scott, J.A. and G.R. Scott. 1978. Ecology and distribution of the butterflies of southern central Colorado. Journal of Research on the Lepidoptera 17(2): 73-128.
Scott, J.A. and G.R. Scott. 1978. Ecology and distribution of the butterflies of southern central Colorado. Journal of Research on the Lepidoptera 17(2): 73-128.
- Web Search Engines for Articles on "Mead's Wood Nymph"
- Additional Sources of Information Related to "Insects"





