View in other NatureServe Network Field Guides
NatureServe
Montana
Utah
Wyoming
Idaho
Wisconsin
British Columbia
South Carolina
Yukon
California
New York
Edwards' Fritillary - Argynnis edwardsii
Native Species
Global Rank:
G5
State Rank:
S5
Agency Status
USFWS:
USFS:
BLM:
External Links
General Description
[From Ferris and Brown 1981, Scott 1986, Glassberg 2001] Forewing 3.2-4.0 cm. A large brightly colored fritillary. Forewings pointed. Dorsal surface bright orange color withbold black border of both wings, postmedian and marginal spots on forewings distinctly paler than surrounding ground color, counting from the body the 3rd forewing black bar does not touch the 2nd black bar; ventral surface green or gray-green with elongate metallic silver spots and narrow buff submarginal band, ventral hindwing marginal pale spots rounded inwardly.
Phenology
One flight; late June to early September (Scott 1986), late May to early September (Glassberg 2001).
Diagnostic Characteristics
Differentiated by combination of dorsal black border, postmedian and marginal spots on forewings distinctly paler than surrounding ground color, counting from the body the 3rd forewing black bar does not touch the 2nd black bar, ventral hindwing marginal pale spots rounded inwardly, and ventral surfaces with strong greenish reflections.
Species Range
Montana Range
Range Descriptions
 Native
Native
Range Comments
Southern Alberta, Saskatchewan, and southwestern Manitoba south to extreme northern New Mexico in the west, western North and South Dakota, western Nebraska and Kansas in the east (Scott 1986, Glassberg 2001); up to 2745 m in Wyoming, 2925 m elevation in Colorado (Brown 1957, Ferris and Brown 1981). Statewide in Montana except the extreme western counties west of the continental divide (Kohler 1980, Stanford and Opler 1993). Uncommon to common (Glassberg 2001).
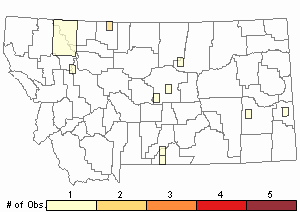
Observations in Montana Natural Heritage Program Database
Number of Observations: 12
(Click on the following maps and charts to see full sized version)
Map Help and Descriptions
Relative Density
Recency
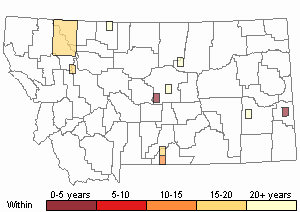
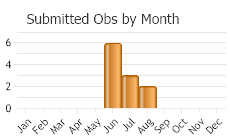
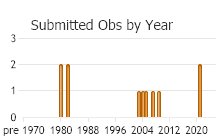
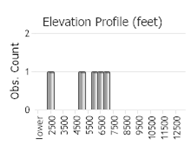 (Observations spanning multiple months or years are excluded from time charts)
(Observations spanning multiple months or years are excluded from time charts)
Migration
Non-migratory.
Habitat
Chaparral, prairie, foothills, montane forest openings (Brown 1957, Ferris and Brown 1981, Scott 1986). In Glacier National Park, reported in mesic montane meadows (Debinski 1993).
Food Habits
Larval food plants include species of Viola. Adults feed on flower nectar (including Agoseris, Apocynum, Astragalus, Buddleja, Carduus, Ceanothus, Centaurea, Chrysothamnus, Cirsium, Eleagnus, Erioganum, Erysimum, Eupatorium, Gaillardia, Grindelia, Heracleum, Jamesia, Liatris, Lithospermum, Medicago, Melilotus, Monarda, Oxytropis, Penstemon, Prunus, Rudbeckia, Sedum, Senecio, Symphoricarpos, Trifolium, Verbena), mud, and dung (Scott 1986, 2014).
Reproductive Characteristics
Females lay eggs singly and haphazardly near the food plants (Viola) or where they will emerge in spring. Eggs usually not laid until about August, unfed first instar larvae (L1) overwinter. Larvae feed on leaves, build no nests. Males patrol throughout the day in open areas in search of females, generally regardless of topography, but also frequently patrol and mate in shrubby areas near hilltops (Scott 1975b, 1986).
References
- Literature Cited AboveLegend:
 View Online Publication
View Online Publication Brown, F.M. 1957. Colorado Butterflies. Proceedings; Numbers Three through Seven. Denver Museum of Natural History, Denver, Co.
Brown, F.M. 1957. Colorado Butterflies. Proceedings; Numbers Three through Seven. Denver Museum of Natural History, Denver, Co. Debinski, D. 1993. Butterflies of Glacier National Park, Montana. Occasional Papers of the Museum of Natural History, the University of Kansas, Lawrence, Kansas. No. 159: 1-13.
Debinski, D. 1993. Butterflies of Glacier National Park, Montana. Occasional Papers of the Museum of Natural History, the University of Kansas, Lawrence, Kansas. No. 159: 1-13. Ferris, C.D. and F.M. Brown (eds). 1981. Butterflies of the Rocky Mountains. Univ. of Oklahoma Press. Norman. 442 pp.
Ferris, C.D. and F.M. Brown (eds). 1981. Butterflies of the Rocky Mountains. Univ. of Oklahoma Press. Norman. 442 pp. Glassberg, J. 2001. Butterflies through Binoculars: A Field Guide to the Butterflies of Western North America. Oxford University Press.
Glassberg, J. 2001. Butterflies through Binoculars: A Field Guide to the Butterflies of Western North America. Oxford University Press. Kohler, S. 1980. Checklist of Montana Butterflies (Rhopalocera). Journal of the Lepidopterists' Society 34(1): 1-19.
Kohler, S. 1980. Checklist of Montana Butterflies (Rhopalocera). Journal of the Lepidopterists' Society 34(1): 1-19. Scott, J.A. 1975b. Mate-locating behavior of western North American butterflies. Journal of Research on the Lepidoptera 14:1-40.
Scott, J.A. 1975b. Mate-locating behavior of western North American butterflies. Journal of Research on the Lepidoptera 14:1-40. Scott, J.A. 1986. The butterflies of North America: a natural history and field guide. Stanford University Press, Stanford, California.
Scott, J.A. 1986. The butterflies of North America: a natural history and field guide. Stanford University Press, Stanford, California. Scott, J.A. 2014. Lepidoptera of North America 13. Flower visitation by Colorado butterflies (40,615 records) with a review of the literature on pollination of Colorado plants and butterfly attraction (Lepidoptera: Hersperioidea and Papilionoidea). Contributions of the C.P. Gillette Museum of Arthopod Diversity. Fort Collins, CO: Colorado State University. 190 p.
Scott, J.A. 2014. Lepidoptera of North America 13. Flower visitation by Colorado butterflies (40,615 records) with a review of the literature on pollination of Colorado plants and butterfly attraction (Lepidoptera: Hersperioidea and Papilionoidea). Contributions of the C.P. Gillette Museum of Arthopod Diversity. Fort Collins, CO: Colorado State University. 190 p. Stanford, R.E. and P.A. Opler. 1993. Atlas of western USA butterflies: including adjacent parts of Canada and Mexico. Unpubl. Report. Denver and Fort Collins, Colorado 275 pp.
Stanford, R.E. and P.A. Opler. 1993. Atlas of western USA butterflies: including adjacent parts of Canada and Mexico. Unpubl. Report. Denver and Fort Collins, Colorado 275 pp.
- Additional ReferencesLegend:
 View Online Publication
View Online Publication
Do you know of a citation we're missing? Allen, T.J., J.P. Brock, and J. Glassberg. 2005. Caterpillars in the field and garden: a field guide to the butterfly caterpillars of North America. Oxford University Press.
Allen, T.J., J.P. Brock, and J. Glassberg. 2005. Caterpillars in the field and garden: a field guide to the butterfly caterpillars of North America. Oxford University Press. Brock, J.P. and K. Kaufman. 2003. Kaufman Field Guide to Butterflies of North America. Houghton Mifflin Company, New York, NY 284 pp.
Brock, J.P. and K. Kaufman. 2003. Kaufman Field Guide to Butterflies of North America. Houghton Mifflin Company, New York, NY 284 pp. Caruthers, J.C., and D. Debinski. 2006. Montane meadow butterfly species distributions in the Greater Yellowstone Ecosystem. University of Wyoming National Park Service Research Center Annual Report, 2006. Vol. 30, Art. 14. 85-96.
Caruthers, J.C., and D. Debinski. 2006. Montane meadow butterfly species distributions in the Greater Yellowstone Ecosystem. University of Wyoming National Park Service Research Center Annual Report, 2006. Vol. 30, Art. 14. 85-96. Forister, M.L., C.A. Halsch, C.C. Nice, J.A. Fordyce, T.E. Dilts, J.C. Oliver, K.L. Prudic, A.M. Shapiro, J.K. Wilson, J. Glassberg. 2021. Fewer butterflies seen by community scientists across the warming and drying landscapes of the American West. Science 371:1042-1045.
Forister, M.L., C.A. Halsch, C.C. Nice, J.A. Fordyce, T.E. Dilts, J.C. Oliver, K.L. Prudic, A.M. Shapiro, J.K. Wilson, J. Glassberg. 2021. Fewer butterflies seen by community scientists across the warming and drying landscapes of the American West. Science 371:1042-1045. Forister, M.L., E.M. Grames, C.A. Halsch, K.J. Burls, C.F. Carroll, K.L. Bell, J.P. Jahner, et al. 2023. Assessing risk for butterflies in the context of climate change, demographic uncertainty, and heterogeneous data sources. Ecological Monographs 93(3):e1584. https://doi.org/10.1002/ecm.1584
Forister, M.L., E.M. Grames, C.A. Halsch, K.J. Burls, C.F. Carroll, K.L. Bell, J.P. Jahner, et al. 2023. Assessing risk for butterflies in the context of climate change, demographic uncertainty, and heterogeneous data sources. Ecological Monographs 93(3):e1584. https://doi.org/10.1002/ecm.1584 Layberry, R.A., P.W. Hall, and J.D. LaFontaine. 1998. The Butterflies of Canada. University of Toronto Press. 280 pp. + color plates.
Layberry, R.A., P.W. Hall, and J.D. LaFontaine. 1998. The Butterflies of Canada. University of Toronto Press. 280 pp. + color plates.
- Web Search Engines for Articles on "Edwards' Fritillary"
- Additional Sources of Information Related to "Insects"





