View in other NatureServe Network Field Guides
NatureServe
Montana
Utah
Wyoming
Idaho
Wisconsin
British Columbia
South Carolina
Yukon
California
New York
California Hairstreak - Satyrium californica
General Description
[From Ferris and Brown 1981; Scott 1986; Opler and Wright 1999; Glasberg 2001; Pyle 2002] Forewing 1.4-1.6 cm. Tailed. Uppersurface gray-brown with smudged orange marks on hindwing. Undersurface generally gray-brown (sometimes paler or darker), with round or oval black postmedian spots, an extensive series of submarginal orange spots especially on hindwing, blue patch by tail capped with orange, black bar basal to tail spot full-"V" chevron-shaped.
Phenology
One flight; mid-June to early August (Scott 1986). Late May to mid-August, mainly June to mid-July (Glassberg 2001). Late June to July in Colorado and Wyoming (Ferris and Brown 1981), early May to early September in Oregon and Washington (Pyle 2002), early June to early August in British Columbia and Oregon (Guppy and Shepard 2001; Warren 2005).
Diagnostic Characteristics
Best determined by undersurface with round or oval black postmedian spots, an extensive series of submarginal orange spots especially on hindwing, blue patch by tail capped with orange, black bar basal to tail spot full-"V" chevron-shaped.
Species Range
Montana Range
Range Descriptions
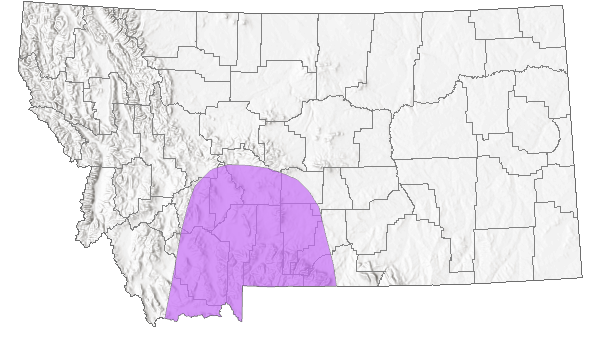
 Native
Native
Range Comments
Southern British Columbia south to northern Baja California, southeast through western Wyoming to southern Colorado (Scott 1986; Opler 1999; Glassberg 2001); 1829 m to 2560 m elevation in Colorado and Wyoming (Brown 1957; Ferris and Brown 1981), 274 m to 2438 m elevation in Oregon (Warren 2005). In Montana, no records prior to 2005, reported from Gallatin, Park, and Sweet Grass counties since 2005 (Kohler 1980; Stanford and Opler 1993; FLMNH Lepidopterists' Society database). Uncommon to common (Glassberg 2001).
Migration
Non-migratory.
Habitat
Oak woodland, chaparral, sagebrush steppe, foothills, canyons, open woodland (Scott 1986; Opler and Wright 1999; Glassberg 2001; Pyle 2002). Habitat in Montana not described but likely similar.
Food Habits
Larval food plants include Amelanchier, Ceanothus, Cercocarpus, Prunus, Purshia, Quercus, and Salix (Scott 1986, 1992; Guppy and Shepard 2001; Pyle 2002; Warren 2005; James and Nunnallee 2011). Adults feed on flower nectar (including Achillea, Aesculus, Apocynum, Asclepias, Ceanothus, Cirsium, Eriogonum, Euphorbia, Holodiscus, Hymenopappus, Marrubium, Melilotus, Mentzelia, Polygonum, Potentilla, Rhus, Rudbeckia, Sedum, Solidago, Tetradymia) and mud (Guppy and Shepard 2001; James and Nunnallee 2011; Scott 2014).
Reproductive Characteristics
Females usually lay eggs in small clusters of 2-5 eggs (sometimes singly) in crevices and small holes on host plant twig, cemented with copious clear glue (Scott 1986, 1992). Eggs hatch in about 5 days (depending on temperature) after overwintering, L1 instars develop to L4 and pupae in 14 days, adults eclose (emerges from pupae) in another 12 days; development from egg-laying to adult eclosion about 31 days (James and Nunnallee 2011). Eggs hibernate, larvae build no nest, feed on leaves or flower buds, attended by ants (especially Formica pilicornis) (Scott 1979; James and Nunnallee 2011). Males perch on tops of hilltop trees 2-6 m tall to await females, sometimes patrol (Scott 1975b, 1986).
References
- Literature Cited AboveLegend:
 View Online Publication
View Online Publication Brown, F.M. 1957. Colorado Butterflies. Proceedings; Numbers Three through Seven. Denver Museum of Natural History, Denver, Co.
Brown, F.M. 1957. Colorado Butterflies. Proceedings; Numbers Three through Seven. Denver Museum of Natural History, Denver, Co. Ferris, C.D. and F.M. Brown (eds). 1981. Butterflies of the Rocky Mountains. Univ. of Oklahoma Press. Norman. 442 pp.
Ferris, C.D. and F.M. Brown (eds). 1981. Butterflies of the Rocky Mountains. Univ. of Oklahoma Press. Norman. 442 pp. Glassberg, J. 2001. Butterflies through Binoculars: A Field Guide to the Butterflies of Western North America. Oxford University Press.
Glassberg, J. 2001. Butterflies through Binoculars: A Field Guide to the Butterflies of Western North America. Oxford University Press. Guppy, C.S. and J.H. Shepard. 2001. Butterflies of British Columbia: including western Alberta, southern Yukon, the Alaska Panhandle, Washington, northern Oregon, northern Idaho, northwestern Montana. UBC Press (Vancouver, BC) and Royal British Columbia Museum (Victoria, BC). 414 pp.
Guppy, C.S. and J.H. Shepard. 2001. Butterflies of British Columbia: including western Alberta, southern Yukon, the Alaska Panhandle, Washington, northern Oregon, northern Idaho, northwestern Montana. UBC Press (Vancouver, BC) and Royal British Columbia Museum (Victoria, BC). 414 pp. James, D.G. and D. Nunnallee. 2011. Life histories of Cascadia butterflies. Corvallis, OR: Oregon State University Press. 447 p.
James, D.G. and D. Nunnallee. 2011. Life histories of Cascadia butterflies. Corvallis, OR: Oregon State University Press. 447 p. Kohler, S. 1980. Checklist of Montana Butterflies (Rhopalocera). Journal of the Lepidopterists' Society 34(1): 1-19.
Kohler, S. 1980. Checklist of Montana Butterflies (Rhopalocera). Journal of the Lepidopterists' Society 34(1): 1-19. Opler, P.A. and A.B. Wright. 1999. A field guide to western butterflies. Second edition. Peterson Field Guides. Houghton Mifflin Company, Boston, Massachusetts. 540 pp.
Opler, P.A. and A.B. Wright. 1999. A field guide to western butterflies. Second edition. Peterson Field Guides. Houghton Mifflin Company, Boston, Massachusetts. 540 pp. Pyle, R.M. 2002. The butterflies of Cascadia: a field guide to all the species of Washington, Oregon, and surrounding territories. Seattle Audubon Society, Seattle, Washington. 420 pp.
Pyle, R.M. 2002. The butterflies of Cascadia: a field guide to all the species of Washington, Oregon, and surrounding territories. Seattle Audubon Society, Seattle, Washington. 420 pp. Scott, J.A. 1975b. Mate-locating behavior of western North American butterflies. Journal of Research on the Lepidoptera 14:1-40.
Scott, J.A. 1975b. Mate-locating behavior of western North American butterflies. Journal of Research on the Lepidoptera 14:1-40. Scott, J.A. 1979. Hibernal diapause of North American Papilionoidea and Hesperioidea. Journal of Research on the Lepidoptera 18(3): 171-200.
Scott, J.A. 1979. Hibernal diapause of North American Papilionoidea and Hesperioidea. Journal of Research on the Lepidoptera 18(3): 171-200. Scott, J.A. 1986. The butterflies of North America: a natural history and field guide. Stanford University Press, Stanford, California.
Scott, J.A. 1986. The butterflies of North America: a natural history and field guide. Stanford University Press, Stanford, California. Scott, J.A. 1992. Hostplant records for butterflies and skippers (mostly from Colorado) 1959-1992, with new life histories and notes on oviposition, immatures, and ecology. Papilio new series #6. 185 p.
Scott, J.A. 1992. Hostplant records for butterflies and skippers (mostly from Colorado) 1959-1992, with new life histories and notes on oviposition, immatures, and ecology. Papilio new series #6. 185 p. Scott, J.A. 2014. Lepidoptera of North America 13. Flower visitation by Colorado butterflies (40,615 records) with a review of the literature on pollination of Colorado plants and butterfly attraction (Lepidoptera: Hersperioidea and Papilionoidea). Contributions of the C.P. Gillette Museum of Arthopod Diversity. Fort Collins, CO: Colorado State University. 190 p.
Scott, J.A. 2014. Lepidoptera of North America 13. Flower visitation by Colorado butterflies (40,615 records) with a review of the literature on pollination of Colorado plants and butterfly attraction (Lepidoptera: Hersperioidea and Papilionoidea). Contributions of the C.P. Gillette Museum of Arthopod Diversity. Fort Collins, CO: Colorado State University. 190 p. Stanford, R.E. and P.A. Opler. 1993. Atlas of western USA butterflies: including adjacent parts of Canada and Mexico. Unpubl. Report. Denver and Fort Collins, Colorado 275 pp.
Stanford, R.E. and P.A. Opler. 1993. Atlas of western USA butterflies: including adjacent parts of Canada and Mexico. Unpubl. Report. Denver and Fort Collins, Colorado 275 pp. Warren, A.D. 2005. Lepidoptera of North America 6: Butterflies of Oregon, their taxonomy, distribution, and biology. Contributions of the C. P. Gillette Museum of Arthropod Diversity, Colorado State University. Fort Collins, Colorado. 406 pp.
Warren, A.D. 2005. Lepidoptera of North America 6: Butterflies of Oregon, their taxonomy, distribution, and biology. Contributions of the C. P. Gillette Museum of Arthropod Diversity, Colorado State University. Fort Collins, Colorado. 406 pp.
- Additional ReferencesLegend:
 View Online Publication
View Online Publication
Do you know of a citation we're missing? Allen, T.J., J.P. Brock, and J. Glassberg. 2005. Caterpillars in the field and garden: a field guide to the butterfly caterpillars of North America. Oxford University Press.
Allen, T.J., J.P. Brock, and J. Glassberg. 2005. Caterpillars in the field and garden: a field guide to the butterfly caterpillars of North America. Oxford University Press. Brock, J.P. and K. Kaufman. 2003. Kaufman Field Guide to Butterflies of North America. Houghton Mifflin Company, New York, NY 284 pp.
Brock, J.P. and K. Kaufman. 2003. Kaufman Field Guide to Butterflies of North America. Houghton Mifflin Company, New York, NY 284 pp. Forister, M.L., C.A. Halsch, C.C. Nice, J.A. Fordyce, T.E. Dilts, J.C. Oliver, K.L. Prudic, A.M. Shapiro, J.K. Wilson, J. Glassberg. 2021. Fewer butterflies seen by community scientists across the warming and drying landscapes of the American West. Science 371:1042-1045.
Forister, M.L., C.A. Halsch, C.C. Nice, J.A. Fordyce, T.E. Dilts, J.C. Oliver, K.L. Prudic, A.M. Shapiro, J.K. Wilson, J. Glassberg. 2021. Fewer butterflies seen by community scientists across the warming and drying landscapes of the American West. Science 371:1042-1045. Forister, M.L., E.M. Grames, C.A. Halsch, K.J. Burls, C.F. Carroll, K.L. Bell, J.P. Jahner, et al. 2023. Assessing risk for butterflies in the context of climate change, demographic uncertainty, and heterogeneous data sources. Ecological Monographs 93(3):e1584. https://doi.org/10.1002/ecm.1584
Forister, M.L., E.M. Grames, C.A. Halsch, K.J. Burls, C.F. Carroll, K.L. Bell, J.P. Jahner, et al. 2023. Assessing risk for butterflies in the context of climate change, demographic uncertainty, and heterogeneous data sources. Ecological Monographs 93(3):e1584. https://doi.org/10.1002/ecm.1584 Layberry, R.A., P.W. Hall, and J.D. LaFontaine. 1998. The Butterflies of Canada. University of Toronto Press. 280 pp. + color plates.
Layberry, R.A., P.W. Hall, and J.D. LaFontaine. 1998. The Butterflies of Canada. University of Toronto Press. 280 pp. + color plates.
- Web Search Engines for Articles on "California Hairstreak"
- Additional Sources of Information Related to "Insects"





