View in other NatureServe Network Field Guides
NatureServe
Montana
Utah
Wyoming
Idaho
Wisconsin
British Columbia
South Carolina
Yukon
California
New York
Little Indian Breadroot - Pediomelum hypogaeum var. hypogaeum
Other Names:
Psoralea hypogaea
State Rank Reason (see State Rank above)
Pediomelum hypogaeum was first documented in Montana from a specimen collected in 1886 in Cascade County (F.W. Anderson (s.n.) NY). Surveys in the 1980s and 1990s resulted in collections made from Fergus, Petroleum, and Rosebud Counties (http://rmh.uwyo.edu and https://www.pnwherbaria.org/). Additional observations found in other counties of southeast Montana should be verified. Pediomelum hypogaeum is categorized as a Potential Species of Concern because populations tend to be smaller and widely spaced, habitat may be limited, and its biology may make it more vulnerable to extirpation or just slow to recover from adverse impacts. Current information on plant locations, population sizes, and threats is needed. See rank details.
- Details on Status Ranking and Review
Population Size
Score2 - Small: Generally 2,000-10,000 individuals.
Range Extent
Score0 - Widespread species within Montana (occurs in 5% or more of the state or generally occurring in 6 or more sub-basins.) as well as outside of Montana.
Area of Occupancy
Score1 - Moderate: Generally occurring in 11-25 Subwatersheds (6th Code HUC’s).
Environmental Specificity
Score1-2 - Moderate to High.
Trends
ScoreNA - Rank factor not assessed.
CommentNo data on trends available.
Threats
Score0-1 - Low to Medium.
Intrinsic Vulnerability
Score1 - Moderate Vulnerability: Specific biological attributes, unusual life history characteristics or limited reproductive potential makes the species susceptible to extirpation from stochastic events or other adverse impacts to its habitat and slow to recover.
Raw Conservation Status Score
Score
5 to 7 total points scored out of a possible 16 (Rarity factors and threats only).
General Description
PLANTS: A perennial herb that is nearly stemless with a rosette of leaves that arises from a deep, club-shaped root (swollen taproot). The root is up to 8 cm long. The subterranean connecting stem at the top of the root produces 1-4 vertical slender-bearing branches which enlarge at the surface to produce the caudex or crown of the season. Sources: Lesica et al. 2012; McGregor [ed.] et al. 1986.
LEAVES: Long-petioled leaves are palmately divided into 3-7 linear-elliptic leaflets that are 25-50 mm long; together the leaves form a rosette. The foliage is covered with dot-like glands and dense, white appressed hairs, but the upper leaf surfaces become glabrous with age. Sources: Lesica et al. 2012; McGregor [ed.] et al. 1986.
INFLORESCENCE: Blue, pea-like flowers are borne in condensed spikes arising either among the bases of the leaf petioles or near the ground-level. The blue petals fade to white with age. The tubular calyx is 6-9 mm long and has four long, narrow lobes and a fifth longer and broader lobe. The upper petal is 10-13 mm long and held forward. The hairy pods (legume) are egg-shaped, about 5 mm long, and each has a beak that is 5-13 mm long. Sources: Lesica et al. 2012; McGregor [ed.] et al. 1986.
Montana's plants belong to variety hypogaeum (Lesica et al. 2012).
Pediomelum is derived from the Greek word pedi meaning 'plain' or 'field' and melum meaning 'sweet' or 'honey', but its reference to the plant is uncertain (Giblin et al. [eds.] 2018).
Phenology
Flowering late May-June.
Diagnostic Characteristics
Pediomelum esculentum has a distinguishable flowering stem with dense, long, stiff spreading hairs (hirsute) on the stem and leaf petiole.
Pediomelum hypogaeum is stemless above the ground and has appressed, stiff, straight, and sharp (strigose) hairs on its stems.
Species Range
Montana Range
Range Descriptions
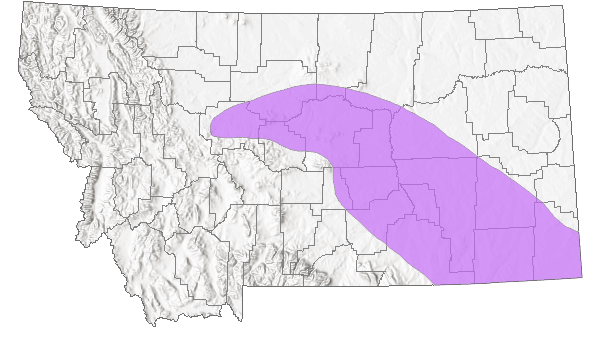
 Native
Native
Range Comments
Montana south to New Mexico and Texas (Lesica et al. 2012).
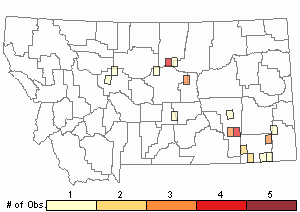
Observations in Montana Natural Heritage Program Database
Number of Observations: 30
(Click on the following maps and charts to see full sized version)
Map Help and Descriptions
Relative Density
Recency
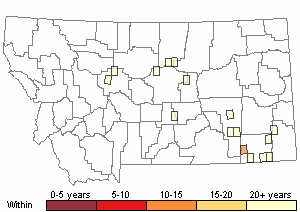
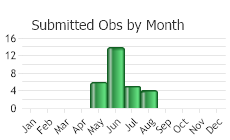
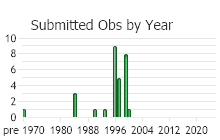
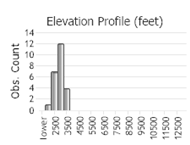 (Observations spanning multiple months or years are excluded from time charts)
(Observations spanning multiple months or years are excluded from time charts)
Habitat
In Montana plants are found in the plains growing in loose, sandy soil of grasslands and open pine woodlands on the plains, below sandstone outcrops and in blowouts (Lesica et al. 2012).
Ecological Systems Associated with this Species
Ecology
POLLINATORS
The following animal species have been reported as pollinators of this plant species or its genus where their geographic ranges overlap: Bombus pensylvanicus, Bombus griseocollis, and Bombus impatiens (Colla and Dumesh 2010).
References
- Literature Cited AboveLegend:
 View Online Publication
View Online Publication Colla, S.R. and S. Dumesh. 2010. The bumble bees of southern Ontario: notes on natural history and distribution. Journal of the Entomological Society of Ontario 141:39-68.
Colla, S.R. and S. Dumesh. 2010. The bumble bees of southern Ontario: notes on natural history and distribution. Journal of the Entomological Society of Ontario 141:39-68. Hitchcock, C.L. and A. Cronquist. 2018. Flora of the Pacific Northwest: An Illustrated Manual. Second Edition. Giblin, D.E., B.S. Legler, P.F. Zika, and R.G. Olmstead (eds). Seattle, WA: University of Washington Press in Association with Burke Museum of Natural History and Culture. 882 p.
Hitchcock, C.L. and A. Cronquist. 2018. Flora of the Pacific Northwest: An Illustrated Manual. Second Edition. Giblin, D.E., B.S. Legler, P.F. Zika, and R.G. Olmstead (eds). Seattle, WA: University of Washington Press in Association with Burke Museum of Natural History and Culture. 882 p. Lesica, P., M.T. Lavin, and P.F. Stickney. 2012. Manual of Montana Vascular Plants. Fort Worth, TX: BRIT Press. viii + 771 p.
Lesica, P., M.T. Lavin, and P.F. Stickney. 2012. Manual of Montana Vascular Plants. Fort Worth, TX: BRIT Press. viii + 771 p. McGregor, R.L. (coordinator), T.M. Barkley, R.E. Brooks, and E.K. Schofield (eds). 1986. Flora of the Great Plains: Great Plains Flora Association. Lawrence, KS: Univ. Press Kansas. 1392 pp.
McGregor, R.L. (coordinator), T.M. Barkley, R.E. Brooks, and E.K. Schofield (eds). 1986. Flora of the Great Plains: Great Plains Flora Association. Lawrence, KS: Univ. Press Kansas. 1392 pp.
- Additional ReferencesLegend:
 View Online Publication
View Online Publication
Do you know of a citation we're missing? Heidel, B.L. 1994. Survey for Psoralea hypogaea in the Great Falls Resource Area, Lewistown District. Unpublished report to the Bureau of Land Management, Montana. Montana Natural Heritage Program, Helena, Montana. 22 pp. plus appendices.
Heidel, B.L. 1994. Survey for Psoralea hypogaea in the Great Falls Resource Area, Lewistown District. Unpublished report to the Bureau of Land Management, Montana. Montana Natural Heritage Program, Helena, Montana. 22 pp. plus appendices. Heidel, B.L. 1997. Woodhawk botanical survey, Fergus County, Montana. Unpublished report to the Bureau of Land Management. Montana Natural Heritage Program, Helena, Montana. 43 pp. plus appendices.
Heidel, B.L. 1997. Woodhawk botanical survey, Fergus County, Montana. Unpublished report to the Bureau of Land Management. Montana Natural Heritage Program, Helena, Montana. 43 pp. plus appendices. Lesica, P., M.T. Lavin, and P.F. Stickney. 2022. Manual of Montana Vascular Plants, Second Edition. Fort Worth, TX: BRIT Press. viii + 779 p.
Lesica, P., M.T. Lavin, and P.F. Stickney. 2022. Manual of Montana Vascular Plants, Second Edition. Fort Worth, TX: BRIT Press. viii + 779 p. Vanderhorst, J.P., S.V. Cooper, and B.L. Heidel. 1998. Botanical and vegetation survey of Carter County, Montana. Unpublished report prepared for the Bureau of Land Management. Montana Natural Heritage Program, Helena. 116 pp. + app.
Vanderhorst, J.P., S.V. Cooper, and B.L. Heidel. 1998. Botanical and vegetation survey of Carter County, Montana. Unpublished report prepared for the Bureau of Land Management. Montana Natural Heritage Program, Helena. 116 pp. + app.
- Web Search Engines for Articles on "Little Indian Breadroot"





